Manausis the capital of the state of Amazons, which makes up the Northern region of Brazil. With a population of 2.21 million inhabitants, the city is one of the most populated in the country and the main one in its region. It plays an important role as an economic center in that area, as it concentrates large industries from various productive sectors in the Manaus Free Trade Zone (ZFM).
Read too: What are the capitals of Brazilian states?
Manaus General Data
Gentile: manauara
Location: North region
Parents: Brazil
Federative unit: Amazons
Intermediate region: Manaus
Immediate region: Manaus
-
Metropolitan region: Manaus Metropolitan Region comprises 13 municipalities:
Manaus, Presidente Figueiredo, Novo Airão, Iranduba, Manacapuru, Rio Preto da Eva, Itacoatiara, Careiro da Várzea, Autazes, Careiro Castanho, Itapiranga, Manaquiri, Silves.
Bordering municipalities: Presidente Figueiredo, Rio Preto da Eva, Itacoatiara, Careiro da Várzea, Iranduba, Novo Airão.
geography
Total area: 11,401.092 km² (IBGE, 2020)
Total population: 2,219,580 inhabitants (IBGE, 2020)
Density: 158.06 inhab./km² (IBGE, 2010)
Climate: hot and humid equatorial
Altitude: 92 meters
Timezone: GMT -4
Historic
Foundation: October 24, 1669
Manaus geography
Manaus is a Brazilian city located in North region from the country. It belongs to the federative unit of Amazonas, and plays the role of state capital. The municipality extends over an area of 11,401,092 km², and is the 35th in area in the state. Among the Brazilian capitals, Manaus is the second largest after Porto Velho, in Rondônia.
The city is on the left bank of the Rio Negro, which joins the Solimões River to give rise to the Amazon River at the height of the Amazonian capital, a beautiful landscape in Manaus that has become a tourist route for those who visit it. In addition, it borders six other municipalities:
Presidente Figueiredo, northeast
Rio Preto da Eva and Itacoatiara, to the east
Path of Várzea and Iranduba, to the south
Novo Airão, to the west and southwest
Since 2007, Manaus integrates the so-called Metropolitan Region of Manaus, formed by another 12 municipalities, in addition to the capital.

Let's see, next, the main physiographic characteristics of the Amazonian capital.
Manaus climate
Located in an area of low latitude and inserted in the biome Amazonian, the weather observed in Manaus is of the type ANDquatorial hot and humid. It is characterized by high levels of relative air humidity and high temperatures throughout the year, including in the Winter. In this season, the advance of the polar air mass can cause the phenomenon of cooling and temporarily drop temperatures. The values, however, are around 18°C. The annual average is 26.7 °C, with maximums that can reach 40 ºC.
The entire region registers high annual rainfall (2300 mm), with a short dry period that lasts from October to December.
Read too: What is the difference between weather and climate?
Manaus relief
The city of Manaus integrates the domain of the Amazonian Plain, according to the classification established by Aziz Ab’Sáber. Thus, it has a flat reliefOand gently undulatingO, with very modest altimetric dimensions. It is located at an altitude of 92 meters above sea level.
Vegetation of Manaus
Part of the Brazilian Amazon, the vegetation cover of Manaus is quite diversified. In some areas, there is the preservation of the dense forest characteristic of the biome in which it is inserted, also called dryland forest. Other formations present in the city are the floodplain forests, igapós, campinaranas and meadows.
Manaus Hydrography
O Rio Negro is the main river that bathes the city of Manaus. The basin of this river is subdivided into smaller ones, and the territory of Manaus is partially or fully inserted in the hydrographic basins of the Puraquequara river and the streams of São Raimundo, Tarumã-Açu and Students.
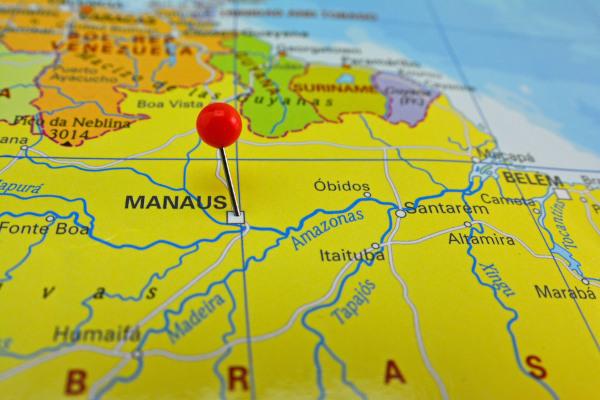
Manaus Map
Manaus is located in the northeast of the state of Amazonas, on the left bank of the Rio Negro, near its confluence with the Rio Solimões.
Manaus Demographics
The Amazonian capital has a population of 2,219,580 population, according to the data of the IBGE for the year 2020. It is the most populous city in the state, comprising just over 52% of all its inhabitants. Manaus is also one of the most populous Brazilian capitals, ranking seventh, and the one with the largest population in the North of the country. The population distribution in Manaus is around 158.06 inhab./km², demonstrating a much higher concentration than that observed in Amazonas, which is 2.23 inhab./km².
The latest IBGE Census indicates that the vast majority of the manauara population lives in urban areas of the city, while about 0.5% live in the countryside. Regarding the composition by age, the age groups that concentrate the greatest number of people are those in the range of 20 to 39 years, which characterizes a young population. The survey also shows that approximately 68% of manauaras declare themselves brown; 26.5%, white; 4.2%, black; 1.15%, yellow; and 0.22%, indigenous.
See too: The 20 most populous cities in the world
Manaus geographic division
The city of Manaus has a total of 63 neighborhoods, as legally established in the year 2010. These units belong to different district zones, which are listed below:
North Zone
West Zone
East Zone I
East Zone II
South Zone
Riverside Rural Area
Rural Road Area
Manaus Economy
The Manaus economy is the sixth largest in Brazil and the main one in the North region of the country. The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of the city is R$ 78.19 billion, while the per capita value is around R$ 36,445 per year. Manaus is the economic, financial and administrative center of the state of Amazonas and also one of the main industrial centers in Brazil, which is due to the presence of the Manaus Free Zone (ZFM) or Manaus Industrial Pole.
ZFM is a free trade area that has differentiated fiscal policies and incentives for industries that intend to settle there. It was created in 1967 with the purpose of attracting companies to the region, promoting its greater economic development and, therefore, encouraging its settlement and greater integration with the rest of the national territory. The area is managed by the Manaus Free Trade Zone Superintendence (Suframa).
Today, ZFM has a wide variety of industries in sectors such as electronics, automobiles, chemicals, information technology and others. It also turns to commercial and agricultural development, acting, therefore, in the three sectors of the economy.
Cattle raising and the production of fruits and other agricultural products (such as cassava, beans, rice and corn) are equally relevant to the Manaus economy. In the trade and services sector, in addition to retail, activities linked to tourism have increasingly expanded its participation in the composition of the Manaus GDP, following a national trend.
Manaus government
The Manaus city government is of the representative democratic type. O Mayor, who exercises the function of head of the municipal Executive Power, and the 41 councilors, which are part of the Legislative Chamber, are elected by the population every four years through direct elections. Manaus is also home to the seat of the government of the state of Amazonas.
Manaus Infrastructure
A large part of Manaus' homes are located in the urban area, although there are at least two thousand units in rural or riverside areas. As shown by the data from the last IBGE Census, the scope of the sewage sanitation network of the Amazonian capital was just over two-thirds (62,4%), a value that stands out on a state scale, which demonstrates the scale of the infrastructure problems in that region.
THE water network, in turn, serves a slightly larger portion, which is approximately 72%. Overall, 50.3% of homes in Manaus receive adequate sanitation, 48.8% semi-adequate, and 0.9% inadequate (IBGE, 2010).
With regard to displacements, the biggest airport in the state and one of the main ones in the North region, which is the Manaus International Airport (or Eduardo Gomes). Rivers are important transport routes in the Amazon, and in the state capital it could not be different. The city is home to the largest floating port in the world, the Port of Manaus, built at the beginning of the 20th century and being used by ships that transport cargo and passengers.
![Partial aerial view of the port of Manaus.[1]](/f/42d251abe3e887a79191fd9f9ed35a9d.jpg)
Manaus Culture
THE culture manauara exhibits great influence of indigenous populations in the Amazon and migrants who moved to that region. Traces are identified through dances, traditional festivals, handicrafts, cuisine and various other forms of expression.
Inserted in the Amazon, Manaus is annually the stage of several festivities that haveêm in order to celebrate the folklore Of region, while others emphasize the religious aspect of its population. One of the main ones is the Amazon Folk Festival, a tradition since the 1950s, as well as music festivals and the Carnival.
The city is home to cultural structures such as libraries, theaters, such as the Amazon Theater, symbol of çcycle of Brubber and stage for thousands of local and national plays, the Museum of the Amazon and the Museum of Natural Sciences of the Amazon, for example.
History of Manaus
As well as other important cities in the region, the creation of Manaus took place with the aim of promoting the defense of Portuguese territory and demonstrate his dominion over those lands. The town that started Manaus was formed after the construction of the Barra de São José Fort, in 1669. A short time later, the district of Barra do Rio Negro (1625) was created, which was elevated to the category of village only at the end of the 18th century.
In the meantime, the history of Manaus was marked by the Manaus War, a conflict that extended from 1723 to 1728 between the natives of the Manaós tribe and the Portuguese colonizers, with the defeat of the natives. A new conflict was established in 1757 with a similar ending.
In the mid-nineteenth century, the place was elevated to the category of city, renamed Cidade da Barra de São José do Rio Negro, shortened to Cidade da Barra when the district of São José do Rio Negro became province. With the city established for being the capital in the year 1856, its name became the City of Manaus.
A few decades later, in the transition to the 20th century, the rubber cycle provided acceleration of urban and economic development in Manaus, which is then experiencing one of its most prosperous. Some of the architectural and urban projects still mark the Manaus landscape, such as the Teatro Amazonas.
The city suffered a hard period of stagnation with the decline of the rubber cycle, which was due to its low competitiveness compared to the product that was commercialized in the Asian continent. The economic recovery started in 1967, when the Manaus Free Trade Zone was created, with the purpose of promoting the industrialization of the Amazon region and intensifying its settlement. Manaus is currently recognized as one of the main industrial centers in the country.
Image credit
[1] Nelson Antoine / Shutterstock
By Paloma Guitarrara
Geography teacher
