O buoyancy is the force acting on objects that are partially or completely immersed in fluids, like air and water. The thrust is avector greatnessthere,measure in newtons, which always points to the samedirection and in the senseopposite to the weight of the immersed body. According to Archimedes' principle, the buoyant force on a body has magnitude equal to Weight of the fluid that has been displaced due to the immersion of the body.
Lookalso: Pascal's theorem and the functioning of hydraulic pistons
definition of thrust
The thrust is a strength which arises when some body occupies space within a fluid. Such strength depends exclusively on the volume of fluid that was displaced, as well as fluid density and local gravity. Based on this information, let's look at the formula used to calculate the modulus of the buoyant force:
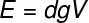
AND – thrust (N)
d – fluid density (kg/m³)
V – body immersed volume or displaced fluid volume (m³)
Before we go any further with some examples of thrust, we'll explain each of the
greatnessinvolved in the calculation of the thrust. If you want to go deeper into the subject, we suggest that you check out our text on Hydrostatics. In this article, you will find a summary of everything that is most important to this area of study in physics.Lookalso: Everything you need to know about waves
thrust (E)
the thrust is vector, therefore, to make calculations with this magnitude, it is necessary that we apply the vector addition rules. Furthermore, because it is a strength, the resolution of more complex exercises requires that, eventually, we apply the Newton's second law, which claims that the net force on a body is equal to the product of its mass and acceleration.
The following figure illustrates a case where a body is completely immersed in a fluid, as weight and buoyancy act. in the same direction (vertical), but in opposite directions, the resulting force can be calculated by the difference of two:
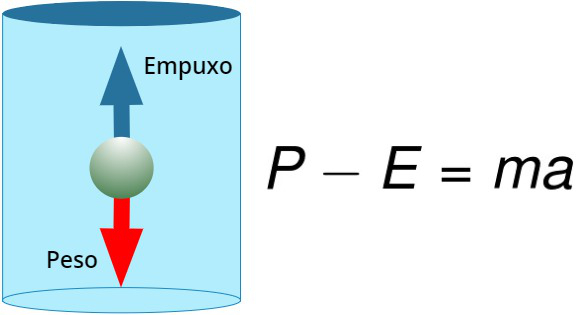
From the presented scheme, it is possible to see how the float balance, that is, it is possible to know if a body will sink or remain afloat:
- If the weight of the body is greater than the thrust exerted by the fluid, the object will sink;
- If the weight of the body is equal to the thrust exerted by the fluid, the object will remain in balance;
- If the body weight is less than the thrust exerted, the object will float to the fluid surface.
Lookalso: How has Quantum Physics contributed to humanity?
Fluid density (d)
THE density, or specific mass of the fluid, refers to the amount of matter per unit of fluid volume. Density is a greatnessclimb, measured in the unit of kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³), according to the International Measurement System (SI).
Check the formula used to calculate the density of the body below:

Originally, the density of all bodies was measured as a function of the density of pure water, so the density of water under normal conditions of pressure and temperature (1 atm and 25 °C) is defined in 1,000 kg/m³.
Although we use SI units to make calculations, it is common for fluid density is expressed in other units, so, in the figure below, we present a scheme that relates at main density measurement units and the relationships between them and the standard unit:
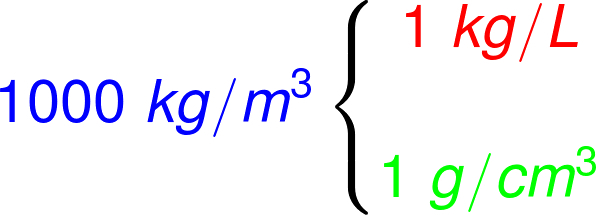
In the figure observed, we present the most common units for fluid density, however, you may come across other units, in which case, you need to know how to use the international unit system prefixesas well as perform volume conversions.
Lookalso:Does cold water help you lose weight?
Severity (g)
gravity is the acceleration that the Earth's mass exerts on all bodies that are around you. At sea level, the gravity da Terra has an intensity of 9.81 m/s², however, most exercises use this measure rounded to 10 m/s², remember to make use of gravity as required by the statement of exercise.
Displaced fluid volume or body volume (V)
The magnitude of volume that is contained in the thrust formula is related to the amount of body volume is embedded in the fluid, or, to displaced fluid volume. The volume of the body in question must be measured in cubic meters (m³).
Archimedes' Principle
According to speculation, the Archimedes' principle was developed when, one day, the Greek mathematician realized that when he got into his bathtub full of water, a large amount of liquid falls out of the bathtub - the same volume that was occupied by your body. After this observation, Archimedes concluded that the mass and, consequently, the weight of the water that fell from the bathtub were not equal to its weight and mass and that this difference would explain the why bodies float.
It is then stated that:
“When any body is inserted into a fluid, a vertical and upward buoyant force arises on the body. This force is equal to the weight of fluid displaced"
Floating Cases
It is possible to compare the densities of the fluid and the submerged body in order to predict whether this body will sink, will float or stay in balance. Let's check out these situations:
→ sinking body: if the object immersed in the fluid sinks, it can be concluded that its density is greater than fluid density, similarly, we say that its weight is greater than the thrust exerted by the fluid.
→ Body in balance: if a body placed on a fluid remains in equilibrium, that is, stopped, we can say that body and fluid densities are equal, as well as its weight and thrust.
→ Floating body: when a body floats, if released into a fluid, the thrust exerted on it is greater than its weight, so we can say that the density of this body is less than the density of the fluid where he finds himself.
See too: Can using a cell phone all the time harm your health? Find it out!
apparent weight
You've probably noticed that some bodies look lighter than they actually are if placed in the water. This is because, when immersed, in addition to the weight, we have the buoyancy acting. The difference between these two forces is known as the apparent weight.
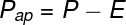
Note that if the weight and thrust have the same magnitude, the apparent weight of the body will be null, that is, in this condition, it is as if the object had no weight at all and therefore, it will be stopped about the fluid.
Examples of buoyancy
Check out some examples of situations in which there is an expressive performance of the buoyant force:
- Because it is less dense than liquid water, ice tends to float;
- Water vapor and hot air tend to rise, since when they are hotter, they take up more space, making their density less than that of cold air;
- Champagne bubbles are made up of carbon dioxide, which is a gas many times less dense than water, so when you open a bottle of champagne, these bubbles are violently expelled from the liquid;
- Floating party balloons do so because of the buoyancy of atmospheric air, as they are filled with gases that are less dense than atmospheric gas, such as helium gas.
solved exercises
Question 1-(Enem 2011) In an experiment carried out to determine the density of water in a lake, some materials were used according to illustrated: a dynamometer D with a graduation from 0 N to 50 N and a massive and homogeneous cube with a 10 cm edge and 3 kg of mass. Initially, the calibration of the dynamometer was checked, verifying a reading of 30 N when the cube was attached to the dynamometer and suspended in the air. By immersing the cube in the lake water, until half its volume was submerged, the reading of 24 N was recorded on the dynamometer.

Considering that the local gravity acceleration is 10 m/s², the lake water density, in kg/m³, is:
a) 0.6
b) 1.2
c) 1.5
d) 2.4
e) 4.8
Resolution
Alternative b.
First, it is necessary to realize that the difference in “weight” recorded on the dynamometer refers to the buoyant force exerted by the lake water, which, in this case, was equal to 6 N. After that, we can apply the buoyancy formula, using the data provided by the exercise, observe the calculation:

In order to do the above calculation, we had to convert the cube's volume, in cubic centimeters, into cubic meters.
Question 2 -(Enem 2010) During construction work on a club, a group of workers had to remove a massive iron sculpture placed at the bottom of an empty swimming pool. Five workers tied ropes to the sculpture and tried to pull it up, without success. If the pool is filled with water, it will be easier for workers to remove the sculpture, as the:
a) sculpture will float. That way, men won't need to strain to remove the sculpture from the bottom.
b) sculpture will be lighter in weight. In this way, the intensity of force required to lift the sculpture will be lower.
c) water will exert a force on the sculpture proportional to its mass, and upwards. This force will be added to the force that the workers use to cancel the action of the weight force of the sculpture.
d) water will exert a downward force on the sculpture, and it will receive an upward force from the pool floor. This force will help to counteract the action of the weight force on the sculpture.
e) water will exert a force on the sculpture proportional to its volume, and upwards. This force will add to the force that the workers exert, and may result in an upward force greater than the weight of the sculpture.
Resolution
Alternative e. When the pool is full of water, the buoyant force will act on it, in the vertical and upward direction, so it will be “lighter” and will be more easily removed from the bottom of the pool.
By Rafael Hellerbrock
Physics teacher
