Rome (or Rome Capital) is a commune located in the Lazio region, in Italy, and which performs the function of national capital. The city was founded in 753 BC. C., and since then it has been among the main historical and cultural centers not only on the European continent but also in the world.
Close to the Mediterranean Sea, Rome has a climate typical of this region, and is also characterized by a modest relief with altitudes that do not exceed 140 meters. Rome's economy is based on the commerce and services sector, with emphasis on tourism. The city receives millions of tourists every year, attracted by the records of Ancient Rome and the elements that express its contemporary customs.
Read too: Ancient Rome — details about one of the greatest civilizations of Antiquity
Topics in this article
- 1 - Summary about Rome
- 2 - General data about Rome
- 3 - Geography of Rome
- 4 - Flag of Rome
- 5 - Map of Rome
-
6 - Economy of Rome
- → Tourism in Rome
- 7 - Infrastructure of Rome
- 8 - Government of Rome
- 9 - Culture of Rome
- 10 - Etymology of Rome
- 11 - History of Rome
Summary about Rome
Rome is a city located in the Lazio region, in western Italy.
It is the national capital of Italy.
It is nicknamed the Eternal City.
It was founded in the year 753 BC. W. by Romulus, who became the first king of Rome.
Located close to the Mediterranean Sea, it has a typically Mediterranean climate and moderate relief with an average altitude of 21 meters. It is crossed by the Tiber River.
It forms the metropolitan region known as the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital.
It is the most populous city in Italy, with 2,745,819 inhabitants.
Rome's economy revolves around tourism and services, ranging from government activities to banking, financial and telecommunications services. The Italian capital is home to the country's main high-tech companies.
Its inhabitants enjoy a high quality of life, with a high annual per capita income.
In terms of infrastructure, Rome stands out in the transport sector, notably road transport.
Rome's culture presents traditional elements that date back to the monarchical and imperial periods, as well as as contemporary aspects that establish the city as an important cultural center in Europe and Europe world.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
General information about Rome
Kind: Roman.
Location: Province of Rome.
Country: Italy (Europe).
Region: part of the Lazio region, in Central Italy.
Metropolitan region: Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, which is made up of a group of 121 Italian communes (or cities). The main commune in this region is Rome.
Bordering communes (cities):
Albano Laziale |
Nuova font |
Monterotondo |
Anguillara Sabazia |
Formello |
Palestrina |
Ardea |
Frascati |
Poly |
Campagnano di Roma |
Gallicano in Lazio |
Pomezia |
Castel Gandolfo |
Grottaferrata |
Riano |
Castel San Pietro Romano |
Guidonia Montecelio |
Sacrofano |
Ciampino |
Marino |
San Gregorio da Sassola |
Vatican CITY |
mint |
Tivoli |
Colonna |
Monte Porzio Catone |
Trevignano Romano |
Fiumicino |
Monte Compatri |
Zagarolo |
Geography of Rome
Total area: 1,287.36 km².
Total population: 2,745,819 inhabitants (est. 2023).
Demographic density: 2,132.9 inhabitants/km².
Climate: Mediterranean influenced by hot winds (pontino) and cold (tramontana) that blow, respectively, from the ocean and the interior during the hot and cold seasons. Temperatures in the city vary between 24º C and 10º C, while annual precipitation is 750 mm on average.
Altitude: 21 meters above sea level.
Highest point: Monte Mário, 139 meters above sea level.
Hydrography: The main watercourse that runs through Rome is the Tiber River. The city is in western Italy, close to the Mediterranean Sea.
Time zone: GMT+1.
Foundation: April 27, 753 a. W.
Flag of Rome

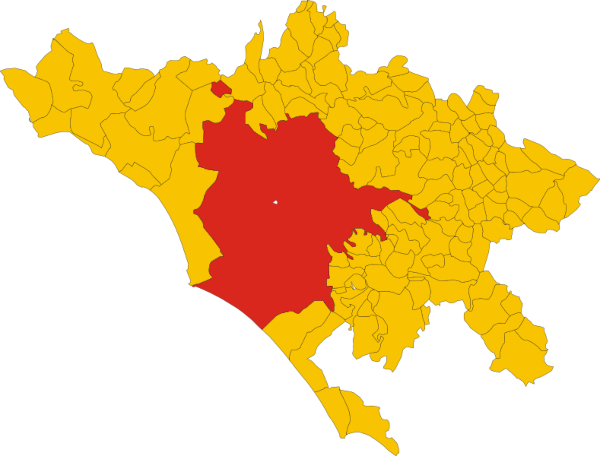
Rome map
The map in the first image indicates the position of the city of Rome (or Rome, as it appears in English in the figure) in Italian territory. Check out:

The second map shows the commune (or city) of Rome surrounded by neighboring or nearby communes, which together form the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital.
Economy of Rome
According to metropolitan GDP, The The city of Rome and its metropolitan region are part of the richest cities on the European continent. According to this indicator, Rome is in 13th place with US$153.5 billion, which corresponds to income for the year 2020. Considering only the Italian metropolitan regions, Rome comes in second place, behind only Milan, in the north of the country.
In 2018, it is known that Rome's economy represented approximately 10% of Italy's entire economy. |1| Furthermore, the population's per capita income exceeds the mark of 35 thousand dollars per year. However, it is interesting to note that although it is a city with a high level of socioeconomic development, it cannot be said that Rome is an industrial city.
The Roman economy does not rely on secondary sector activities, but yes in the activities of tertiary sector, a segment that concentrates commerce and service activities. Rome, as the national capital, houses the main services and institutions of the Italian republic. Thus, Italian government buildings, official agencies linked to international organizations of which Italy is a member, as well as their respective employees, live in Rome and contribute to the collection of foreign exchange in the city.
Rome has strong ties with the Catholic Church. Let us remember that the headquarters of this institution is in Vatican City, which consists of an enclave in the interior of the Italian capital and which is governed by the Holy See, therefore independent of Rome and the Italy. Despite this, there are many Vatican employees who live in Roman territory, in addition to the millions of tourists who annually visit the headquarters of the Catholic Church and stay in the capital Italian.
Transport and communications are also important services for the Roman economy. The first of them, in fact, dates back to older periods in the city's history. Rome is also home to the main financial institutions and companies in the technology sector advanced sector of Italy, notably those in the IT, aerospace and telecommunications.
→ Tourism in Rome
The tourism is the main economic activity in Rome, being the largest source of revenue in the Italian capital. Included in this sector are the expenses that visitors incur in the city, accommodation services, transport, food, recreation, souvenir shops and all other elements that are part of this activity economic. Italy is today the fifth most visited country in the world, while Rome ranks 12th among the most sought after cities by tourists. Annually, the Italian capital receives 8.7 million people.
Rome shelters hundreds of tourist attractions that retell the history of this city that was the capital of one of the greatest empires and ancient civilizations. Because of this, the physical structures and spaces that date from this period are part of the city's urban landscape. These constructions mix with modern buildings and contemporary cultural spaces, making Rome one of the main tourist destinations in Italy and the world.
◦ Rome tourist attractions
Next, discover the main tourist attractions in Rome.
Coliseum
![View from inside the Colosseum, Rome's main tourist attraction. [1]](/f/2c7fed95cfb87e2c1d667c5757461de3.jpg)
The Coliseum It is an amphitheater built between the years 70 and 72 AD. C., during the Flavian dynasty. The arena had a capacity for 50,000 people, and was widely used to hold Roman gladiator fights, reenactments and even public executions.
Trevi Fountain

Trevi Fountain is a fountain located in the rione (neighborhood) Trevi, in Rome. It is located in front of Palazzo Poli. This monument, formed by the fountain itself and the sculpture of the god Neptune, It was built in the 18th century and is, today, one of the most visited tourist attractions in the city. A tradition of throwing coins into the fountain to make requests was created, with an estimate of 3,000 euros thrown in daily.
Pantheon
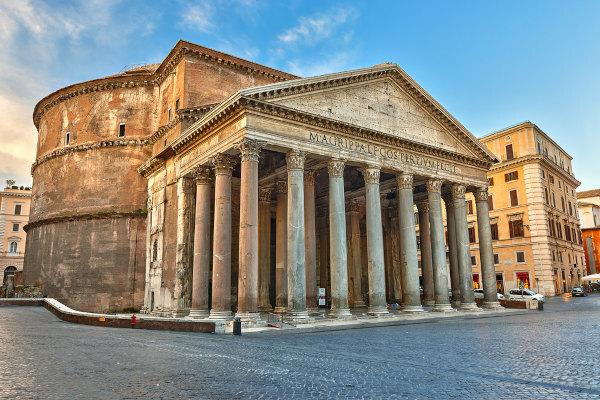

The Pantheon is a building that was built in time of the Roman Empire, between 27 a. W. and 14 d. W., having been restored a century later. During the 7th century, the Pantheon was transferred to the Catholic Church. A curious fact about this building is that some important figures from political and cultural history Italian women were buried in the Pantheon, as was the case of the Renaissance painter Raphael, who died in 1520.
Also access: Vatican — details about the enclave located in Rome (Italy) that houses the headquarters of the Catholic Church
Rome Infrastructure
The city of Rome has a high quality of life due to several factors, one of which is the infrastructure offered to its population. The highlight of the city's physical network is transport, as it Pomegranate é the center of a huge travel network that covers almost all of Italy. This aspect of transport in the capital is a legacy of the period of the Roman Empire, when roads connected the entire territory that made up its domains.
The transport network in Rome is of the radial type, and mainly benefits cars. However, traffic in the city can become slow at peak times, making it difficult to get around efficiently. Trains and subways are also used for daily travel in Rome. In the first case, it is possible to travel to another European country from the Italian capital. For this purpose, there are also three large airports in the city. Rome also has a seaport, called Porto Civitavecchia or Port of Rome.
Government of Rome
The commune of Rome is classified as a special commune, which is called Rome Capital. She is governed by the mayor, elected by popular vote in a two-round election, and also by the communal committee and communal council. The communal committee is also an organ of the Executive Branch of Rome, while the council is responsible for urban services, security and assistance to the city's population. The seat of government in Rome is in the Palazzo Senatorio on the Capitoline Hill.
The administrative division of the commune of Rome is made into 15 municipalities or subcommunes, numbered from I to XV:
Administrative division of the commune of Rome | ||
Historic Center (I) |
Rome delle Torri (VI) |
Arvalia/Portuense (XI) |
Parioli (II) |
Appio-Latino/Tuscolana/Cinecittà (VII) |
Monte Verde (XII) |
Monte Sacro (III) |
Appia Antica (VIII) |
Aurellio (XIII) |
Tiburtin (IV) |
Eur (IX) |
Monte Mario (XIV) |
Prenestino/Centocelle (V) |
Ostia/Acilia (X) |
Milvio (XV) |
Culture of Rome

Rome is one of the main cultural centers of Italy and the European continent. The city was built thousands of years ago, and people of different origins and nationalities passed through it who contributed, and still contribute, to its multiculturalism. Furthermore, there is a very close relationship between Roman culture and religion and the Church. Catholic, an institution that attracts millions of tourists and pilgrims to the Italian capital every the years.
The landscape of Rome is full of buildings that refer to the period of the founding of Rome and the empire that began with it, confirming its nickname of Eternal City. The city is also known as Capital of the World, given its historical, political and cultural importance.
The culture of Rome presents elements that reflect all stages of the development of art in Europe, from the medieval period to contemporary art, with a notable influence on the Renaissance and Baroque styles. Among these elements are sculptures, churches and cathedrals, galleries, monuments such as obelisks, gardens and Roman villas. Other of these elements can be found in museums, such as the Capitoline Museum.
Literature, cinema and typically Italian and Mediterranean cuisine are equally important to Roman culture. The city is also one of the world's fashion capitals.
Etymology of Rome

The most widespread explanation of the origin of the name “Roma” is associated with the founding myth of the Italian city. The myth says that the brothers Romulus (Romulus) and Remus (Remus), sons of the god Mars and Rhea Sylvia, were thrown into the Tiber River as punishment for their mother. However, the babies were found by a wolf, later called Capitolina, who suckled them and did not let them die. Romulus was later the founder of Rome and its first king, which explains the name of the city.
There are other explanations for the attribution of the name “Rome” to the capital of Italy. One of them says that the Tiber River, which crosses the city, was named Rumen, of Greek origin, before receiving its current name.
History of Rome
The region where the city of Rome is located, in Latium, went through a process of occupation during the Middle Ages. Bronze, although permanent settlements began to appear only in the subsequent millennium along the course of the Tiber. The fact is that it is an area of very ancient occupation and through which people of different ethnicities and origins passed through, notably the Etruscans. The city of Rome itself was only founded in 753 BC. W. by its first king, Romulus.
Initially the city of Rome It was governed by a monarchical regime that lasted until 509 BC. W. During the monarchy, Roman society was divided into patricians (the wealthiest class), clients, commoners and slaves. The last Roman monarch took power in 535 BC. C., but was deposed in a coup two decades later, which began the republican period in Rome. The Roman Republic lasted from 509 a. W. to 27 a. W., an interval that was marked by the Punic Wars.
The Roman Republic gave way to the Roman Empire from 27 BC. C., and this system of government extended until the year 476 d.W. The imperial period was marked by a series of territorial disputes and the expansion of Rome, which began to polarize power. political, economic and military in Europe and in the domains conquered, or taken, on other continents, such as Asia and Africa. After a relative period of stability, a crisis in the slave system and the subsequent political and economy that settled in the Roman Empire, combined with the Germanic invasions, caused its end in the 10th century.
During the Middle Ages the city of Rome became part of the Byzantine Empire, which originated after the fall and split of the Roman Empire. During this period, the Catholic Church gained strength in Rome and part of the European continent, becoming not only a religious authority but also a political one. Rome only became a Republic again in 1848, that is, already in the 19th century. The city was one of the last to be incorporated into unified Italy, which happened in 1870. A year later, in 1871, Rome was officially considered the country's capital.
It is interesting to note that, at the time, the territory belonging to the Catholic Church was still integrated into Italian territory. The Vatican only became an independent state in 1929, with the signing of the Lateran Treaty. As a result, it became an enclave in the city of Rome.
Between the end of World War II and the beginning of the 1990s, the ruler of the city of Rome was elected through the communal council. The first direct election for mayor of Rome took place only in 1993. Since then, the Italian capital has had just six mayors.
Grades
|1|BRONZINI, Raffaello. (Coord.) The economy of Rome in the years two-thousand. Occasional Papers (Economic and financial questions), n. 793, sep. 2023. Available in: https://www.bancaditalia.it/pubblicazioni/qef/2023-0793/index.html.
Image credit
[1]Viacheslav Lopatin/Shutterstock
Sources
About Rome. Available in: https://www.aboutroma.com/index.html.
NATIONAL GEOGRAPHIC. Encyclopedic Entry: The Colosseum. National Geographic, 19 Oct. 2023. Available in: https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/colosseum/.
RING, Richard; FOOT, John; EHRLICH, Blake. Rome (national capital, Italy). Encyclopaedia Britannica, [n.d.]. Available in: https://www.britannica.com/place/Rome.
SHAW, Brandon. The Unfathomable History Of The Pantheon In Rome. The Roman Guy, 5 Dec. 2022. Available in: https://theromanguy.com/italy-travel-blog/italy-travel-blog/rome/pantheon/story-of-the-pantheon-in-rome/.
Visit Rome. Available in: https://romesite.com/.
WILDE, Robert. A Brief History of Rome. ThoughtCo., 19 Feb. 2019. Available in: https://www.thoughtco.com/brief-history-of-rome-1221658.
ZAINIB, Attiya. 40 Most Visited Cities in the World in 2023. Yahoo! Finance, 04 Oct. 2023. Available in: https://finance.yahoo.com/news/40-most-visited-cities-world-193722500.html.
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
GUITARRARA, Paloma. "Pomegranate"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/geografia/roma.htm. Accessed on November 13, 2023.

