Since there are thousands of organic compounds, the phenomenon of isomerism can take several forms. Therefore, isomerism can be basically classified into two types: flat or constitutional isomerism and space isomerism or stereoisomerism. Each type mentioned can be subdivided, as shown in the following diagram:
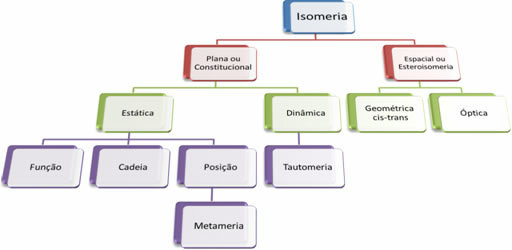
See each case:
1. Flat or Constitutional Isomerism: Isomers of this type have the same molecular formula and are distinguished by flat structural formulas. There are five cases of plane isomerism: function, chain, position, metamerism and tautomerism.
1.1.Functional or functional isomerism: The difference between the isomers is in the functional group.
Example: Molecular formula C3H6O
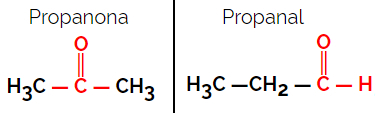
Note that propanone is from the ketone group and propanal is from the aldehyde group.
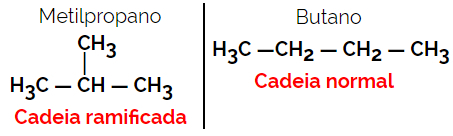
1.2. Chain or skeletal isomers: The difference between the isomers is in the type of chain. For example, one isomer is open-chain and the other closed-chain, or one is normal-chain and the other branched-chain, or one is a homogeneous chain and the other is a heterogeneous chain.
Example: Molecular formula C4H10
1.3.Positional or Positional Isomerism: The difference is in the position of an unsaturation, a functional group, a heteroatom or a substituent.
Example: Molecular formula C4H6

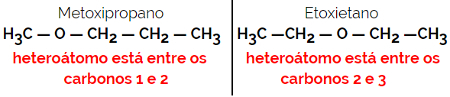
1.4.Compensation Isomerism or Metamery: It is a special type of position isomerism, where the difference is the position of the heteroatom.
Example: Molecular formula C4H10O
1.5.Dynamic Isomery or Tautomery: It is a special type of function isomerism, in which the isomers coexist in dynamic equilibrium in solution. The two main types of tautomeria are between a ketone and an enol (ketoenol balance) and between an aldehyde and an enol (aldoenol balance).
Example: Molecular formula C3H6O
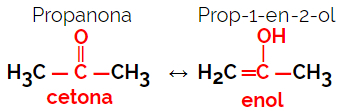
2. Space Isomerism or Steroisomerism: In this case, the difference between the isomers can only be visualized through the orientation of their atoms in space. There are two types of stereoisomerism: geometric isomerism and optical isomerism.
2.1.Geometric or cis-trans isomers: The difference is that the isomer named as cis it has the same carbon ligands in a double bond or in cyclic compounds on the same side of the plane. The isomer ligands trans are on opposite sides.
Example: Molecular formula C2H2Cl2

These compounds are called stereoisomers.
2.2.Optical isomer: Occurs when isomers are able to deflect a beam of polarized light. If it bends the polarized light beam to the left, it is a levorotary isomer, but if it bends to the right it is called a right-handed isomer.
Example:
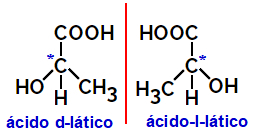
Asymmetric molecules like the ones shown above, which are mirror images of each other and which are not superimposable, are called enantiomers.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/tipos-isomeria.htm
