Irene Curie (1897-1956), daughter of Marie Curie, and her husband Frederic Joliot (1900-1958) carried out, in the year 1934, artificial transmutation experiments, in which they bombed aluminum 1327Al with alpha particles (24α) and were able to obtain a phosphorus isotope (1530P) and a neutron.
1327Al+ 24α → 1530P + 01no

Most interestingly, however, they observed that this phosphorus isotope was radioactive and that it emitted a particle with mass equal to the electron; however, its charge was positive. They also saw that when alpha particle bombardment was stopped, aluminum stopped emitting neutrons, but continued to fire positrons. the same way alpha and beta particles are emitted in natural radioactivity – indicating that positrons were actually emitted by phosphorus and not by aluminum.
This new radioactive particle was given the name of positron, or positive beta particle, being represented by +10and or β+, or yet, +10β. It is now known that positron is actually an anti-beta-negative particle.
The nuclear reaction of this process studied by Irene and Frederic is represented by:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
1530P → +10and + 1430Yes
Note that when the radioisotope, which in this case is phosphorus, emits a positron, its atomic number (Z = protons) decreases by one unit and its mass number (A = protons + neutrons) remains unchanged. See two more examples:
815O→ +10and + 715O (Note that 15 = 0 + 15 and 8 = 1 + 7)
611Ç → +10and + 511B (Note that 11 = 0 + 11 and 6 = 1 + 5)
Positrons are emitted by radioisotopes that have a high number of protons.
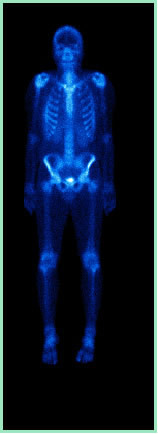
Positron emission is used in medicine in scintigraphic imaging diagnostics, known as positron emission tomography (PET). This diagnostic method studies the bone marrow through the injection of the radioactive marker and is mainly useful in the evaluation of inflammatory/infectious processes (acute osteomyelitis). This radioactive marker has the ability to aggregate to the bone matrix in proportion to the blood flow in the region and metabolic activity. With this, a photograph of the body or some localized images is taken, when indicated.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Discovery of Positrons"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/descoberta-dos-positrons.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
