THE firstlawinNewton, also known as principlegivesinertia, states that the whole body remains in its state of rest or in a straight and uniform movement if the forces acting on it cancel each other out. The law of inertia was conceived by the English physicist Isaac Newton and was based on the observations made by the Italian Galileo Galilei. Along with the fundamental principle of dynamics and the law of action and reaction, the law of inertia constitutes the set of laws that underlie the theoretical basis of Classic Mechanics.
Read too: Seven Most Common Mistakes Made in the Study of Physics
What is inertia?
THE inertia is an inherent property of matter, that is, all bodies that have some amount of pasta they have inertia. The quantitative measure of inertia of a body is its mass, which can be measured in kilograms, for example. Inertia indicates the tendency of a body to remain in its state of motion, in other words, a body with a lot of inertia is strongly opposed to changes in its speed.
Inertia is the property of a body that makes it oppose any agent that tries to set it in motion or, if it is in motion, change the magnitude or direction of its velocity. A moving body keeps moving not because of its inertia, but because of the absence of a force capable of slowing it down, changing its direction, or accelerating it. |
We can feel the inertia when we are inside a moving vehicle, for example. When the vehicle is accelerated, we feel our body being pressed against the car seat. Likewise, when the car is braked sharply, we tend to keep moving at a constant speed and in a straight line. Therefore, to perceive the action of inertia, we need to be in some accelerated frame of reference, only in this way is it possible to perceive the opposition to the change in the state of motion. Look at the figure below:
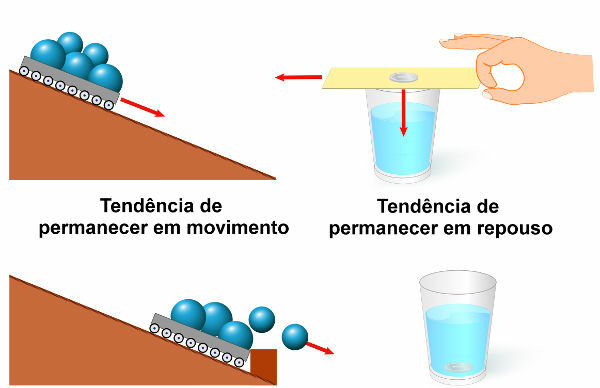
Now, using some more technical terms, we say that if the net force on a body is null, this body could be in rest as in uniform rectilinear motion, as shown in the following diagram:
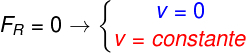
Also, the greater the inertia of a body, the greater the force needed to change its state of motion. Inertia is measured by the amount of mass in a body.
Calculation of inertia
According to the Newton's 2nd Law, the inertia of a body can be calculated by the ratio between the applied force and the acceleration which is obtained through the application of that force.
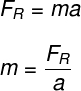
The above list shows us that the inertia of a body is proportional à strength which is applied on it and inverselyproportional yours acceleration, that is, the greater the inertia of a body, the greater the force needed to put it in or out of its current state of motion.
Lookalso: Tips for Solving Newton's Law Exercises
Examples of inertia
- If we quickly pull a tablecloth off a table full of objects, it is possible to remove it without dropping any of them thanks to the tendency of these objects to maintain their resting state. This is because when we pull the towel at high speed, the frictional force between the objects and the towel is negligible, thanks to the behavior of the dynamic friction coefficient.
- When a car has a collision, the vehicle's occupants are “thrown” forward as they tend to keep moving in a straight line. One way to prevent this from happening is to apply a force that resists this movement, which is why the use of seat belts is mandatory.
- When we spin several times, we get dizzy because the fluid inside the ear keeps spinning because of its inertia.
- The g-force, used in aeronautical applications, is actually the inertia that airplane pilots feel when making sharp turns or at high speed.

Exercises on Newton's First Law
Question 1) Headrests are present in most vehicles today, as there is a large possibility that occupants of a vehicle will break their necks in the event of a rear-end collision. car. The physical principle capable of explaining the need for headrests is (a):
a) Newton's first law.
b) Newton's second law.
c) law of action and reaction.
d) buoyancy theorem.
e) balance of forces.
Template: Letter a
Resolution: Head restraints are necessary due to the tendency of occupants' heads to remain at rest when rear-end collisions occur, for example.
Question 2) Most washing machines have a centrifugal function, used to partially dry clothes. the physical principle that explains CORRECTLY the operation of the centrifugation process is (a):
a) centrifugal force.
b) principle of inertia.
c) rotation.
d) translation.
e) torque.
Template: Letter B
Resolution: During the centrifugation process, the liquid contained inside the washing machines is expelled thanks to its inertia, since, for keep its rotational movement, a centripetal force acts on the liquid towards the center of the machine, so that the inertia of the liquid opposes this strength.
Question 3) In cartoons, it is common to see scenes in which a large anvil is released, destroying the floors of several floors until it reaches the ground. Although exaggerated, the behavior of the matter is similar to what we see in cartoons. The physical explanation for this behavior is given by:
a) law of inertia, which states that moving bodies tend to remain in motion.
b) law of action and reaction, which states that the force that the anvil exerts on the ground is equal to the force that the ground exerts on the anvil.
c) law of gravity, which explains that the anvil only falls due to the action of gravitational acceleration.
d) law of conservation of quantity of energy, which states that all initial mechanical energy is kept constant.
e) Coulomb's law, which states that the force of electrical attraction is responsible for accelerating the anvil towards the ground.
Template: Letter A. What explains the incessant fall of the anvil is Newton's first law. According to this law, also known as the law of inertia, the mass of the anvil makes its tendency to keep moving very large.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/primeira-lei-newton.htm


