As well as the sulfonic acids and the amines, the isonitriles are organic compounds originated from inorganic substances, more specifically, from an inorganic acid called isocyanhydric acid.
You isonitriles they are widely used in various organic syntheses (production of new organic substances) and in the manufacture of pesticides and pesticides. These compounds originate when isocyanic acid reacts with a alcohol, for example. In this reaction, the hydrogen atom of the acid is replaced by the alcohol radical. Hydrogen joins the hydroxyl of alcohol and forms a water molecule.
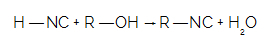
When HNC reacts with an alcohol, we have the formation of isonitrile and a water molecule
The isocyanhydric acid that gives rise to isonitriles has the following structural formula:
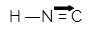
Between the carbon atom and the nitrogen atom, there is a double bond and a dative bond. This region of isonitrile is extremely polar because of the resonance phenomenon between the double bond electrons and the dative bond electrons.
Due to the resonance effect between the carbon and nitrogen atom, isonitriles have a lower stability in relation to nitriles, that is, they can decompose (transform into another substance) easily. So when an isonitrile is heated, it easily converts to a
nitrile.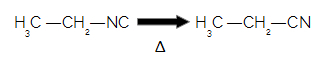
When heating an isonitrile, it turns into nitrile
As for the physical characteristics, isonitriles:
are less dense than water;
have high melting and boiling points when compared to substances of approximate molar mass;
Its physical state depends on the size of the molar mass. Higher molar mass isonitriles are solid;
They are poorly soluble in water.
To carry out the nomenclature of an isonitrile, the rule of the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) is as follows:
Branch name + carbylamine
NOTE: The name carbylamine refers to the NC group. Thus, any group linked to the NC is considered a radical in the nomenclature.
See some examples:
Ethylcarbylamine: Isonitrile with the ethyl radical

Vinylcarbylamine: Isonitrile with the vinyl radical
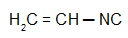
Isobutylcarbylamine: Isonitrile with the isobutyl radical
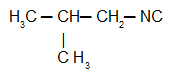
In addition to the IUPAC nomenclature, isonitriles still have the usual nomenclature, guided by the following rule:
Isocyanide + de + radical name + a
Ethyl isocyanide: Isonitrile with the ethyl radical

Vinyl Isocyanide: Isonitrile with the vinyl radical
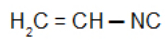
Isobutyl isocyanide: Isonitrile with the isobutyl radical:
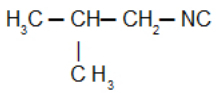
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias

