THE spermatogenesis it is a process in which the formation of male gametes occurs, that is, the sperm. This process takes place within the sex glands or gonads, which, in males, are the testicles. This process takes place from puberty to the end of the individual's life.
US testicles thousands of thin and twisted tubes are found, the seminiferous tubes, where are the spermatogonia (2n). At spermatogonia they multiply through mitosis until adolescence, a period in which they start to multiply with greater intensity. After multiplication, the growth phase occurs, in which some spermatogonia grow and duplicate their chromosomes, transforming into primary spermatocytes (2n), also called spermatocytes I. You primary spermatocytes will undergo meiosis, giving rise to two haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes (n) or spermatocytes II, which will undergo another meiosis, originating four haploid cells, called spermatids. The two means that the spermatocytes sufferers represent the maturation stage.
The next phase is called speciation and in it the spermatids start to transform into sperm. At this stage, the spermatids they lose practically all the cytoplasm and begin a process in which they will develop, from the centriole, a flagellum.
At the beginning of the scourge of sperm we can find mitochondria that have the function of providing energy, being that in the head of the sperm we can find the acrosome, originating from the Golgi complex, which contains enzymes with the function of facilitating the penetration of the gamete into the egg. the core of sperm it is where the paternal chromosomes are stored.
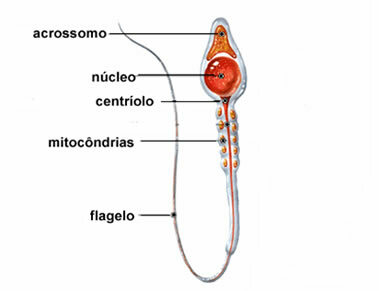
In the figure above we can see the structures that make up a sperm
By Paula Louredo
Graduated in Biology
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/espermatogenese.htm



