triangles they are polygons formed by three sides. Polygons, in turn, are geometric figures formed by straight segments which, two by two, touch each other at their extreme points, but which do not intersect at any other point. Therefore, the triangles inherit from polygons some basic characteristics and properties.
Elements of a triangle
You triangles have the same elements as polygons, with the exception of diagonals. The other elements of the polygons that the triangles have are:
sides: are the straight segments that form the polygon;
vertices: are the meeting points between the sides;
anglesinternal: are the angles that can be observed between two adjacent sides of a triangle;
anglesexternal: are the angles that can be observed between one side of a triangle and the extension of the side adjacent to it.

Triangle Classifications
You triangles can be classified from your number of sides. A triangle must belong to one of the following classifications:
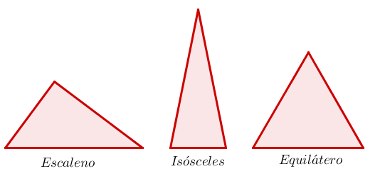
Scalene: triangle that has all sides with different measurements;
Isosceles: triangle that has two sides with equal measures;
Equilateral: triangle that has three sides with equal measures.
Another possible classification for the triangles it refers to the measurements of its angles. Look:
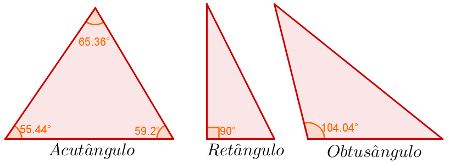
Acuteangle: Triangle that has all angles with measurements smaller than 90°;
Rectangle: Triangle that has an angle with a measure equal to 90°;
Obtuse angle: Triangle that has an angle measuring greater than 90°.
Triangle properties
The following properties are valid for any triangle, regardless of its shape or size.
The sum of the measurements of the internal angles of a triangle will always be equal to 180°;
The sum of the measurements of the outside angles of a triangle will always be equal to 360°;
The measure of an outside angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measurements of the two internal angles not adjacent to it;
The sum of the measurements of two sides of a triangle it is always greater than the measurement of the third side;
the biggest side of a triangle opposes its greatest angle;
the shortest side of a triangle is opposed to its smallest angle.
By Luiz Paulo Moreira
Graduated in Mathematics
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/matematica/o-que-e-triangulo.htm
