The acronym TNT stands for trinitrotoluene. It is a nitro compound and its chemical name is 2-methyl-1,3,5-trinitrobenzene. Its formula is shown below:
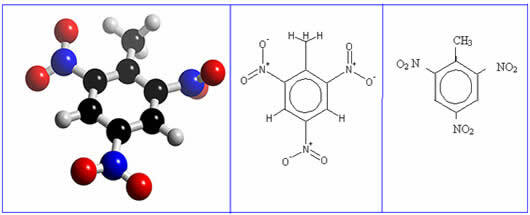
It is a yellow crystalline solid that has a high explosive potential. TNT is so explosive that it detonates with just a temperature of 80°C or an electrical spark. This is because in its structure there are enough oxygen atoms for combustion to take place.
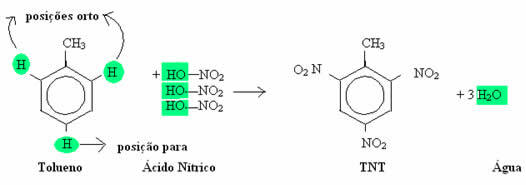
The method for obtaining trinitrotoluene is the total nitration of toluene, that is, when toluene reacts with nitric acid (HNO3). This total nitration means that nitrations will be made until all possible replacements are made. In the case of toluene, a maximum of three substitutions in the nucleus of the benzene ring are possible: two in ortho and one in para. Let's look at this replacement reaction below:
TNT, as well as tretyl explosives (N-methyl-2,4,6-trinitrophenyl-nitramine) and RDX (Cyclotrimethylenetrinitro-amine), was invented at the beginning of the 20th century, mainly due to the First World War.
Despite being often used as a weapon, its peaceful use is also very extensive. Plastic explosives, for example, often used in building implosions and other buildings, are actually TNT itself interconnected to a device. This device emits an electrical spark when activated, which causes the TNT to explode.

By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/tnt-trinitrotolueno.htm