Phytoplankton comprise the set of photosynthetic and unicellular microscopic algae that inhabit aquatic ecosystems.
Phytoplankton are found in suspension “floating” in open water, usually close to the surface. This is because in this region of the water body, called the photic zone, the phytoplankton receive the sunlight necessary to carry out photosynthesis.
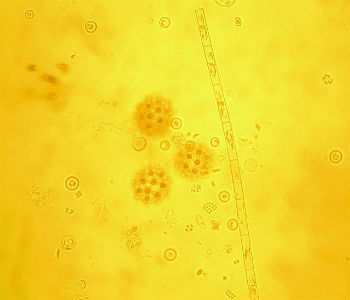
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton is one of the types of plankton. Remember, plankton encompasses the microorganisms that are part of the aquatic ecosystems. It can be of the zooplankton and phytoplankton types.
Learn more about Plankton.
Features
The algae that make up phytoplankton are considered inferior plants. This is because they do not have a complex structure but carry out photosynthesis.
Algae can be found isolated or in colonies. They also come in a wide variety of shapes. The only cell that makes up the alga can be rounded, oval, needle-shaped, with projections, bristles or thorns.
Some environmental factors interfere with algae growth. The main ones are:
- The offer of sunlight in the photic zone;
- Water temperature;
- The availability of nutrients;
- Competition with other aquatic plants that use the same resources as the environment;
- Parasitism and predation.
Examples of Phytoplankton
Several groups of algae make up phytoplankton. The most abundant and representative groups are the dinoflagellates and diatoms.
Dinoflagellates (Dinophyta)
They are flagellated protist organisms. Dinoflagellates are cell wall coated with rigid cellulose plates. They are characterized by a unicellular form with two flagella, with different size, function and orientation.
Most of the species in the group are found in salt water. Dinoflagellates are responsible for the phenomenon of Red tide.
Other species of dinoflagellates can produce bioluminescence. THE bioluminescence it is the production of light through a biochemical process. Dinoflagellate algae can produce a blue-green light in seawater, a phenomenon easily observed at night.
Diatoms (Baccillariophyta)
Diatomaceous algae are found in marine and freshwater environments. They can live in isolation or in colonies.
Externally, its main feature is a silica carapace that may have thorns or extensions, facilitating flotation.
Learn more about Algae.
Importance of Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton is an important primary producer in aquatic ecosystems, representing the basis of food chain. When carrying out photosynthesis, phytoplankton converts inorganic material into organic and oxygenates the water.
In addition, it also serves as food for zooplankton and some fish.
Mistakenly, the Amazon is considered the lung of the world. Actually, marine phytoplankton is the true lung of the world, as it releases large amounts of oxygen into the atmosphere. Phytoplankton produce more than 50% of all the oxygen on Earth and absorb up to 30% of the carbon dioxide emitted by man.
This function of phytoplankton is extremely important for the biosphere and fundamental for the survival of living beings.
Also read about the Protist Kingdom.