You lipids, also called lipids, lipids or lipids, are a class of esterswhich encompasses all the fatty substances of the vegetable and animal kingdoms; hence the origin of its name, since in Greek the term lipos means “fat”.
Therefore, they include as sources of lipids in their diet: oils, oils, butter, margarine, mayonnaise, fatty foods such as nuts, peanuts, avocados, coconuts and chocolate.

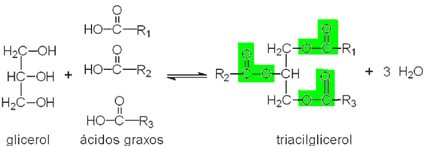
- Glycerides: Generically, these lipids are formed in living beings (animal and plant origin) through reactions between higher fatty acids and glycerol, which is a glycerin trialcohol molecule (propanetriol), as shown.
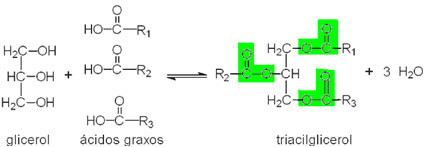
Note that highlighted we have three characteristic groups of the ester function, so this compound is classified as a triester. Since they are derived from glycerol, triesters are called triglycerides or triglycerides.
The radicals R1, R2 and R3 can be derived from different esters. The saturation or instauration of these radicals will determine whether the glyceride will be an oil or a fat, because we have to:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)

Example of a fat:
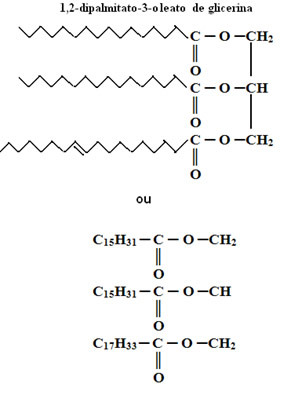
Note that in this case, two out of three of the radicals are saturated, so this triglyceride is a fat.
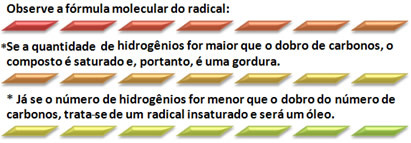
For you to know if the radicals are saturated or unsaturated it is not necessary to write the complete structural formula, just follow the following practical rule:
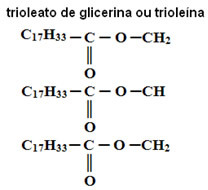
For example, in the following compound, in the three radicals the amount of hydrogens (33) is less than twice the amount of carbons (17). Thus, this compound has three unsaturated radicals and is therefore an oil.
Since the only difference between oil and fat is unsaturation, it is possible to transform oil into fat by means of a hydrogenation reaction, which is the method used by the industry in the manufacture of margarine or vegetable shortening from oils vegetable.
Generically, we have:

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Lipids"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/lipidios.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.