At Endogenous Stress Zones correspond to the areas where the tectonic plates meet and are characterized by having a high geological instability due to volcanic and tectonic activities caused by the action of the convection currents. Thus, we have two main types of endogenous zones: the divergence zones and the convergence zones.
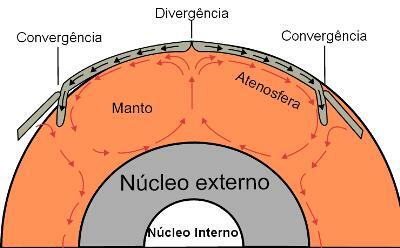
The divergence and convergence zones that arise from the movement of tectonic plates¹
As we can see in the figure above, these two types of endogenous forces are characterized, respectively, by the distance and by the approach or meeting of tectonic plates, thus presenting specific characteristics caused by such processes.
In the divergence zones, where there is the separation of the tectonic plates, the opening of true cracks in the Earth is registered. In general, these activities usually take place in oceanic regions, where the earth's crust is thinner. Due to this dynamic, large earthquakes occur - such as those that cause the tsunamis –, in addition to intense volcanic activity, which promotes the emission of lava and the consequent formation of oceanic islands and submerged mountain ranges, called
mid-ocean ridges.In the convergence zones, with the approach of the tectonic plates, two distinct phenomena can occur, the subduction Or the obduction.
At subduction, which occurs when there is a collision between an oceanic plate and a continental plate, the first dips and the second is pressed in the opposite direction to its displacement. In the case of the oceanic plate, thanks to its "dive" towards the Earth's mantle, a melting process occurs, better known as Fusion, due to the high temperatures. With the continental plate, a series of phenomena of relief transformation occurs, with the formation of folds and mountain ranges. Among these mountain ranges, we have the formation of the highest altitudes on the planet, in the Cordillera of the Himalayas, in southern Asia, beyond the constitution of the Andes Mountains, in western America. South.
At obduction – also known as collision –, two tectonic plates are pressed against each other, and the result is their displacement in the horizontal direction in opposite directions. In this case, we have the formation of geological faults, of extensive valleys or relative depressions, in addition to intense seismic activity, causing the record of the largest earthquakes on the planet.
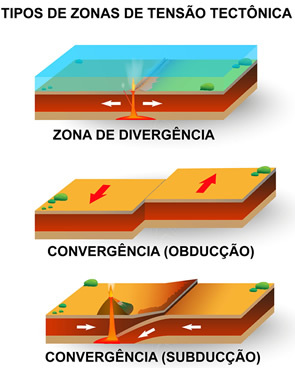
Representative scheme of the tectonic movements explained above
In general terms, we can note that tectonic movements are directly responsible for original composition and formation of the reliefs, it being up to the exogenous forces of the Earth to shape them or transform them. In order for human beings to occupy their geographical space, it is therefore important to know geological behaviors to facilitate planning actions and predict or avoid major catastrophes.
________________
¹ Image credits: Surachit and Wikimedia Commons.
By Rodolfo Alves Pena
Graduated in Geography
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/zonas-endogenas-tensao.htm