Cartesian is an adjective referring to discards, French philosopher, physicist and mathematician, “considered the father of modern philosophy”, whose Latin name was Cartesius, who named the Cartesian thinking.
O Cartesian rationalism it is a thought established by Descartes in his works “Discourse on Method” (1637) and “Metaphysical Meditations” (1641), where he expresses his concern with the problem of knowledge.
The starting point is the search for a first truth that cannot be doubted. Therefore, he converts his doubts into a method to lead the Reason well and look for the truth in Sciences.
O Cartesian thinking begins by doubting everything, convinced that both traditional opinion and the experiences of humanity are guides of doubtful merit, decided to adopt a new method entirely free of influence both.
O Cartesian method it is based on pure deduction, it consists of starting with simple and self-evident truths or axioms, and then reasoning on the basis of it, until arriving at particular conclusions.
Descartes stated that everything was doubtful, nothing could be considered “a priori” as certain, except for one thing: “If I doubt, I think, if I think, I exist”: “cogito, ergo sum”, “I think, therefore I exist”, the starting point of Methodical Doubt, from which all his thinking is built.
Learn more about the meaning of I think therefore I am.
Cartesian dualism
Cartesian Dualism or Psychophysical Dualism (or even Body-Consciousness Dichotomy) is a concept according to which the human being is a double being, composed of a thinking substance and a substance extensive.
This is because the body is a physical and physiological reality and, as such, it has mass, extension in space and movement, as well as developing activities of food, digestion, etc., always subject to the deterministic laws of nature, whereas mental phenomena have neither extension nor location in space.
The mind performs activities of remembering, reasoning, knowing and willing, without submitting to physical laws, but they are the place of freedom.
Cartesian person
The expression "Cartesian person" is used to characterize an inflexible person, who always think and act the same.
The Cartesian mind is egocentric and when it thinks of the other, its evaluation is always about the advantage it will be able to obtain from the situation.
Cartesian system
The Cartesian Coordinate System was created by René Descartes and allows locating points in a given space through a set of information.
The Cartesian Coordinate System is an important tool for the development of works in the field of geometry, calculus, construction graphics and also in the preparation of work related to geographic location, such as the creation of the Global Positioning System (GPS).
Cartesian plan
The orthogonal Cartesian system is used to locate and represent points in the Cartesian coordinate system, consisting of two perpendicular lines that intersect, forming two axes.
The horizontal axis is called the abscissa or x axis, the vertical axis is called the ordinate axis or y axis.
The origin point is the zero point, the intersection point of the axes. The system is divided into four parts, each forming a quadrant. Each point on the Cartesian plane is given by an ordered pair (X, Y).
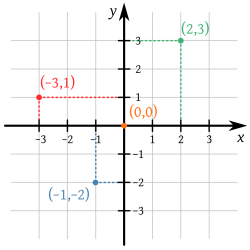
Learn more about Cartesian Plan.
See also the meaning of Rationalism.