Ametals are elements that have a tendency to gain electrons and form anions (negatively charged species). This means that they are dischargedelectronegativity, or high tendency to attract electrons. We say that the more electronegative a metal is, the more reactive it will be.
Experimentally, it was possible to determine the order of reactivity of the non-metals, which is given by the following:
F > O > N > Cℓ > Br > I > S > C > P > H
See the electronegativity values, respectively:
4,0 > 3,5 > 3,0 > 3,0 > 2,8 > 2,5 > 2,5 > 2,5 < 2,1
There is a kind of "trick" to decorate this row of electronegativity of non-metals, which is given by the sentence below, in which the initial of each word corresponds to the symbol of the elements in question:
“Fhi Odo not have NO Clube, bri got ISOuch Çdying Pfor the Hhospital"
But why do we need to know the reactivity of non-metals? One reason is to determine whether the chemical reaction will take place or not.
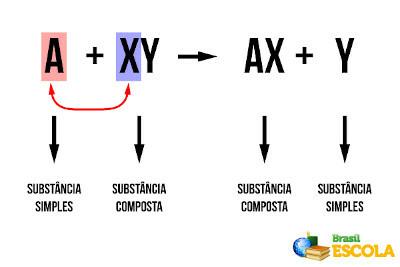
At simple exchange or displacement reactions are those in which a simple substance (formed only by one type of chemical element) reacts with a compound substance and displaces one of the elements of that substance, forming a new simple substance and another composed. Generically, we have:

Generic Displacement Reaction
See that “A” has shifted “Y” and joined “X”. This is also a redox reaction, as there is electron transfer. Considering that "A" and "Y" are non-metals, we have that "A" gains electrons (reduced), forming an anion, and is part of the compound substance "AX". On the other hand, the “Y”, which was an anion in the compound substance “XY”, lost electrons (it underwent oxidation) and formed the new simple substance “Y”.
When this type of reaction occurs, it is necessary to analyze the reactivity of the non-metals to see if the element of the simple substance will actually have the reactivity necessary to displace the nonmetal from the substance. composed. Consider, for example, the reaction between fluorine and sodium chloride:
F2(aq) + 2 NaCl(here) → ?
Does fluoride (F2) can it displace chlorine from sodium chloride (NaCl) and form a new compound with sodium? In the reactivity line of non-metals, fluorine is more reactive than chlorine. So it does manage to displace chlorine from NaCl, and the reaction occurs as follows:
F2(aq) + 2 NaCl(here) → 2 NaF(here) + Cl2(aq)
Since it is more electronegative, the F2(aq) reduced, and each fluorine atom gained an electron, forming the anion F-(here). This anion forms an ionic bond with the Na cation.+(here), generating sodium fluoride (NaF). Meanwhile, the Cl anion-(here), which was part of sodium chloride (NaCl), oxidized and formed chlorine atoms that joined and formed the simple substance Cl2.
Now see another example below. Will this reaction take place?
I2(aq) + KCl(here) → ?
If we look at the reactivity queue of ametals, we will see that will not occur no redox reactions between these substances, as Cl is more reactive than I, therefore, I2 it will not have the necessary force to displace Cl from the KCl substance.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/ordem-reatividade-dos-ametais.htm