Nowadays practically all cameras are digital. However, the first cameras were based on a process that involved the use of films where the captured images were recorded.
But, before its registration, how was the formation of images carried out?
The formation of the images was based on the principle of dark hole camera, which is an empty black box with a small hole on one side, into which light transmitted by an object enters. On the opposite side of the camera, the inverted image of the object is formed. Every camera is based on this system.
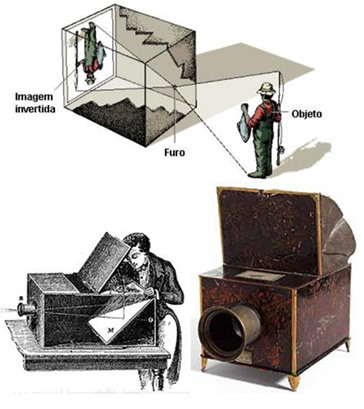
The image is inverted because the property of light propagates in a straight line.
In this way, it is possible to produce an image of a scene or object, but it was not yet known how to register it. It was only in 1827 that photography was invented, when Frenchman Joseph Niepce (1765-1833) managed to record the first photograph using a light-sensitive material: the photographic film.
The photographic film contains a suspension of silver salts, such as silver chloride and silver bromide, which
darken when hit by light. This happens not because of the presence of chloride or bromide, but because of silver. occurs to reduction of silver ions (Ag+) when it is struck by light, giving rise to finely divided metallic silver, which is black. Thus, a contrast is seen in the negatives that reproduce the image. The reduction of silver ions also takes place at the time of development, as will be explained a little further on.Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
The reduction of a compound occurs when it gains electrons from another chemical species and its NOX (oxidation number) decreases. Simultaneously with this process, the oxidation of the other compound takes place, which acted as the reducing agent, donating the electrons. Therefore, the case of image formation on a photographic film involves an oxidation-reduction reaction, where the silver salt contained in the film reduces and the substance that constitutes the developer oxidizes.
Generically, the process can be represented by:
AgX(s) + revealing →Ag(s) + X-(here) + other products
Where X is a halogen, such as chlorine and bromine.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Recording of images on photographic films"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/registro-imagens-filmes-fotograficos.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

Photosensitive lenses, oxidation-reduction reactions, loss or gain of electrons, photosynthetic lenses in sunglasses, composition of photochromatic glass, tetrahedral oxygen atoms, crystal structure of silver chloride, ultraviolet light, silver metal