Ontology is the branch of philosophy that studies the nature of being, existence and reality itself.
Ontology is classified in philosophy as the general branch of metaphysics (different from cosmology, psychology and theology, which are specific branches), as it deals with the most comprehensive and abstract themes in the area. For this reason, it is common that the terms ontology and metaphysics are used as synonyms, although the first is inserted in the second.
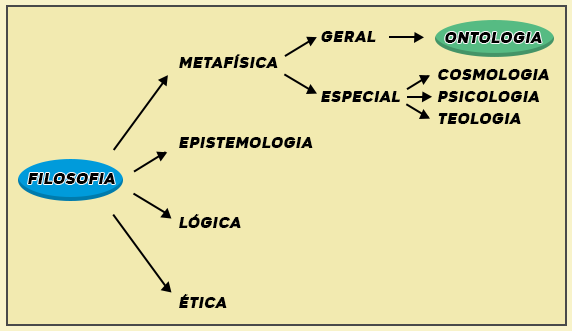
The word ontology is formed from the Greek ontos (to be) and logy (studies), and encompasses general issues related to the meaning of being and existence. This term was popularized thanks to the German philosopher Christian Wolff, who defined ontology as philosophia cousin (first philosophy) or science of being as being.
In the nineteenth century, ontology was transformed by neoscholastics into the first rational science that addressed the supreme genres of being. The philosophical current known as German idealism, by Hegel, started from the idea of self-consciousness to recover ontology as the "logic of being".
In the 20th century, the link between ontology and general metaphysics gave way to new concepts, such as that of Husserl, who sees ontology as a formal and material science of essences. For Heidegger, fundamental ontology is the first step towards the metaphysics of existence.
Some of the key questions in this area are:
- What can be considered existing?
- What does it mean to be?
- What entities exist and why?
- What are the various modes of existence?
Over time, numerous philosophers have used different methodologies and classifications to answer these and other questions.
ontology dichotomies
Through the different philosophical positions that address the above issues, ontological science is organized into various dichotomies (divisions), such as:
Monism and Dualism
THE monistic ontology (ontological monism) understands that reality is composed of only one element, the universe. For this theory, all other things are different ways the universe is structured.
THE dualistic ontology (ontological dualism) argues that reality is formed by two planes: a material (body) and a spiritual (soul) plane. The main defenders of this current were Plato and Descartes.
Determinism and Indeterminism
O ontological determinism it is the theory that understands nature as a system in which everything is interconnected and, therefore, there is no free will. For this current, all choices are actually the result of events that have already happened.
O ontological indeterminism it moves away from the rigid connection of cause and effect typical of determinism and bases free will on anthropological issues, not advocating, therefore, that all choices are made by chance.
Materialism and Idealism
THE materialistic ontology (ontological materialism) defends the idea that for something to be real, it must be material.
To the idealistic ontology (ontological idealism), reality is actually spiritual, and all matter is an illusory representation of truth.
ontological proof
The “ontological argument” or “ontological proof” is the argument that ontology uses to defend the existence of God. The first and most famous ontological argument is attributed to the theologian Anselm of Canterbury, who reflected that if the idea of a God perfect is present even in the minds of people who do not believe in its existence, so God must exist in reality as well.
legal ontology
Ontology, in the legal field, is the part of the Philosophy of Law that studies the essence and reason for being of a law, doctrine or jurisprudence.
ontology in computer science
In Information Science and Technology, ontologies are classifications used to categorize or group information into classes.
Ontologies are also applied in Semantic Web and Artificial Intelligence to assimilate and code the knowledge, defining the relationships between the concepts of a given domain (an area of knowledge).

