The polarity of molecules is a very important aspect, as the characteristics of substances are determined, among other factors, by the fact that their molecules are polar or non-polar.
The determination of the polarity of a molecule can be performed by means of the Dipole Moment or Resulting Dipole Moment, whose symbol is 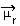 . If we are just talking about the dipole moment of each bond in the molecule, then the symbol is the Greek letter mi (µ).
. If we are just talking about the dipole moment of each bond in the molecule, then the symbol is the Greek letter mi (µ).

The molecule will be non-polar if the dipole moment is equal to zero, but if it is non-zero, it means it is polar.

There are two important things to consider in determining this resulting dipole moment. Let's see what they are:
1) electronegativity difference between the atoms of the elements participating in the reaction. For example, the HF molecule has a marked difference in electronegativity, as fluorine attracts, much more than hydrogen, the pair of electrons in the bond. Thus, the distribution of charges is not symmetrical, with electrical dipoles.
This dipole is represented by a vector that faces the end that concentrates the most electrons, that is, from the least to the most electronegative atom. So, in this case, the vector, which is the only one, will be the resulting vector, as indicated below:
Note that the vector value is the same as the dipole moment, which is given in debye unit (D=3.33. 10-30 coulomb. subway). Since the dipole moment is non-zero, the molecule and bond are polar.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
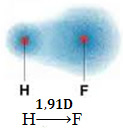
In the molecule below, we also have a molecule with only two atoms, however, in this case, it corresponds to a simple substance, that is, it is formed by only one type of element. Therefore, there is no electronegativity difference; atoms also attract electrons, which are symmetrically distributed. The resulting dipole moment is equal to zero, so both the bond and the molecule are apolar.
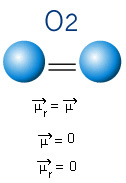
2) Molecule Geometry, that is, the spatial arrangement of the vectors. The BF molecule3 it has three polar bonds, in which fluorine is the most electronegative, thus having the vectors directed towards it. However, since the spatial arrangement of the atoms is trigonal flat, this makes the electrons have a symmetrical distribution around the central atom. Thus, the result is that these three vectors cancel each other out and the dipole moment is equal to zero. Therefore, the BF molecule3 é apolate.
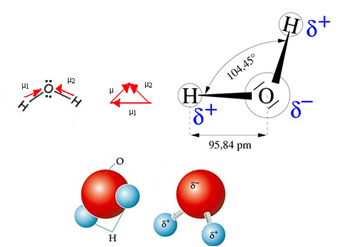
The water molecule has two vectors, however, its spatial geometry is not flat, but in the shape of a V. Note in the following figure that this way their vectors do not cancel each other out, the electrons are distributed asymmetrically and more concentrated in the most electronegative atom, which is oxygen. Thus, the dipole moment is different from zero and the water molecule is polar:
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry

