Know some of the most important discoveries gives Physics that happened totally by chance, understand what the consequences of these discoveries were and how they changed our way of life.
#1 - X-rays
Did you know that the X ray were discovered unintentionally? Around 1895, the German physicist WilhelmRoentgen performed several researches related to the production of electromagnetic waves using tubesinrayscathode, like those used in older televisions, called CRT.
Lookalso: Difference between fluorescence and phosphorescence
Roentgen was able to notice, during one of his experiments, that a small fluorescent plate in his room emitted a faint glow when the cathode ray tube was turned on. Roentgen used several obstacles that isolated the tube from the plate, and his conclusion was that that tube emitted some type of radiation hitherto unknown, capable of pass through several different materials.
Finally, the physicist attached a photographic film in front of his cathode ray tube and realized that it was possible to capture incredible images that revealed the
internal structure of diverse bodies and even of the bones.At the time of its discovery, X-rays started to be widely used for the study and investigation of fractures and other types of diseases, even before the discovery of Potential harms of using this type of radiation.
Currently, several imaging exams are performed using X-rays, such as radiography and the tomography. In addition, some types of cancer are fought through exposure to X-rays, by a technique called radiotherapy.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
#2 - Cosmic Background Radiation and the Big Bang
THE cosmic background radiation is frequency in microwave which spreads evenly throughout space, being present in all directions of the Universe.
This electromagnetic wave frequency is an indication that, at some distant moment, just a few thousand years after its origin, the Universe had suffered a great inflation, increasing in size several times.
The rapid removal of galaxies and nebulae made the light emitted by them, which is still propagating through the Universe, to have suffered an increase in its length of wave, due to a physical phenomenon called Doppler effect.
The discovery of this important type of radiation, responsible for strengthening the arguments of the theory of big Bang, was, however, totally accidental. At the time, engineers from the US telecommunications company Bell, Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, were trying to reduce a noise perceived in one of their powerful antennas. This low-intensity noise, located in the microwave range, could be picked up in whatever directions the antenna was aligned with.
The engineers published a scientific article in which the frequency and characteristics of this radiation were indicated, which was explained by cosmologists a few years later as the remnant radiation of the origins of Universe. In 1978, engineers Arnopenzias and RobertWilson they were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics for their discovery.
Lookalso:Curiosities about the Solar System
In addition to its contribution to the understanding of the origins of the Universe, the determination of the cosmic background radiation was of fundamental importance for the telecommunications, to the Astronomy and also for sensitive experiments involving the production or capture of particleshigh energy.
Today, through corrections made by computers, it is possible to clean the noise of the cosmic background radiation, thus producing results of experiments more accurate and better fundraising in electromagnetic signals.
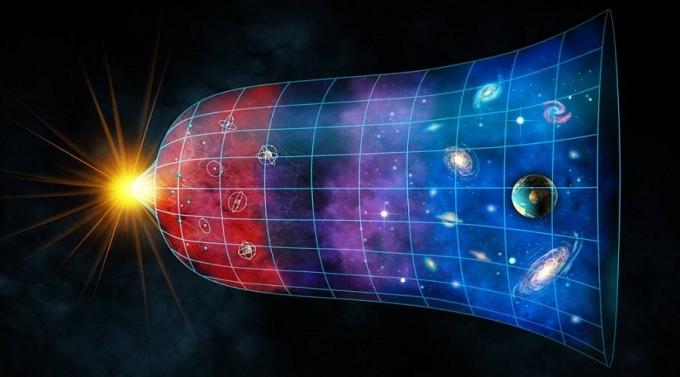
The main evidence of the expansion of the Universe is the cosmic background radiation.
#3 - Teflon
Teflon is the trade name given to the substance. polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), an inert polymer (which hardly reacts with other substances), highly resistant to corrosion, waterproof, in addition to presenting very low values of coefficient of friction.
There are some myths around the emergence of teflon, one of them says that teflon was created by NASA, which employs them in their ships. However, teflon was an accidental discovery made by chemist Roy Plunket in 1938.
At the time, Roy was researching new refrigerant gases, in particular, testing the properties of TFE (tetrafluoroethylene) gas. On one occasion, he noticed that the gas polymerized, forming a substance with very interesting physical and chemical properties and potential applicationstechnological and commercials. A few years later, PTFE was registered and widely marketed under the name Teflon.

Teflon is a material of great importance due to its various technological applications.
See too: How much does it cost to recharge your cell phone battery?
#4 - Atomic nucleus
For a long time, it was believed that the atom was formed by an even distribution of positive charges, encrusted with small negative charges that could be removed and put back on. That atomic model, able to explain electrostatic phenomena, was known as “raisin pudding” and its end was near.
In 1911, Ernest Rutherford performed an experiment in which he bombarded a very thin gold leaf with extremely fast alpha particles. Rutherford hoped that if atoms were like "raisin pudding," alpha particles would suffer low deflections in their trajectory. However, the experiment showed that, at some point in the atoms, there was a core extremely dense, which concentrated almost the entire mass of atoms. Today, we know that 99,9% of all volume on one atom é empty.
Rutherford's discovery began what we call the Modern physics, due to its model to explain the structure of atoms, the Rutherford atomic model. Modern physics began to study the phenomena that occur in the nucleus of the atom, such as its discrete energy transitions and the emission of electromagnetic and corpuscular radiation. Based on these studies, the first theories that tried to explain the quantum behavior of nature emerged.

Rutherford was able to perceive the existence of atomic nuclei using an experimental setup similar to the one shown above.
#5 - Microwave oven

Percy Lebaron Spencer was an American physicist responsible for discovering the heating caused by microwaves.
In 1945, Percy was working on the development of the magnetron, a device capable of emitting high-intensity electromagnetic waves used in microwave ovens current. Around this time, he noticed that the candy bar in his pocket had melted. Intrigued, Percy placed a bowl of corn in front of the magnetron, and to his surprise, some grains popped from the microwave heating.
Two years later, the technology was patented by the physicist and marketed as a household appliance used to heat food.
See too:Five fun facts about the rays that will make your hair stand on end
By Me. Rafael Helerbrock