Exposing yourself to the Sun during a certain time, the skin of the human body can produce erythema, which is a redness generated in the skin because of the dilation of blood vessels. Sunscreen creates a layer on the skin, protecting it from the action of the sun's rays and preventing burns and other problems that may arise from this exposure.
Sunscreen protects the skin from the action of ultraviolet rays
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) is an index that determines the maximum time of exposure to the sun for which the skin is protected by a sunscreen. Suppose that for a certain individual the time of exposure to the sun, with the skin unprotected, is ten minutes. If he uses a SPF 30 sunscreen, for example, the time of exposure to the sun, without damage to the skin, will be 30 times longer, that is, 300 minutes.
How is the FPS determined?
The FPS is determined based on the knowledge of the Minimum Erythema Dose (DME), that is, the minimum time of exposure to the sun's rays for the redness of the skin to occur. The FPS is defined by the ratio of DME to a DME-protected skin of unprotected skin.

The DME for unprotected skin depends on the individual's skin type. Thus, the lighter the skin, the shorter the time of exposure to the sun's rays capable of causing burns.
Types of solar radiation
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
At radiations from the Sun, which reach the skin and can even generate cancer, are the type ultraviolet (UV). When analyzing the electromagnetic spectrum, it is possible to notice that ultraviolet radiation has frequencies higher than the frequencies that make up the visible spectrum and therefore cannot be perceived by the human eye. These radiations are classified as UVA, UVB and UVC.
GRAPE: It has wave-length between 315 nm (1 nm = 1 x 10 – 9 m) and 400 nm, is little attenuated by the ozone layer and reaches the deepest layers of human skin;
UVB: it has a wavelength between 280 nm and 315 nm, is partially absorbed by the ozone layer and does not penetrate deep regions of human skin;
UVC: it has a wavelength between 100 nm and 280 nm and is totally absorbed by the ozone layer.
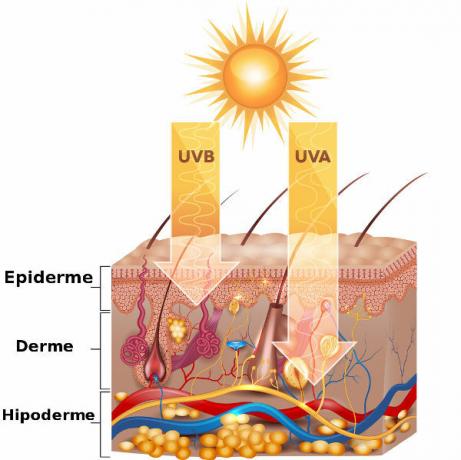
UV rays are linked to skin burns, premature aging, eye problems and can, in the long run, lead to skin cancer. In correct amounts, UV radiation brings benefits, such as fixing the vitamin D.
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
JUNIOR, Joab Silas da Silva. "Sun Protection Factor (SPF)"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/fator-protecao-solar-fps.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.