inorganic salts they are formed by the ionic association of at least one cation (formed by any metal or by ammonium) and an anion (simple or compound).
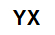
General molecular formula of a salt
When added to water, the salts dissociate, releasing at least one cation other than hydronium (H+) and an anion other than hydroxide (OH-).
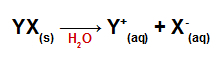
Dissociation equation for any salt
Classification of salts
Salts, in general, can have the following classifications:
simple salt: salt formed by just one cation and one anion. Examples: NaCl, CaSO4, KCN, NH4CO3 etc.
Hydrogenated salt: it has two cations (one of which must be hydronium) and an anion. Examples: NaHCO3, CaHBO3 etc.
Hydroxyl salt: it has a cation and two anions (one of which must be the hydroxide). Examples: MgOHCl, Al(OH)2ClO3 etc.
Hydrated salt: presents water molecules associated with its crystalline structure. Examples: CaCl2.2H2O, CuSO4.6H2The etc.
Double salt: it has two cations (all different from hydronium) and one anion or one cation and two anions (all different from hydroxide). Examples: Type4CN, AgFeBO3 etc.
Alum: is the salt formed by two sulfates with NOx cations equal to +1 and +3, plus 24 molecules of water. Examples: Ag2ONLY4.Al2(ONLY4)3.24H2o, na2ONLY4.Sb2(ONLY4)3.24H2O
Salt naming rule
Anion name + de + cation name
→ K3DUST4
Salt has the phosphate anion (PO4-3) and the potassium cation (K+1), hence its name is potassium phosphate.
→ Case3
The salt has the sulfite anion (SO3-2) and the calcium cation (Ca+2), hence its name is calcium sulphite.
NOTE: If the cation is not silver, zinc or an element that belongs to the IA, IIA and IIIA families, we must indicate its NOX with a roman numeral in front of the cation's name.
→ Cu2ONLY4
The salt has the sulfate anion (SO4-2) and the calcium cation (Cu+1), hence its name is copper sulfate I.
Hydrogenated salt: For this salt, before the anion name, we must write the prefix referring to the amount of hydrogen in the formula. This prefix must be separate from the word hydrogen by a hyphen.
→ NaHCO3
Salt has a hydrogen, carbonate anion and sodium cation, so its name is sodium monohydrogen carbonate.
Hydroxyl salt: For this salt, before the anion name, we must write the prefix referring to the amount of hydroxyls in the formula. This prefix must be separate from the word hydroxy by a hyphen.
→ Al(OH)2ClO3
The salt has two hydroxyls, the chlorate anion and the aluminum cation, so its name is aluminum dihydroxy-chlorate.
Hydrated salt: For this salt, after the name of the cation, we must write the prefix referring to the amount of water molecules in the formula. This prefix must be separate from the word hydrated by a hyphen.
→ CaCl2.2H2O
Salt has two water molecules, the chloride anion and the calcium cation, so its name is calcium chloride dihydrate.
Double salt with two cations: For this salt, we must write the double word in parentheses after the anion name and then the most electropositive cation name and the other cation.
→ AgFeBO3
This salt has silver (more electropositive cation) and iron II cation, in addition to the borate anion. Its name is borate (double) of silver and iron II.
-
Double salt with two anions:
Name of most electronegative anion + hyphen + name of least electronegative anion + de + cation name
→ Type4CN
This salt contains the titanium IV cation, in addition to the phosphate (more electronegative anion) and the cyanide anion. Its name is titanium cyanide phosphate IV.
Alum salt: For this salt, we ignore the general rule. Just write the term alum followed by the +3 charge cation name and the +1 charge cation name, respectively, separated by the conjunction e.
→ In2ONLY4.Sb2(ONLY4)3.24H2O
The alum salt has the +3 antimony cation and the +1 sodium cation, so its name is antimony III alum and sodium.
Physical characteristics of salts
They are solid at room temperature;
They have high melting and boiling points;
They are formed from ionic bonds;
They conduct an electric current in a liquid state (after undergoing fusion) or when dissolved in water;
Generally speaking, they are soluble in water, but there are salts that are considered practically insoluble.
Chemical properties of salts
Salts are compounds that have the ability to chemically react (provided they do not have the same cation or the same anion as another substance) with several groups of substances, namely:
In a double exchange reaction with an acid: they form a new salt and a new acid.
In a double exchange reaction with a base: they form a new salt and a new base.
In a double exchange reaction with another salt: form two new salts.
Some salts have the ability to suffer decomposition when subjected to heat, forming two or more new substances. If we heat the sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), for example, it will decompose, forming sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-sao-sais-inorganicos.htm
