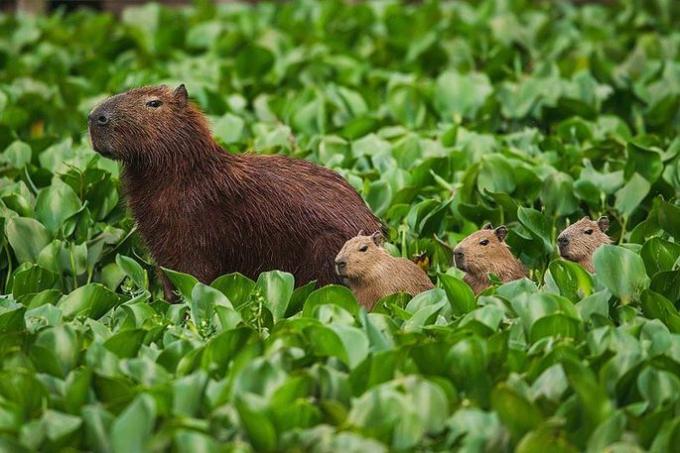
You eggs are female gametes formed from oogonia (precursor cells) in a process called ovulogenesis or oogenesis. O human egg it is, in fact, a secondary oocyte, which is spherical in shape and consists of plasma membrane, cytoplasm and nucleus. The egg of humans and all other placental mammals is called an allecite (a = no; lecito = calf).
The membrane that surrounds the egg, also called the yolk membrane, is a thick layer of glycoproteins adhered to the ovular plasma membrane, commonly known as zona pellucida. THE zona pellucida it is also lined with ovarian follicular cells, which nourished the oocyte throughout its development. These cells have the function of protecting the egg against mechanical shocks and also of allowing the entry of only one sperm into the gamete.
Below the egg's plasma membrane we find small membranous pouches containing digestive enzymes called cortical granules. When a sperm enters the egg, the cortical granules fuse into the membrane, releasing their enzymes. that alter the glycoproteins present in the ovular envelope, destroying its ability to bind to sperm. Thus, no other sperm are able to cross the zona pellucida.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
When fertilization of the egg by sperm occurs, the basal bodies of the sperm flagellum give rise to the centrioles of the zygote, with the rest of the tail and the mitochondria degenerating.
In the nucleus of the egg we find the caryotheca involving the female's chromosomes. After the egg is fertilized, there is a process called caryogamy (caryo = nucleus; gamia = marriage) and which consists of the fusion of the nuclei of the two gametes. In this phase, the karyotheca of the two nuclei will degenerate, releasing the chromosomes of the two gametes into the cytoplasm of the zygote, and then several processes will take place until the formation of the embryo begins.
by Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
MORAES, Paula Louredo. "Human egg"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/ovulo-humano.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.