Climate corresponds to the set of weather variations in a given location. To establish the climate of a place it is necessary to analyze the atmospheric phenomena over a period of approximately 30 years. The climate is directly related to plant formation.
In the Brazilian territory there is a great climatic diversity, as the country has a large territorial extension with differences in relief, altitude and dynamics of air masses and sea currents, all of these factors influence the climate of a region.
Most of the area of Brazil is located in the Intertropical Zone, that is, in the low latitudes, with hot and humid climates. Another interesting factor of the Brazilian climate refers to the thermal amplitude (difference between the averages maximum and minimum temperature annuals), as it approaches the equator, the thermal amplitude is smaller.
Mind Map: Types of Climate in Brazil
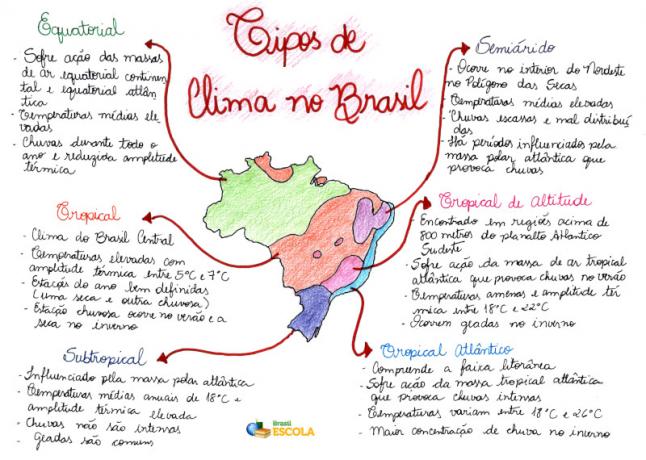
* To download the mind map in PDF, Click here!
The criterion used in Brazil to classify the different types of climate is related to the origin, nature and, mainly, movement of air masses existing in the country (equatorial, tropical and polar). According to climate analyzes carried out in the Brazilian territory, it was possible to establish
six types of different climates, are they:Equatorial– Present in the Amazon, north of Mato Grosso and west of Maranhão, it suffers direct action from the continental equatorial and Atlantic equatorial air masses, with warm and humid air. It has high average temperatures (from 25 °C to 27 °C), rainfall throughout the year and reduced temperature range (less than 3 °C).
Tropical– Climate of central Brazil, also present in the eastern portion of Maranhão, extensive part of the territory of Piauí, in the western portion of Bahia and Minas Gerais, in addition to being found in the far north of the country, in Roraima. It is characterized by high temperature (18 °C to 28 °C), with a temperature range from 5 °C to 7 °C, and well-defined seasons (one rainy and the other dry). The rainy season occurs in summer; in winter there is a reduction in relative humidity due to the period of the dry season. The rainfall index is around 1.5 thousand millimeters per year.
Altitude Tropical – It is found in the highest parts, above 800 meters, of the Southeast Atlantic plateau. It mainly covers the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais, Rio de Janeiro and Espírito Santo. It is under the influence of the Atlantic tropical air mass, which causes rain in the summer. It has a mild temperature, between 18 °C and 22 °C, and annual thermal amplitude between 7 °C and 9 °C. In winter, frosts occur quite frequently, due to the action of cold fronts caused by the collision between the tropical and polar masses.
Tropical Atlantic – Also known as humid tropical, it comprises the coastal strip from Rio Grande do Norte to Paraná. It suffers the direct action of the Atlantic tropical mass, which, being hot and humid, causes heavy rains. The temperature ranges from 18 °C to 26 °C, it has a greater thermal amplitude as one moves towards the south. In the Northeast, the highest concentration of rain occurs in winter, while in the Southeast, it occurs in summer. The average pluviometric index is high, of 2 thousand millimeters per year.
Subtropical– Occurs in latitudes below the tropic of Capricorn. It is present in the south of the state of São Paulo and in most parts of Paraná, Santa Catarina and Rio Grande do Sul. It is influenced by the Atlantic polar mass, has an average annual temperature of 18 °C and high thermal amplitude (10 °C). The rains are not very intense, a thousand millimeters annually, however, they occur in a well distributed way in the region. In this climatic region of Brazil, frost and snow are common. Summer is very hot and the temperature can exceed 30 °C. The winter, quite cold, presents the lowest temperatures in the country, below 0 °C.
semiarid– Occurs in the interior of the Northeast, in the region known as Polígono das Droughts. It corresponds to almost the entire northeastern hinterland and the middle and lower valleys of the São Francisco river. It is characterized by high temperatures (average of 27 °C) and scarce and poorly distributed rainfall, around 700 millimeters per year. There are periods when the Atlantic equatorial mass (super-humid) reaches the north coast of the Northeast region and reaches the sertão, causing heavy rains in February, March and April.
By Wagner de Cerqueira
Graduated in Geography
*Mental Map by Rafaela Sousa
Graduated in Geography
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/brasil/os-climas-brasil.htm
