Pollution is any change caused in the environment, which can be a natural or agrarian ecosystem, an urban system or even on a microscale. The pollution that causes changes in the environment is called environment pollution.
The term pollution comes from the Latin pollute, which means “to get dirty”.
Pollution can cause changes in the proportions or characteristics of one of the elements that make up the environment itself. It is the case of the increased concentration of carbon dioxide or carbon dioxide naturally present in the atmosphere.
Pollution can result from the introduction of natural substances, however foreign to certain ecosystems. This is the case of the dumping of organic matter into the bed of a river or the crude oil spill at sea.
Pollution can be caused by the introduction of artificial substances and, therefore, foreign to any ecosystem. For example: the deposition of pesticides and plastic containers on soil and water, the release of artificial radioactive elements into the atmosphere, soil and water.
What are the main types of pollution?
There are different types of pollution: soil, water, air, thermal and radioactive. There are also urban pollutions, such as sound and visual.
Learn about each of the types of pollution and pollutants that cause them.
Ground pollution

Soil pollution occurs when chemical products (such as fertilizers and pesticides), garbage or sewage residues that change their original state are deposited in it. Garbage thrown directly onto the ground and household waste that is dumped in inappropriate places is one of the biggest causes of soil pollution.
Pollution and soil contamination can make land unproductive for planting and can also pose risks to people's health.
Contamination happens because the garbage that is deposited on the ground, after the decomposition process, changes the living conditions of bacteria, fungi and worms that are responsible for maintaining the balance of the ecosystem of the place.
Water pollution
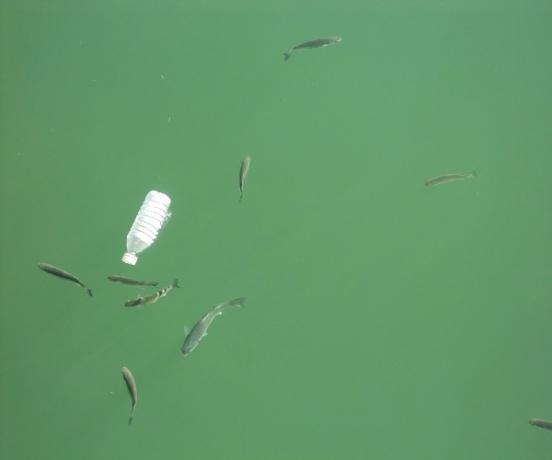

As with the soil, water pollution is also caused by the dumping of garbage, sewage and chemicals into the seas, oceans, lakes and rivers. Household, agricultural and industrial waste are the main responsible for water pollution.
Polluted water loses its quality and can cause health problems and increase contamination by various diseases, especially infections. Another consequence of water pollution is the alteration of the environment in which marine animals live, which can cause an imbalance that alters living conditions and causes the death of animals.
Water pollution can also cause cyanobacteria overgrowth, which increases algae growth on the water surface. This phenomenon, called eutrophication, hinders the entry of light and oxygen into the waters and can cause the mortality of marine animals.
Air pollution

Air pollution, also called atmospheric pollution, occurs mainly through the emission of polluting gases, residues from industrial burning and the use of aerosol products. The residue from burning fuel (carbon monoxide) from cars is a major cause of air pollution in large cities.
Some natural factors also influence air pollution, such as methane gas that results from the digestive process of animals and the burning residue of active volcanoes.
The environmental impacts of air pollution are: increased acid rain, damage to the ecosystem in general and the increase in global warming, which raises the temperature in a globalized manner.
For people who live in cities with a high rate of air pollution, the consequences are the worsening of respiratory problems in general, such as sinusitis, rhinitis and bronchitis.
Air pollution is measured by the air quality index (IQA). This index checks whether the air pollution in a given location is at acceptable levels or not.
thermal pollution

Thermal pollution is the increase in water and air temperature. The heating of water takes place mainly in hydroelectric plants. Global warming also has an influence on the increase in thermal pollution.
This type of pollution is not as well known as the others, but it is equally harmful to the environment.
The most serious consequence of thermal pollution is that the water from the plants changes the temperature of the seas and oceans, which can cause an imbalance in the aquatic ecosystem. The imbalance can cause changes in the lives of aquatic animals and other forms of life in the ecosystem.
know more about greenhouse effect and global warming.
radioactive pollution
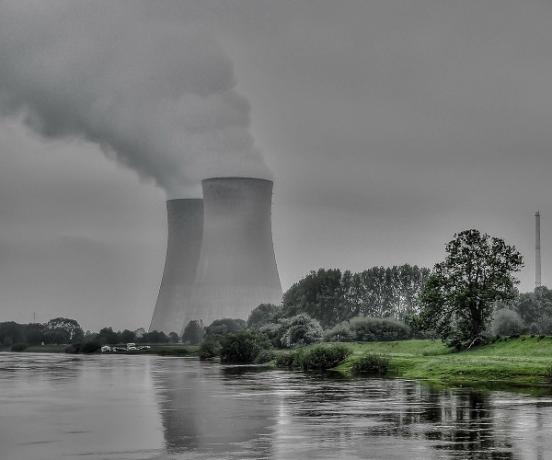

Radioactive pollution, which is also called nuclear, is the pollution of waste from radioactive materials. These residues, called radioactive waste, originate in nuclear power plants by the process of producing nuclear energy or atomic energy.
Radioactive pollution is the most dangerous to the planet for the consequences it can generate. Examples of this are nuclear accidents and the use of atomic bombs.
Radioactive pollution can have serious consequences on the lives of human beings who are exposed to it. In addition to causing death, exposure to radioactive pollution can lead to the appearance of serious diseases (such as tumors, internal injuries and infections) and various deficiencies.
Radioactive pollution also causes serious damage to the environment because, because of its destructive potential, it can completely alter ecosystems.
Noise pollution

Noise pollution is characterized by the excess of sounds, when considering the healthy noise level to which a person may be exposed.
Noise pollution is considered a very common problem in large cities, due to traffic, construction, nightclubs and any other noise that is part of the routine of cities, especially the most busy.
In addition to causing harm to human beings, noise pollution can also harm the environment, especially to animals. For people the most common consequences are irritability, sleep disorders, stress, mood swings and heart problems. In some more serious cases, noise pollution can lead to deafness.
Noise pollution is measured in decibels, which indicate the frequency of sound emitted. The World Health Organization (WHO) considers that the level of healthy exposure to sound is no. maximum 50 decibels.
Visual pollution

Visual pollution happens when there is an excess of visual content information capable of causing changes in the quality of life of a person who is exposed to it. As with noise pollution, visual pollution is a very common problem in big cities.
Some examples of visual pollution are the exaggerated use of posters, billboards, luminous symbols, advertisements, signs and electricity and internet wires.
The excess of visual information that is taken to those who live with this type of pollution can cause feelings of anxiety, discomfort, fatigue and mental confusion.
Visual pollution can also have consequences on life in cities because it can cause traffic accidents and difficulties in locomotion of pedestrians, due to the excess of information and difficulty in perceiving the necessary information due to the confusion visual.
Learn more about types of pollution.
Main consequences of environmental pollution
Depending on the type of pollution, the consequences can be different. See some more in addition to those already mentioned:
Pollution and Biodiversity
Pollution is one of the main threats to biodiversity, that is, to the wide variety of life that survives in different environments, from the depths of the oceans to the highest peaks of the mountains.
Biodiversity is responsible for ensuring the balance of the world's ecosystems. The ecosystem is the set of living beings and environmental factors in a given area that interact in balance, exchanging energy and matter.
Therefore, pollution is a risk to natural systems, it is a risk to the balance between plants, animals, climate and soil.
Learn more about biodiversity.
Air pollution and acid rain
The phenomenon of acid rain is a result of exaggerated elevation of atmospheric acidity levels, as a result of the release of pollutants produced by human activities.
Although the rains, even in unpolluted environments, are always acidic, the increase in this acidity caused by the emission of pollutants from industries, transport and others combustion sources, result in the concentration of acids with high corrosion capacity, destroying in addition to several ecosystems, important monuments of history human.
Learn more about the meaning of acid rain.
Pollution and the food chain
The food chain is the set of living beings that depend on each other for survival in nature. Pollution and human interference in ecosystems transform nature and cause changes in the food chain, with the extinction of animal and plant species, with soil erosion, forest burning, air pollution and soil and Water.
Read more about food chain.
What are sustainable cities?
Sustainable cities are cities that try to find a formula that guarantees the prosperity and quality of life, while preserving the environmental heritage and resulting in the least possible impact on the environment environment.
Sustainable economies, with clean technologies, bury old structures based on predatory models. Reduce the emission of greenhouse gases, eliminate water waste, use renewable energy, recycle garbage, clean up rivers, reduce the use of pesticides, are some of the measures that, in addition to improving the quality of life, preserve the life.
Learn more about sustainable cities, environment pollution and atmospheric pollution.