At intermolecular forces, generically called Van der Waals Forces, there are three: induced dipole-induced dipole, hydrogen bonds and permanent dipole-permanent dipole. In this text, we will consider only the last of these three forces:
The power permanent dipole-permanent dipole, or simply, dipole-dipole occurs only in polar molecules, that is, those that do not have a uniform load distribution along its surface. To cite an example, in the HCl molecule (hydrochloric gas) the electronic cloud is more displaced towards the chlorine atom, as it is more electronegative than hydrogen.
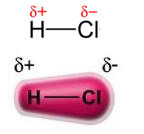
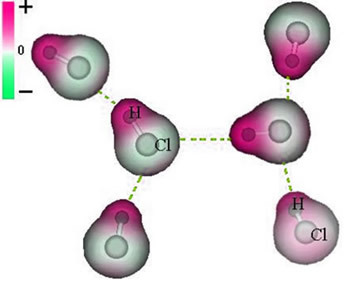
Note that around the chlorine atom there is an accumulation of electrons, which causes the formation of a negative pole, which is symbolized by the Greek letter delta (-δ). As a result, in the region around the hydrogen atom a positive pole (+δ), as it has low electronic density. The HCl molecule then constitutes a electric dipole and, therefore, when coming into contact with other neighboring HCl molecules, there is an attraction force between the opposite poles of the molecules, as can be seen below:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
This attractive force, which is established between the negative end of the dipole of one molecule with the positive end of the dipole of another molecule, constitutes the dipole-dipole force..
So, as the name says, the dipole is permanent, so it only occurs in polar compounds. And the higher the polarity of a molecule, the more intense the dipole-dipole interactions in the substance.
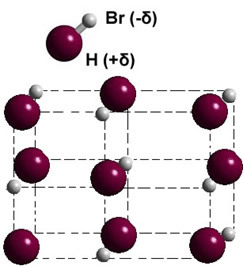
If it is in the solid phase, the formation of the permanent dipole guides the position of each molecule in space, forming dipolar crystals; as in the case of hydrogen bromide illustrated below:
Other examples of polar substances that have the dipole-dipole strength between their molecules are: H2S, CO, HCCl3, ONLY2.
This intermolecular force is of medium intensity, as it is stronger than the induced dipole-induced dipole attraction force, but less intense than the hydrogen bond. This is why their melting and boiling points are higher than those of substances that have an induced dipole strength. As the permanent dipole force is stronger, it is necessary to supply more energy for the interactions of its molecules to break down.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Dipole-dipole intermolecular force"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/forca-intermolecular-dipolo-dipolo.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
e) OS2, HBr, HCl, H2O.
c) Knowing that the boiling temperatures of CH3Cl and CH3I are 24.0 °C and 42.4 °C, respectively, indicate which compound presents, in the liquid phase, more intense intermolecular forces.



