By handling two plane mirrors, we can obtain the formation of images through the association of mirrors. If we place two plane mirrors forming a 90º angle between them, we will obtain the formation of three images. As the angle between them decreases, the number of images formed increases.
When we put these mirrors face to face we can see infinite images being formed. But how are these images formed when the mirrors are placed in parallel?
The figure below shows us this particular case where the mirrors are arranged in parallel.
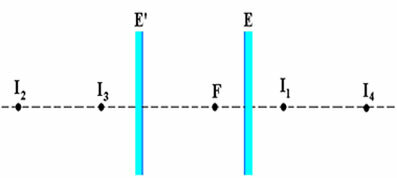
Imaging in parallel mirrors
The image formed from F in relation to the mirrorAND is the point I1. This image becomes the object for the mirror AND’, then producing the image I2, which will be the object for the mirror AND, and so on. Likewise, the image of F in relation to the mirror AND'is the point I3, which will function as an object for AND, producing the imageI4, and so on. In this way, infinite images, as we can see in the figure below.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Iinfinite images formed between two parallel mirrors
Now let's look at a special parallel mirror situation where the object is not between the mirrors. For that, let's check out a rudimentary periscope. With it, the viewer can see the image A’B’ of an object AB which is above him. We can verify that the image is right.
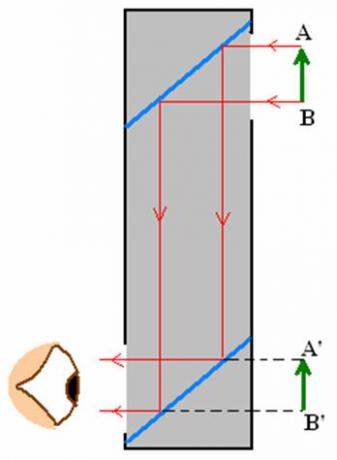
Periscope
Periscopes are used in submarines, and are a little more complex systems, consisting of several lenses and prisms instead of mirrors. As seen in the figure above, using two small mirrors and cardboard, we can build a homemade periscope.
By Domitiano Marques
Graduated in Physics
Brazil School Team
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SILVA, Domitiano Correa Marques da. "Parallel Mirrors"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/espelhos-paralelos.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.