Chemistry studies matter and the transformations it undergoes. Matter, in turn, is everything that occupies space in space and, therefore, has mass and volume. It can be found in two basic ways: substances and mixtures.
As explained in the text “What is a substance?”, a substance is configured when a given material is formed only by one type of component (which can be particles such as atoms, molecules, unit formulas, electrons or ions) and, as a result, has physical properties such as melting point, boiling point and density, fixed and well. defined.
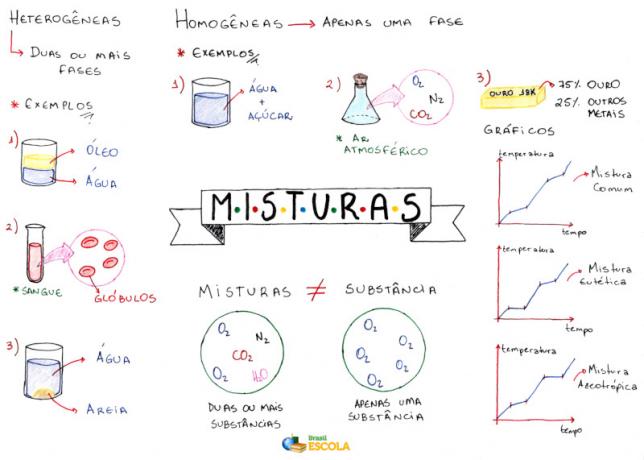
Already mixtures are systems formed by two or more compound or simple substances that are different. In this way, they present undefined and variable physical properties. These properties depend on the amount of each substance in the mixture and their nature.
Mind Map: Mixtures
* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
For example, the common ethyl alcohol that we use for cleaning and disinfection is not a pure substance, as it is not just made up of ethanol molecules (H
3C-CH2-OH). As the label on the bottle of this product indicates, it is a mixture of ethanol and water (H2O). For example, if you see on the label that the alcohol has a concentration of 96ºGL (Gay-Lussac degrees), it means that in 100 parts of this mixture, there are 96 parts of ethanol and 4 parts of water, that is, a bottle of 100 mL of hydrated alcohol has 96 mL of ethanol and 4 mL of Water.Mixtures can be classified into homogeneous and heterogeneous. In the case of hydrated alcohol, we have a homogeneous mixture. But what is a homogeneous mixture? It is a mixture where we cannot see the separation of its components. Its entire length is uniform and has a single phase.
These homogeneous mixtures are also called solutions, having dispersed particles with a diameter smaller than 1 nm, that is, not even with an ultramicroscope it is possible to see more than one phase in these materials. Furthermore, its components cannot be separated by physical methods such as centrifuges or filtration.
Blood is a mixture. To the naked eye, it looks like it's a homogeneous mixture, but it's not, because under the microscope we see its components. Furthermore, when placing it in a centrifuge, these constituents are separated.

Centrifuged blood and its image under the microscope
Homogeneous mixtures or solutions can be in all three physical states. The hydrated alcohol mentioned is an example of liquid mixture. air is a gas mixture composed of several gases, the main ones being nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2). Metal alloys are solid mixtures, such as steel which is composed of approximately 98.5% Fe (iron), 0.5 to 1.7% C (carbon) and traces of Si (silicon), S (sulfur) and P (phosphorus).
At heterogeneous mixtures, on the other hand, are those that have more than one phase, such as mixing water and oil, water and sand, granite (mixture of quartz, mica and feldspar) and so on.

Example of three-phase heterogeneous mixture
As mentioned, the physical properties of the mixtures are neither constant nor determined. However, there are certain mixtures that are exceptions, the mixtures azeotropics and eutectic. Azeotropic mixtures have a constant boiling or condensation point, behaving, at that point, as a pure substance.. The 96% alcohol mentioned is an azeotropic mixture because it has a constant boiling point at 78.2°C.
Now yes, eutectic mixtures are those that behave as if they were a pure substance only during the solidification or melting point. An example is the metallic alloy made of 40% cadmium and 60% bismuth, which has a constant melting point equal to 140°C.
But the vast majority of mixtures change their physical state not at a fixed temperature, but at non-specific temperature ranges.
Mental map By Mother Victor Ricardo Ferreira
Chemistry teacher
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-uma-mistura.htm
