RNA (ribonucleic acid) is a molecule responsible for protein synthesis of the body's cells. Its main function is the production of proteins.
Through the DNA molecule, RNA is produced in the cell nucleus and is also found in the cell's cytoplasm. The acronym for RNA comes from the English language: RiboNucleic Acid.
RNA structure
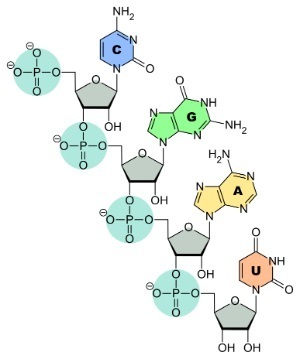 Structural formula of the RNA molecule
Structural formula of the RNA molecule
The RNA molecule is composed of ribonucleotides, which are formed by a ribose (sugar), a phosphate and nitrogenous bases.
Nitrogen bases are classified into:
- Adenine (A) and Guanine (G): purines
- Cytosine (C) and Uracil (U): pyrimidines
RNA Types
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA): receives this name because it is the main constituent of ribosomes. It has the greatest weight, being primarily responsible for protein synthesis.
- Messenger RNA (mRNA): together with ribosomal RNA, it helps in protein synthesis, guiding the order of amino acids for protein formation. It is responsible for carrying the genetic information received from the DNA from the cell nucleus to the cytoplasm. Its weight is less than ribosomal RNA.
- RNA Carrier (tRNA): its name already indicates that its function is to transport the amino acid molecules that will be used in protein synthesis. It transports these molecules to the ribosomes, where they join together and form proteins. Compared with the others, this one has the least weight.
RNA Polymerase
RNA polymerase is the name of the enzyme that helps catalyze RNA synthesis. From a DNA molecule it is formed by a process called transcription.
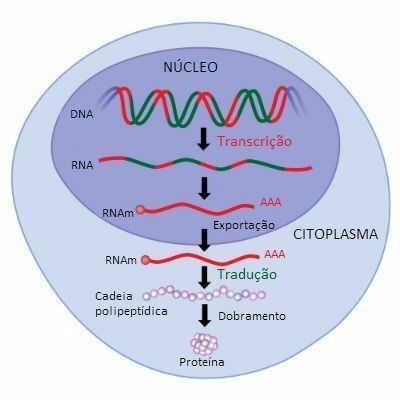 Stages of gene or genetic expression
Stages of gene or genetic expression
Ribozymes
Enzymatic proteins formed by RNA are called ribozymes. These enzymes are related to protein synthesis in cells.
Its main function is to accelerate the speed of some chemical reactions, remaining chemically intact after the reaction.
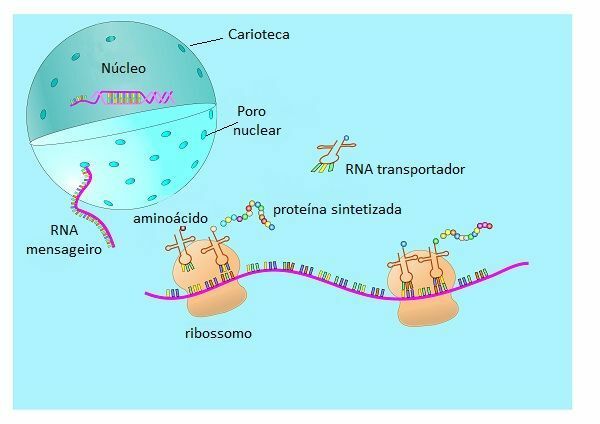 Representation of the protein synthesis process that starts in the nucleus and then takes place in the cytoplasm
Representation of the protein synthesis process that starts in the nucleus and then takes place in the cytoplasm
Learn more about Proteins and the Protein synthesis.
Difference between DNA and RNA
both the DNA and RNA are genetic materials responsible for the transmission of hereditary characters.
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that carries all the genetic information of an organism and is present in the nucleus of the cells of all living beings.
Its function is to transmit genetic information to RNA. Regarding the pentose it contains, RNA is formed by a ribose, while DNA by a deoxyribose.
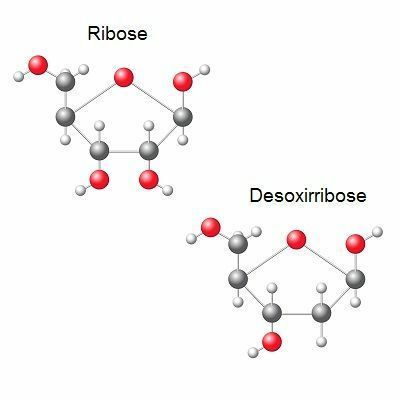 Structure of RNA and DNA pentoses
Structure of RNA and DNA pentoses
In terms of size, RNA is smaller than DNA. That's because RNA is made up of a single strand (ie, a single strand), while DNA is made up of a double helix. Thus, RNA is formed from a strand of DNA.
As for the structure of DNA and RNA, they are similar, however, the DNA strand is formed by the following nitrogen bases:
- Adenine (A)
- Guanine (G)
- Cytosine (C)
- Thymine (T)
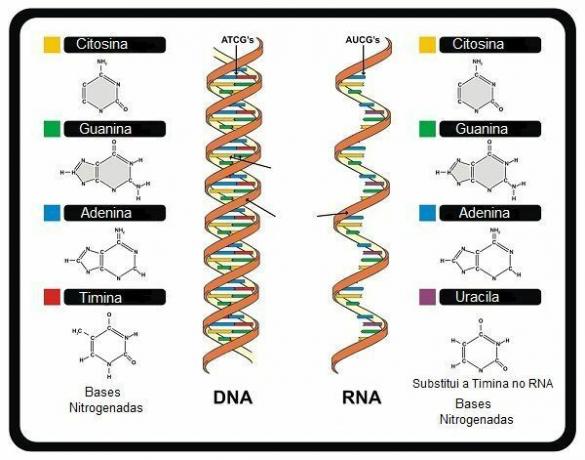 Comparison between a DNA (double stranded) and an RNA (single stranded) molecule
Comparison between a DNA (double stranded) and an RNA (single stranded) molecule
OBS: In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil.
Learn about the differences betweenDNA and RNA.
Did you know?
The Retrovirus of AIDS, O HIV, is formed by RNA. As such, your genetic information is in the form of RNA.
Understand more about the characteristics of Virus.
Learn more about the topic by reading the articles:
- Nucleotides
- What are Nucleic Acids?
- Cell Organelles
- Molecular biology
- Cell Core
- reverse transcriptase

