At the Kingdom Fungi including fungi, organisms heterotrophic, multicellular or unicellular, which were once considered primitive plants. One of the differences between these two groups is the fact that plants have chlorophyll, a feature absent in fungi. There are more than 100,000 species of fungi described, and experts believe that more than 1000 are discovered each year.
These species play an important ecological role, acting, for example, with bacteria, in the process of decomposition. Also, some have great economic potential, and others are responsible for triggering diseases in our body. As known representatives of fungi, we can cite the molds, molds and mushrooms.
Read too:Dermatophytoses - skin infections caused by fungi
General characteristics of fungi
Fungi are heterotrophic organisms and eukaryotes that can be unicellular or multicellular. The vast majority of species are filamentous, and these filaments are called hyphae. Some fungi are formed by several densely joined hyphae, which form the so-called mycelium. Mycelium can be seen in mushrooms, for example.
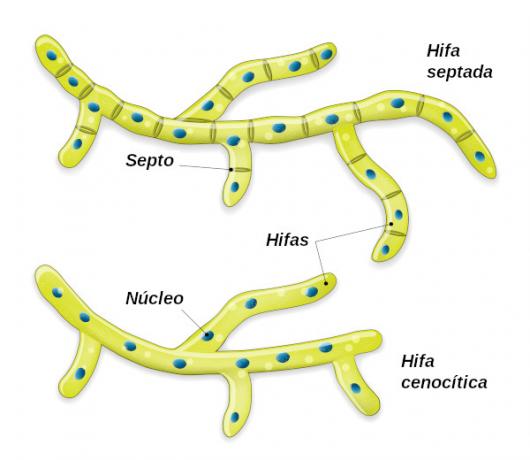
Most fungi have septate hyphaes, that is, which are divided by the so-called septa. You septa are transverse walls perforated by a pore that allows communication between the cells, guaranteeing the passage even of cell organelles.
The hyphae that do not have these septa are called aseptate or coenocytic. What is observed in them is a large continuous cytoplasm with several scattered nuclei. in fungi parasites, the hyphae are called haustories and are capable of extracting from their host the substances necessary for their development.
As mentioned, not all fungi are filamentous, there are unicellular fungi, such as yeasts. It is worth noting that the yeast, despite what many people think, are not a taxonomic group, being related only to the morphological form of growth. There are about 600 known yeast species.
The cells that form fungi present chitin-rich cell walls, a type of polysaccharide also found in the exoskeleton of arthropods. When we talk about cell walls, many people relate it to the one found in plants, but the The composition of the cell wall of fungi is different from that of vegetables, as in the latter we find the presence of cellulose.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Fungi nutrition
Fungi nutrition is heterotrophic, that is, they are organisms incapable of synthesizing their own food. These living things generally release enzymes onto the food and then absorb the nutrients they need. It is worth noting that there are parasitic fungi, species that live in symbiosis, and saprophytic fungi, which live on organic matter taken from dead beings. In both cases, nutrition is of the heterotrophic type.

Some fungi, to produce the energy they need, carry out the process of fermentation. This is the case of some yeasts that, because they have this property, are used very economically. In fungi, theglycogenis the main reserve carbohydrate.
Fungi reproduction
The reproduction of fungi occurs, for the most part, through the formation of spores, which can be produced from manner asexual or sexual. These spores help the fungi to spread through the environment, as many are dry and small, allowing them to be suspended in the air.
Some spores are sticky and spread through the medium, adhering to the body of insects, for example, and there are those released by the fungi themselves. When they find a suitable place, the spores germinate and give rise to a new fungus.
THE sexual reproduction it usually starts with the attraction of hyphae that release sexual signaling molecules. These molecules attract hyphae, which, when they meet, fuse. When the cytoplasm of two mycelia unites, we have the plasmogamy process. The nuclei of each individual do not merge immediately in some species, and may take hours, days and even months and years.
The next stage is called karyogamy, which occurs when haploid nuclei fuse. Here, the zygote is formed, which is a diploid stage. Division through meiosis restores the haploid condition, and spores are formed. Therefore, it is clear that sexual reproduction consists of three stages: plasmogamy, caryogamy and meiosis.
At asexual reproduction, it is also noticed the production of spores, however, it is usually observed that the filamentous fungi produce them by mitosis. Another form of asexual reproduction observed in fungi is by budding. It can be identified in yeast, in which a small sprout based on the mother cell appears. Yeasts can also reproduce by fission, and some fungi can still reproduce asexually by fragmentation of their hyphae.
Know more: Cissiparity - type of asexual reproduction that can occur in some yeasts
Main groups of fungi

There are different proposals in the scientific literature for the classification of fungi. We will present, below, the classification traditionally used and which presents the division into five strands:
Chytridia (Phylum Chytridiomycota): mainly aquatic organisms. The mycelium is cenocytic. They have flagellated spores.
Zygomycetes (Phylum Zygomycota): they have hyphae, mainly, coenocytic. In this group we have the famous molds, which grow, for example, on bread and fruit.
Glomeromycetes (Phylum Glomeromycota): mycorrhizal fungi. It is estimated that more than 80% of all plant species have mutualistic associations with this type of fungus. The mycelium has hyphae, mainly coenocytic.
Ascomycetes (Phylum Ascomycota): fungi with septate or unicellular hyphae. Organisms belonging to this group have varied life habits, being found in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Its typical reproductive structure are the asci, which are cup-shaped. They are considered the largest group of fungi.
Basidiomycetes (Phylum basidiomycota): have septate hyphae. Its typical reproduction structure is the basidia. In this group of fungi are included the mushrooms and the wood ear.
Read more:Hallucinogenic mushrooms - the main ones have psilocybin as an active ingredient
Importance of fungi
Fungi are living beings that are very important for the environment and also for human beings. See below some of its main actions:

Fungi act as decomposers: ensuring cycling in the middle. In this process, organic matter is broken down, carbon dioxide is released, and important substances, such as nitrogen, are returned to the environment. Despite all the importance of decomposition, this property of fungi is often responsible for harm to humans, as these organisms can attack various products, such as food, wood, paints, fabrics and roles.
Fungi perform important symbiotic relationships: have a relationship mutualistic, for example, with vegetable roots. This relationship is called mycorrhiza and helps the plant get the minerals it needs more efficiently. The plant, in turn, provides organic compounds for the fungus. Fungi can also associate with green algae or cyanobacteria and form so-called lichen. In this association, the organisms photosynthesizers they provide the organic compounds that the fungus needs, while fungi provide mineral nutrients and an environment conducive to the development of algae or cyanobacteria.
Fungi are used as raw material for the production of medicines: have components that can be used in the manufacture of medicines, such as antibiotics penicillin. That antibiotic it was the first used on a large scale, and today it is important in the treatment of syphilis. Another drug produced based on fungi is cyclosporine, used in transplant patients in order to prevent organ rejection.
Fungi are used as food: because they carry out fermentation, some species of yeast are used, for example, in baking. Fungi are also used in the wine and beer industry and to provide characteristic flavors and aromas to different types of cheese. In addition, many species are consumed without any processing, such as mushrooms.
Fungi can cause disease in humans: some of them are candidiasis, athlete's foot, onychomycosis (infection that affects the nails), pityriasis versicolor and some types of pneumonia. It is worth noting that fungi can cause diseases in other animals and even in plants.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher
For a long time, fungi were classified in the kingdom Plantae, along with plants. However, a clear feature allows us to recognize the reasons for these being separated into distinct realms. What such obvious feature can this be?
a) The fact that fungi are prokaryotes.
b) The fact that fungi have chlorophyll b, different from chlorophyll a present in plants.
c) Fungi do not photosynthesize.
d) Fungi reproduce by spores, unlike plants that reproduce by seeds.
e) fungi are autotrophic decomposers.
Substance present in the wall of fungal hyphae, also present in the skeleton of some animals such as crustaceans and insects:


