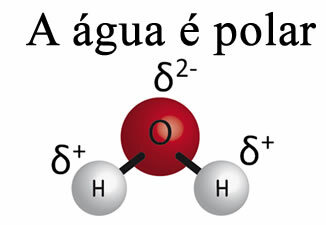
Water alone cannot remove grease from materials. This is because Thewater is polar, as shown in the image below, because of the difference in electronegativity that exists between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms of their molecules. On the other hand, the fat is non-polar and therefore water does not dissolve fats.
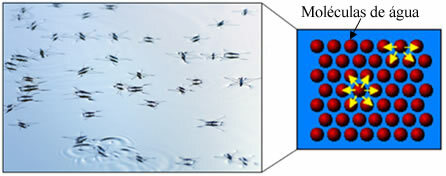
In addition, water has something called superficial tension. You can understand this better in the text. Surface Tension of Water, but basically it is a kind of elastic film or membrane that forms on the surface of water, which prevents it from penetrating fabrics and other materials to remove dirt. Water molecules attract each other in all directions through hydrogen bonds, but surface molecules only interact with molecules on the side and below, creating a difference in cohesion forces, which causes the surface molecules to contract and form this surface tension.
That's where soaps and detergents come in (from the Latin detoxify = clear), which are also called surface active agents
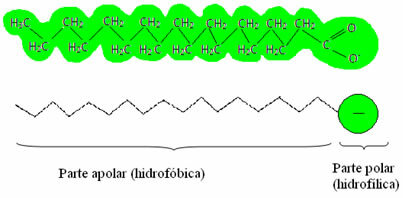
, as they have the ability to reduce the surface tension of water and, in addition, interact with both water and fat. How does this happen?Soaps and detergents have fatty acid salts, which are long molecules formed by a non-polar part (what is hydrophobic – hydro = water; phobes = aversion) and a polar end (hydrophilic – hydro = water; phyla = friend). Below we have a typical structure of a soap:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Detergents are usually salts of long-chain sulfonic acids:
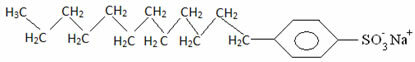
Thus, the non-polar part of these molecules present in soaps and detergents interacts with the fat, while the polar end interacts with water, grouping itself into small globules, called from micelles, in which the hydrophilic parts face the outside of the micelle in contact with the water molecules, and the fat is on the inside, in contact with the non-polar or hydrophobic part, a process similar to that shown in the image a follow:
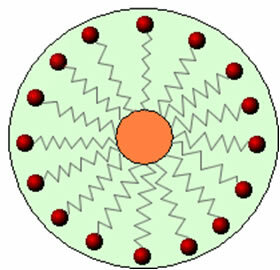
In this way, the greasy dirt is trapped in the center of the micelles and can be removed. Another point is that detergents and soaps have the ability to lower the surface tension of water, because decrease the interactions between its molecules, thus making it easier for it to penetrate various materials to remove the dirt.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Chemistry of Soaps and Detergents"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/quimica-dos-saboes-detergentes.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Detergents and pollution, soap residues suffer decomposition by microorganisms in water from rivers, biodegradables, detergents, foam layer that prevents oxygen gas from entering the water, chains branched.
Chemistry

Synthetic Substances, methylene-dimethoxy- methamphetamine, strongly psychoactive substance, ecstasy, MDMA, saccharin, cyclamate, plastics, acrylic, detergents, natural rubber, organic rubbers, synthetic rubber, hydrocarbons synthetics, pulley