Our body has a nervous system with great ability to perceive the environment and our internal environment. For this, it has specialized cells, the neurons, which guarantee the transmission of information through the propagation of the nerve impulse.
O nervous impulse it is an electrical current that rapidly travels across the membrane in the neuron. This impulse is essential to ensure communication between these nerve cells.
→ How does the nerve impulse propagate?
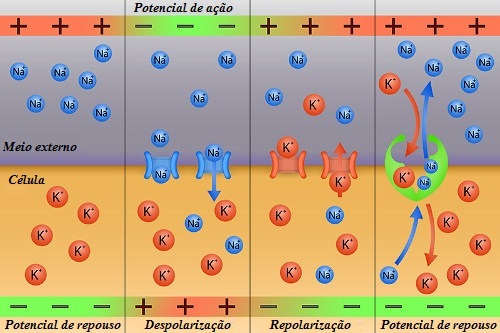
For the nerve impulse to be propagated, it is necessary that the neuron has the resting potential membrane and that its inner surface is negatively charged from 70 to 90 millivolts. This phase is known as polarization.
In rest, the plasma membrane of the axon pumps Na+ to the external medium and, at the same time, transfers K ions+ into the cell. At this time, passive diffusion of sodium into the cell and potassium outward can also occur. Potassium passes to the external environment faster than sodium enters, causing more positive charges to remain outside the cell. It is these actions that determine the resting potential.
When the neuron undergoes stimulation, a transient change in membrane potential occurs. At this point, the opening of the ion channels and the rapid entry of Na+, which was in great quantity, in the extracellular environment. When this ion enters, the potential change and the interior of the axon becomes positive (depolarization).
This set of sequential changes that guarantee the transition of potential is called action potential. This change makes Na channels+ close and cause the K channels to open+. the K ion+ starts to diffuse out, and the resting membrane potential returns to normal (repolarization).
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Watch the nerve impulse step by step.
Title: Nervous impulse
→ Does the nerve impulse propagate rapidly?
Nerve impulse propagation events occur quickly. The change from resting potential to action potential and its return to rest takes approximately 5 ms. It is also worth noting that it occurs in only one part of the membrane and propagates along the axon. Upon reaching the end of this structure, it promotes the release of neurotransmitters that will stimulate or inhibit other cells.
For a new stimulus to occur, the nerve cell must wait a period of time, called absolute refractory period, in which there is no response to stimuli. After a certain period, strong stimuli can trigger the stimulus.
→ Everything or nothing!
It is often said that a nerve impulse occurs according to the all-or-nothing principle. This means that an impulse will not be generated unless the stimulus has a certain intensity, called the excitation threshold. Also, regardless of the intensity, the impulse will be the same.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Nervous impulse"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/impulso-nervoso.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.