Due to the differences in atmospheric pressure, the air circulates from higher pressure areas for lower pressure locations. When this movement occurs through large blocks of air with similar characteristics (pressure, temperature and humidity), the air masses, which are fundamental for weather variations in the country, as they transfer part of their characteristics to the climate of the region in which they exercise influence, thus contributing to the occurrence of most meteorological phenomena, such as rain, snow, hail, the increase or decrease of temperature etc.
According to the region in which these air masses originate, they have different characteristics, and may be wetter if they are formed in the ocean; droughts, when formed on the continent; hot, when they form near the equator and the tropics; or cold, when they form near the polar zones. In Brazil, the main air masses that influence the climate are:
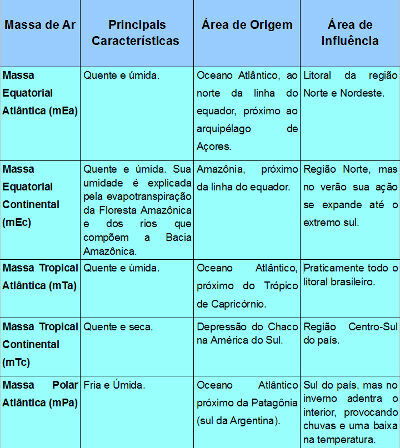
In summer, the air masses mEa, mEc, mTa and mTc are the ones that most influence the Brazilian climate. As these doughs are hot and have a lot of moisture, this season is very hot and humid. In winter, the interference of these masses decreases, and mPa starts to act more on the Brazilian space, causing temperature drops throughout Brazil. As mPa originates in the extreme south of the continent, its performance decreases as it moves into the interior of the country, as the air masses heat up as they move. Thus, the lowest temperatures are recorded in the south, and the highest are in the north. When the mPa manages to penetrate Brazil and reach the north of the country, temperatures in the region drop by more than 10°C. This phenomenon is known as chilling.
By Thamires Olimpia
Graduated in Geography
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/brasil/massas-ar-que-influenciam-brasil.htm

