To carry out everyday tasks and maintain your body's vital functions, you need energy. This energy is derived and replaced through food consumption. When being burned in our body, food releases an amount of energy that depends on the composition of each one.
This amount of energy supplied is called "calorie", whose symbol is the cal. We can more accurately define what calorie represents in terms of energy, as follows:

For example, if 1.0 g of sugar raises the temperature of 1000 g of water by 4°C, it means that 1 g of water absorbs 4 lime of energy. But since the considered mass is 1000 g, the total energy absorbed is 4000 cal or 4 kcal.
Since the calorie values of foods are often very large, the cal unit is hardly used. More kcal is used (1 kcal = 103 cal or 1 kcal = 1000 cal).
On many food packages the Cal symbol appears (note the capital letter), to represent the energy values of the food in “nutritional calories”, which actually means kcal.

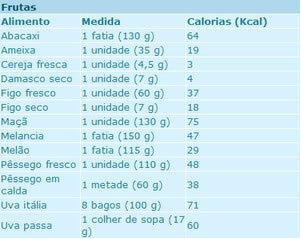
This unit (Cal) is used only by some people in the health field, but it should be avoided, as it is not part of the IS. This situation generates a lot of confusion not only in the matter of food, but also when it indicates the amount of energy that will be burned by the body through physical exercise. Note that in the table below, which indicates the caloric content of some foods, the terms Calorie and kilocalorie (kcal) are used (not recommended, as already explained) as synonyms:
Although these units are widely used, the unit recommended by the SI (International System of Units) is the joule (1 cal = 4.18 J) or the kilojoule (1 kcal = 4.18 kJ).

In fact, it's not just food that releases energy when burned. A coal, for example, also releases energy when burned in the form of heat and light. Another example is the burning of gasoline, where 1 L releases 7 750 000 calories. Thus, the term “calories” applies to any phenomenon involving heat exchange.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/conteudo-calorifico-ou-calorias.htm


