the plants are sessile organisms, which means they don't move around. Thus, they could be easily consumed by predators, however, certain plants have certain chemical compounds that repel the herbivores that consume them. In addition, these compounds help prevent virus, bacterial or fungal infections and even competition with other plants.
Among these chemical compounds, we can cite as an example the terpenes, compounds derived from isoprene or 2-methyl-buta-1,3-diene, an alkadiene whose formula is shown below:
H2C C ─ CH ═ CH2
│
CH3
By joining two or more units of the isoprene molecule, open or closed chain terpenes are obtained. Low molecular weight terpenes have a very effective repellent action as they are very volatile.
An important terpene for reducing predation on certain plants is the limonene present in the trees of pine. Beetles avoid landing on these plants and preying on them. Limonene is a terpene found in the skin of some citrus fruits, such as lemons and oranges. It consists of two isoprene units:

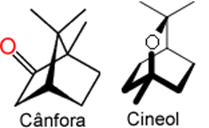
Two monoterpenes are present in the species. sage lucophylla and Artemisia callifornica, shrubs typical of the chaparral vegetation that develop mainly in California and Chile. These two species release oxygenated monoterpenes camphor and cineole in summer, when the temperature is high, being released more easily. They fall to the ground preventing other plants from growing in the spring and preventing the increase in population diversity of other plant species.
Below is an image of a chaparral and the two monoterpenes mentioned:

Chaparral Image*
You tannins are another class of organic compounds used by plants to repel predators. They comprise a wide variety of plant-derived polyphenols, with molar mass of 500 and 3000. One of the sensations that tannins provoke is bitterness, making the ingested plant unpleasant to the animal's taste. This bitterness is related to flavanols. Howler monkeys, also known as barbados (Alouatta spp.), are a great example, they prefer young leaves and avoid mature leaves with more tannin.
However, although some chemicals prevent certain predators, others they can become immune and even use them as their means of defense when feeding on plants that contain them.
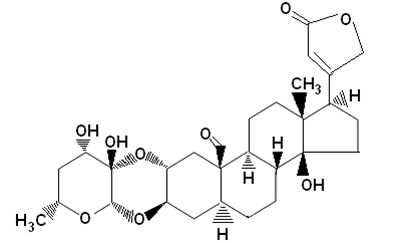
For example, milkweed contains cardioactive glycosides, such as calotropin shown below, which are chemical compounds that are toxic to mammals and animals. However, the monarch butterfly larvae (Danaus plexippus) can not only eat milkweed but even store the poison.
* Credits for the image: Stan Shebs/ Wikipedia commons
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/compostos-quimicos-na-defesa-das-plantas.htm

