Carbon has four electrons in its valence shell, which means it can form four bonds, so it can join other atoms. as: H, O, N, Cl. This property that carbon has explains the variety of organic compounds that exist in nature, which is why it is said that carbon is tetravalent.
In the year 1874, Van’t Hoff and Le Bel created a spatial model for carbon. This model had carbon atoms represented by regular tetrahedrons, with carbon occupying the center of the tetrahedron and its four valences corresponding to its four vertices.
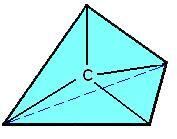
Spatial formula of carbon.
In this model, the different types of bonds that occur between carbon atoms were represented as follows:
The) simple link - tetrahedrons are connected by a vertex (single bond);


b) Double bond - the tetrahedrons are joined by two vertices (an edge);

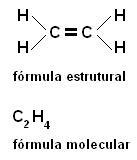
c) Triple link - the tetrahedrons are joined by three vertices (one face);
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

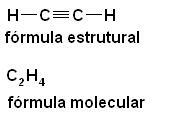
The evolution of the atomic model showed that the atom has a nucleus and an electrosphere, which enabled the emergence of new models to explain the bonds made by carbon: in the year 1915, Lewis presented a new proposal for the bonding of the atoms of carbon. According to Lewis, atoms bonded through electronic pairs in the valence layer. This representation was called the Lewis Electronic Formula, and the type of bond in which atoms join through electronic pairs is known as covalent bond.

Lewis Electronic Formula
The vast majority of organic molecules are three-dimensional, so there is a need to use models that show not only the structure, but also the geometry. Therefore, the spatial formula is more suitable for understanding the structure of carbon.
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SOUZA, Líria Alves de. "Carbon Structural Formulas"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/formulas-estruturais-carbono.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.