thermal conduction or simply conduction is a heat transfer process that occurs inside solids, due to a differenceintemperature. In driving, the Thermal energy is transferred between the atoms and molecules on one solid without the transfer of matter, until the condition of thermal equilibrium.
This phenomenon occurs in all substances, regardless of their physical state, despite morefrequentinsolids. This happens because, in the solid state, the fixed position of the atoms, which are arranged in a crystalline lattice, favors the exchange of energy between atoms due to the frequency at which collisions occur between these particles.
Lookalso:Everything you need to know about Thermology
How does thermal conduction occur?
The process of drivingthermal is characterized by the interaction between atoms of many differenttemperatures. When we heat up a body, its atoms start to oscillate with greater amplitude. Those more agitated atoms transfer part of your kinetic energy to the neighboring atoms by collisions and vibrations, in this way they slow down, while the any lessagitatedwinvelocity. Through this mechanism, heat is gradually transferred from the higher temperature regions towards the lower temperature regions, until the entire system is at the same temperature.
US gases, for example, heat transfer by conduction occurs exclusively through collisions between atoms. US non-metallic solids, thermal conduction takes place through vibrations along the material's crystal lattice. US metallic solids – the best heat conductors –, conduction occurs both by propagating vibrations in the crystal lattice and by the chaotic movement of free electrons.

Insulators and thermal conductors
Different states of matter transmit heat through different mechanisms. The materials called conductors, for example, are those capable of transferring heat with large ease - is the case with most metals. The materials insulators, in turn, they are those that hinder the passage of heat, such as the polystyrene, a rubber, The wood etc.
Differences between conduction, convection and radiation
Driving, convection and radiation are the three different forms of propagation of the heat. The common point between these three processes is that there must be a differenceintemperature between different bodies or at different points on the same body.
THE driving, as said, it occurs through direct contact between molecules, which, when colliding, transfer kinetic energy to its neighboring molecules. In this type of heat transfer, there is no matter transport. Convection, in turn, occurs exclusively in fluids and, as well as in driving, only occurs in material means. The difference between conduction and convection is that, in convection, there are transportinpasta by convective currents. THE radiation and the transferinheat per electromagnetic wavesTherefore, this heat transfer process can take place in a vacuum.

Heat flux or Fourier's law
The amount of heat that is transferred between two points inside bodies, every second, is called flowinheat. This concept concerns how quickly heat is transferred inside a body. Some materials have a great capacity for heat transfer, therefore, we say that they are good conductors of heat, as they are able to dissipate it more quickly.
O flowinheat, which is defined as a function of a constant k, is measured in watts (W), according to the International System of Units, but it can also be measured in caloriespersecond. This energy flow is proportional à differenceintemperature between two points of a body and corresponds to the amount of energy that flows, in the form of heat, to each square meter of surface, during the period of time of one second.
THE formula used to calculate thermal conduction, also known as heat flow formula or LawinFourier is as follows:

Φ – heat flux (cal/s or W)
Q – heat (lime or J)
t – time interval(s)
A - area (m² or cm²)
T2 and T1 – temperature of points 1 and 2 (K or ºC)
k – thermal conductivity coefficient (J/s.m. K or cal/s.cm.ºC)
O thermal conductivity coefficient (k) determines whether or not a body is a good conductor of heat. This coefficient relates to a large number of properties of matter, such as the temperature,statephysicist,purity,density etc. Also, the formula shows that the amount of heat Q flowing through an area THE, for a period of time t, is proportional to the temperature difference (T2 - T1) between the two faces of this area and also inverselyproportional to thickness and, which separates them. Observe the following diagram, which shows the thermal conduction in a solid medium, according to the presented variables:

Exercises on thermal conduction
Question 1) During a sunny day, a large amount of heat – around 180 cal – passes through the windows of a vehicle that has been parked outdoors for a period of 15 minutes. Determine the heat flow through the windows of this vehicle in this situation.
a) 10,000 cal/s
b) 2000 cal/s
c) 50 cal/s
d) 300 cal/s
e) 500 cal/s
Template: Letter B
Resolution:
To solve the exercise, simply calculate the amount of heat that passes through the vehicle's windows every second. Watch:
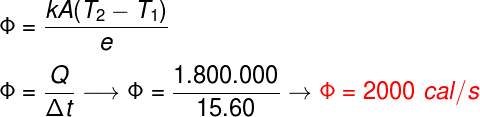
According to the calculation, about 2000 calories pass through the vehicle windows every second, so the correct alternative is the letter B.
Question 2) Mark the alternative where heat conduction only occurs:
a) Hot water being mixed with cold water.
b) Paper being burned by sunlight, concentrated by a magnifying glass.
c) Iron burning a shirt.
d) Water vapor cooking a vegetable.
Template: Letter C
Resolution:
Among the processes listed, the first is a convection heat transfer; then we have radiation, in the letter B; driving, in the letter C; finally, in the last alternative, convection again. Therefore, the correct alternative is the letter C.
By M.e Rafael Helerbrock
Physics teacher
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/fisica/conducao-termica.htm

