Spectrumelectromagnetic is the range of all frequencies in electromagnetic waves existing. The electromagnetic spectrum is generally presented in ascending order of frequencies, starting with the radio waves, passing through the radiationvisible up to radiationgamma, of higher frequency.
Frequency and length of electromagnetic waves
The frequency of electromagnetic waves, in turn, concerns the numberinoscillations that your electric field performs every second, moreover, waves with higher frequencies carry more energy with them. In ascending order of frequency, the waves are distributed in the electromagnetic spectrum, classified into: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays and gamma rays.
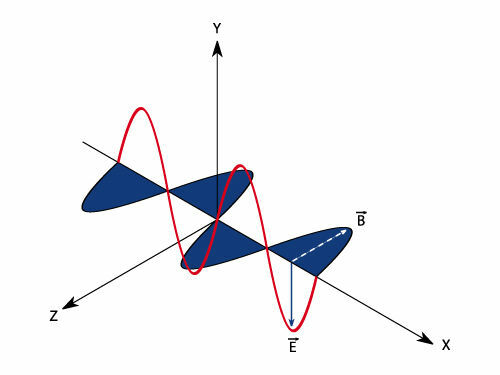
The number of oscillations in the electric field is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave.
According to theory undulatory, we can determine the frequency of a wave as the ratio of its propagation speed to its wavelength:
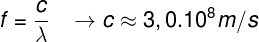
f – wave frequency (Hz)
ç – speed of light in vacuum (m/s)
λ – wavelength (m)
In the table below, we have the frequency and wavelength ranges corresponding to some colors of the visible electromagnetic spectrum:
Color |
Frequency (THz – 1012 Hz) |
Wavelength (nm – 10-9 m) |
Red |
480-405 |
625 - 740 |
Orange |
510-480 |
590-625 |
Yellow |
530-510 |
565-590 |
Green |
600-530 |
500-565 |
Blue |
680-620 |
440-485 |
Violet |
790-680 |
380-440 |
Looking carefully at the table above, you can see that the color Violet presents the highest frequency of the visible spectrum and, consequently, the shortest wavelength, since these two quantities are inversely proportional.
See too:Wave classification
visible electromagnetic spectrum
The visible spectrum refers to electromagnetic waves whose frequencies are located between infrared and ultraviolet. These waves, which have frequencies that extend from 4.3.1014 Hz up to 7.5.1014 H, are those that can be perceived by the eyehuman and interpreted by the brain.
Electromagnetic spectrum colors
The figure below shows the visible electromagnetic spectrum, showing the peak frequency corresponding to each color, note:
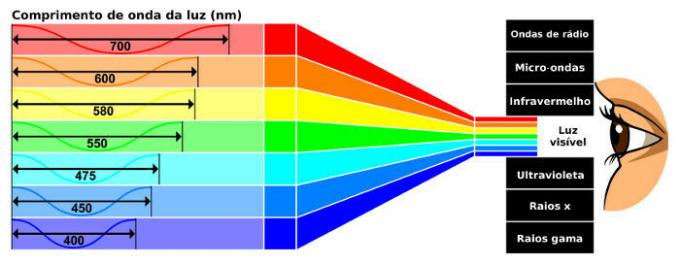
Only a small fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum can be perceived by the human eye.
In ascending order of frequencies, the colors in the visible spectrum are: Red, Orange, yellow, green,cyan,blue and Violet. Next, we will present a little about the properties and technological uses of each of the frequency ranges in the electromagnetic spectrum.
radio waves
Radio waves are a range of frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum that are widely used in radio technologies. telecommunications. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, extending between 1 mm (10-3 m) up to 100 km. This type of wave is used to transmit television, radio, cell phone, internet and GPS signals.

Mobile phone antennas use radio waves.
microwave
Microwaves are electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths extend between 1 m and 1 mm or 300 GHz and 300 MHz, respectively. Thus, microwaves are within the range of radio waves. Despite this, they have frequencies a little higher than radio waves and are used in applicationsmany different.
The main technological uses of microwaves are wireless networks (wi-fi routers), radar, communication with satellites, astronomical observations, food heating, among others.
Infra-red
Infrared is an electromagnetic wave with a frequency lower than visible light (300 GHz to 430 Thz) and, therefore, invisible to the human eye. Most of the thermal radiation emitted by bodies at room temperature is infrared radiation. As it is a very large frequency range, with several technological applications, infrared is subdivided into smaller regions: near, medium and far infrared.
In addition to being able to be used to Warm, because of its ability to make the molecules of a body vibrate, infrared is used for cooking food, for heating of environments, for the production of presence and movement detection systems, parking sensors, remote controls and vision cameras thermal.

Thermal vision is useful in the absence of visible light, it detects infrared rays emanating from heated bodies.
Lookalso: What is the speed of light?
visible light
The range of the electromagnetic spectrum that can be seen by the human eye is known as visible light, whose wavelength extends between 400 nm and 700 nm, so all the images we see are about the iinterpretation that the brain produces of the electromagnetic waves that are emitted or reflected by the bodies around us. The human eye is able to perceive these frequencies of light thanks to two special types of cells that line the back of the eye: cones and rods.
You cones and the rods they are photoreceptor cells, that is, they are capable of perceiving light signals. While rods are responsible for the perception of movement and the formation of images in black and white (as when we try to see in the dark), cones provide us with color vision. There are three types of cones in the human eye and each of them is able to perceive one of the following colors: red, green or blue.
For Physics, therefore, the colors we see are just phenomenaphysiological that depend on the capture of light and its interpretation by the brain. Furthermore, the ratio between each of the frequencies of red, green and blue is capable of producing all the tones we know. When emitted together, these three colors produce white light, which is not a color but a superposition of visible frequencies.
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation corresponds to the set of frequencies of electromagnetic waves that are higher than the frequencies of visible light and lower than the frequencies of X-rays. This type of radiation has three subdivisions that are not exact: ultravioletnext (380 nm to 200 nm), ultravioletdistant (200nm to 10nm) and ultravioletextreme (1 to 31 nm).
Ultraviolet rays can also be subdivided into UV-A (320-400 nm), UV-B (280-320 nm) and UV-C(1-280 nm) rays. Such classification concerns the forms of interaction these ultraviolet frequencies with living organisms and the environment.
Despite all being produced by the Sun, 99% of the ultraviolet radiation that reaches the Earth's surface is of the type GRAPE, the radiation UV-B, however, although less present, it is mainly responsible for damage to human skin, such as burns and damage to DNA molecules in epithelial cells.
O UV-C, in turn, it is the most frequent ultraviolet, capable of destroying microorganisms and sterilizing objects. All UV-C radiation produced by the Sun is absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere.
Ultraviolet rays can be used for artificial tanning, as they induce the formation of melanin; in fluorescent lamps, causing the phosphor present in these lamps emits white light; in analysis of molecules that can undergo structural changes when exposed to ultraviolet light; and also in treatments for fight cancer of skin.
Lookalso: Do you know what black light is?
X ray
You X ray they are a form of electromagnetic radiation with a higher frequency than ultraviolet, however, their frequency is lower than the characteristic frequency of gamma rays. X-rays extend across the electromagnetic spectrum between frequencies of 3.1016 Hz and 3.1019 Hz, which correspond to very short wavelengths, between 0.01 nm and 10 nm (1 nm = 10-9 m).
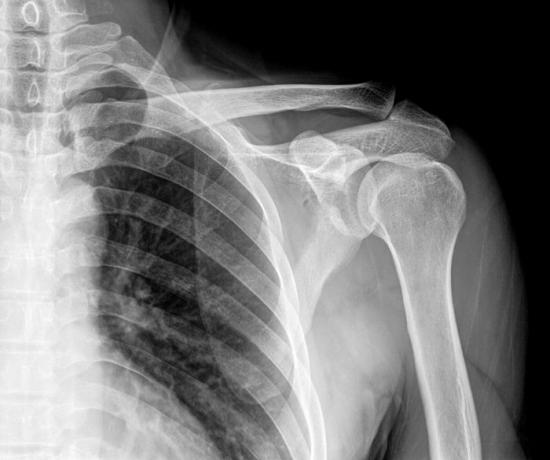
X-rays are absorbed by the bones, so it is possible for us to produce images of the interior of the human body.
X-rays have a great ability to penetration and are absorbed by human bones, for this reason, this type of radiation is widely used for imaging exams, such as radiography and tomography.
Also, X-rays are a way of ionizing radiation, as they can damage the genetic code of cells. It is for this reason that X radiation is also used in sessions of radiotherapy.
Gamma
You gamma are a form of electromagnetic radiation from highfrequency (between 1019 Hz and 1024 Hz), usually produced by the nuclear decay of radioactive elements, by the annihilation between pairs of particles and antiparticles, or in phenomena astronomical events of large proportions, such as the emergence of novae and supernovae, star collisions and eruptions solar.
Gamma radiation carries an enormous amount of energy, being able to pass through obstacles such as concrete walls with relative ease. Furthermore, it is a highly ionizing radiation, capable of causing irreversible damage to various tissues. Despite its dangers, gamma radiation is widely used in medicinenuclear, for the treatment of cancer and also in complex surgeries, such as the removal of intracranial tumors.
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/espectro-eletromagnetico.htm
