O phylum mollusk It has almost 50,000 species of invertebrate animals soft-bodied what have a shell, like oysters, snails, snails and shellfish. In number of species, this phylum just stays behind the string Arthropod.
However, this shell that is a important feature of molluscs it is not always visible, as is the case with squids that have an internal shell and octopuses that do not have a shell. The shells serve to protect the bodies of these animals against possible damage and also from possible dehydration.
they can live in terrestrial environment, as long as it is humid, but they are found more frequently in aquatic environments, both freshwater and marine.
Index
- classification of molluscs
- gastropods
- Bivalves or Pelecipods
- Cephalopods
- shellfish feeding
- Breath of molluscs
- Reproduction of molluscs
- mollusc locomotion
- Curiosities
classification of molluscs
gastropods
Gastropods are animals belonging to Gastropoda class which is the highest class of the phylum mollusk. These are molluscs that have a single spiral-shaped shell and have a very diverse morphology, ranging from microscopic size to several centimeters.
Members of this class can be found in the most diverse ecosystems, from gardens to mountains and ocean bottoms. Some species can be parasites.
The visceral mass is inside this shell, has a prominent head, often with eyes, has 2 to 4 sensory tentacles, and a mouth with a radula. They have muscular feet in the ventral position, hence the name derived from the Greek: “spend“, stomach and “pruning", foot.
THE gastropod feeding it can be mostly herbivorous for terrestrial animals and herbivores, detritivores and carnivorous predators for marine animals. Among the representatives of this group are snails, snails and slugs.

Bivalves or Pelecipods
THE bivalvia class is represented by molluscs formed by two articulated shells, that is, they open up. These shells are carbonated, equal and called valves. The location of the union of the valves is called the hinge.
They are joined by adductor muscles that regulate their opening and closing, andThese muscles form scars inside the shells and these scars are important in the classification of bivalves.
Bivalves are exclusively aquatic animals with diversified morphology, mainly in terms of shell carbonation. They are the only molluscs that do not have a radula and feed by filtration through siphons that pump water in and out of the animal's body.
The body is between the shells and basically consists of a visceral mass, the foot is most often absent. Scallops, mussels and oysters are examples of bivalve animals.

Cephalopods
You cephalopods are the molluscs belonging to class Cephalopod, are structurally more complex and are represented by animals that do not have an external shell, such as squids and octopuses. They have a body with bilateral symmetry, eyes very similar to those of vertebrates, and a well-developed nervous system.
The bodies of these animals have tentacles that are filled with suckers that serve both to hold the animal to a substrate and to capture prey. They have a mouth with radula and skin with cells called chromatophores, which can change color, favoring communication and camouflage.
- Free Online Inclusive Education Course
- Free Online Toy Library and Learning Course
- Free Online Math Games Course in Early Childhood Education
- Free Online Pedagogical Cultural Workshops Course
The octopus has a unique defense system, it has a black ink gland in the digestive system, this ink is released when it is attacked, thus confusing the predator and facilitating escape.

shellfish feeding
the cbody of molluscs is divided intohead, foot and visceral mass. Their head has the sense organs and mouth that may have a tongue with very sharp teeth, called a radula, which is used to scrape food.
They have a complete digestive system, that is, they have a mouth and anus. Digestion is done with the help of enzymes and nutrient absorption through the blood.
Breath of molluscs
THE shellfish breath varies depending on the environment in which they live. The molluscs that live in water breathe gill, is the case of octopus, squid and oysters.
Those who live in the wet terrestrial environment do lung breathing, like snails, for example. Those that live below ground or in trees, such as slugs, breathe cutaneously, that is, they breathe through the surface of the body.
Reproduction of molluscs
THE mollusc reproduction it is sexual, that is, with exchange of gametes. With the exception of bivalves, which are hermaphrodites, all other molluscs are dioecious, that is, they have separate sexes.
However, fertilization can be internal or external. External fertilization needs water, where sperm released by males and the eggs released by the females meet.
During internal fertilization, sperm are released into the female's body.
mollusc locomotion
In terrestrial molluscs, the feet have muscles that are able to pull the shell down and propel it forward, causing them to move slowly on the surface.
In aquatic molluscs, there is an opening called siphon that fills with water and expels quickly, performing a movement called jet propulsion that propels the animal forward. This is the main means of locomotion for squid and octopus, for example.
Curiosities
- Many molluscs can be used in food, they are called “seafood”. Some are even considered as elite foods such as escargot.
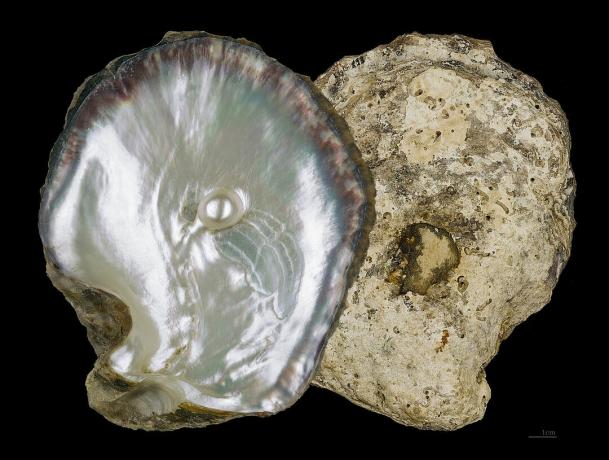
- They are also of great economic importance because the pearl oysters produce pearls of high commercial value.

See too:
- Phylum Mollusca – List of exercises
- 11 Invertebrate Animals
- Vertebrate and Invertebrate Animals - What They Are and Examples
- Animalia Kingdom: Invertebrates and Strings
The password has been sent to your email.