Viagra is the name given to the first drug that was developed with the aim of helping men who have a disorder called erectile dysfunction (ED) or sexual impotence. This disorder, which affects about 22 to 52% of the male population, has a great negative impact on men's quality of life.
it is understood by erectile dysfunction or sexual impotence the difficulty a man has in keeping his penis erect to perform or maintain sexual intercourse. This problem can be triggered by several factors, especially diabetes, aging, hypertension, high cholesterol levels, atherosclerosis, depression, sedentary lifestyle and the use of tobacco and some types of medications, such as propranolol and fluoxetine. It was believed for a long time that psychological factors were the main cause of this disorder, but today it is known that vascular problems are the main cause of the dysfunction.
THE erection it is a neurovascular process that occurs thanks to sexual stimulation and an increase in the amount of blood in the corpus cavernosum. This region, composed of two longitudinal columns on the dorsal part, constitutes most of the
penis and it is formed by several lacunar spaces that are interconnected and allow blood flow at the time of erection. As blood enters the corpus cavernosum tissue, it expands and compresses the vessels that supply the penis, trapping blood in the organ and making it erect.For an erection to occur, it is necessary for the body's cells to release a substance called nitrogen monoxide (NO) within the corpus cavernosum. The presence of substance NO promotes the production of an enzyme called guanylate cyclase, which induces the production of a substance called Cyclic guanosine monophosphatase (Gmpc), which promotes penile muscle relaxation, blood supply and, consequently, erection. However, its presence triggers the production of an enzyme that acts against it (degrading it) and inhibits erection. The enzyme in question is phosphodiesterase-5.
Thus, the phosphodiesterase enzyme acts against guanosine monophosphatase, causing a contraction of the penis muscles and, consequently, the exit of blood from its interior. With that, the erection is stopped.
In men who have erectile dysfunction, the release of the enzyme phosphodiesterase occurs very quickly. For this reason, a man loses an erection faster or not at all. It is precisely on this issue that viagra acts, that is, it prevents the phosphodiesterase enzyme from being produced, allowing the complete and longer-term action of the guanosine monophosphatase.
chemically speaking, O viagra it is composed of an active principle (substance that acts on a certain disease) called Sildenafil. This substance has in its composition the chemical elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N) and sulfur (S), which form chemical functions such as amine, ether and amide. See the structural formula of Sildenafil:
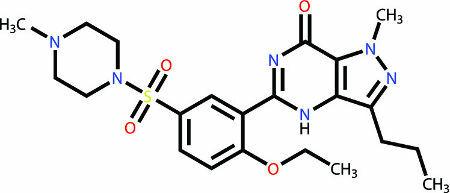
Structural formula of the active ingredient in Viagra
In addition to Sildenafil, two other molecules were developed by scientists for the treatment of dysfunction male erectiles, such as Cialis (whose active ingredient is Tadalafil) and Levitra (whose active ingredient is verdenafil). See the structural formula of Tadalafil and Verdenafil:
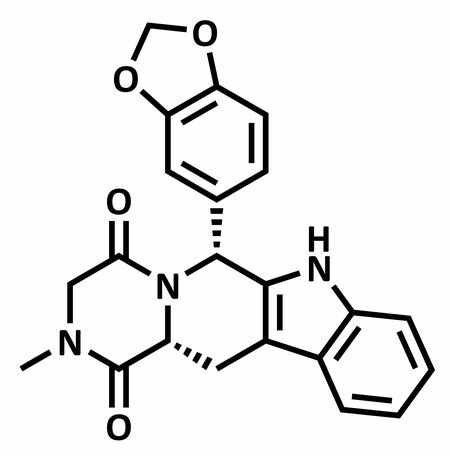
Structural formula of Cialis active ingredient
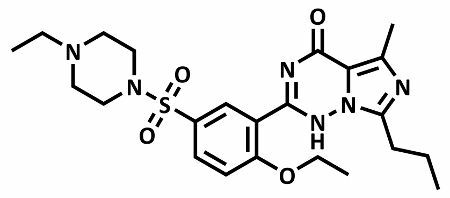
Levitra's active ingredient structural formula
Analyzing and comparing the structural formulas of the active principles used to treat the dysfunction erectile, we can observe that they have the same organic functions, but with structural details many different. The action caused by both in the human body is similar, that is, their basic action is to inhibit the production of the enzyme phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5), which maintains the erection for longer.
See a list of organic functions present in each of the active principles:
Sildenafil: amine, amide, ether and sulfur;
Tadalafil: amine, amide and ether;
Verdanafil: amine, amide, ether and sulfur.
The structural differences in the chemical molecules make each one of them act in the inhibition of the phosphodiesterase enzyme in a different way. This difference is in the enzyme's inhibition time. Sildenafil starts to work about 12 minutes after ingestion and lasts for up to 12 hours. Verdanafil starts to work about 15 minutes after ingestion and lasts for up to 12 hours. Tadalafil works about 40 minutes after ingestion, but its effect can last for up to 36 hours.
It is important to note that, in addition to phosphodiesterase inhibitors, there are other treatments for erectile dysfunction, such as intracavernous self-injection with vasoactive drugs and prosthesis implantation penile. In addition, it is recommended that, in addition to these treatments, psychological monitoring is carried out.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias and Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/quimica-viagra.htm