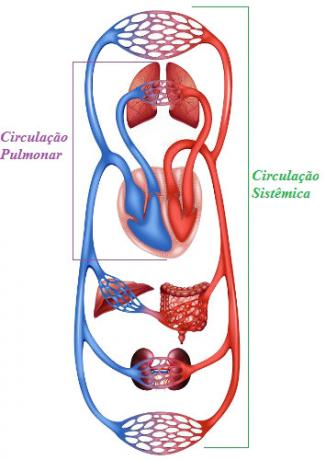
O Cardiovascular system is composed of the heart, blood vessels and the blood, which circulates inside the vessels (closed circulation) thanks to the impulse provided by the heart. In mammals, the circulatory system has two circuits, which characterizes a double circulation, and two major circulation systems: systemic and pulmonary circulation.
→ Systemic Circulation or Large Circulation
In systemic circulation, blood is taken from the heart to tissues and then back to the heart. This circulation begins when blood leaves the left ventricle through the aorta artery. Branches depart from this artery that supply the entire body. In blood capillaries, the blood exchanges gas with tissue cells and becomes rich in carbon dioxide.
After gas exchange, blood is collected by the venules that carry the blood to the superior and inferior vena cava. The vena cava carries blood to the heart, flowing into the right atrium.
Therefore, systemic circulation presents the following path:
Heart → Body Systems → Heart
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In systemic circulation, blood travels to the body and returns to the heart. In the pulmonary, the blood goes towards the lung and returns to the heart.
→ Pulmonary Circulation or Small Circulation
In the pulmonary circulation, blood is carried from the heart to the lung and later back to the heart. This circulation begins when blood leaves the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery and into the lungs. The pulmonary artery branches and follows each to a lung. In this organ, they branch into small-caliber arteries to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli. In the alveoli, gas exchange occurs (bruise), which are characterized by the passage of carbon dioxide from the blood to the interior of the alveoli and the oxygen present in the alveoli to the interior of the capillary.
After the process of hematosis, the blood goes through the venules and, later, to the pulmonary veins. These veins are responsible for bringing blood back to the heart. Blood reaches this organ through the left atrium.
Therefore, we can summarize the path of pulmonary circulation as follows:
Heart → Lung → Heart
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
SANTOS, Vanessa Sardinha dos. "Systemic and pulmonary circulation"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/circulacao-sistemica-pulmonar.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.