Sudden illness is an expression used to describe acute, unexpected, and sudden medical events that require immediate medical attention. Its main causes include heart attack, cardiac arrhythmias, strokes, heart attacks, seizures, severe allergies, among others. Symptoms vary depending on the cause, but often include loss of consciousness, chest pain, shortness of breath, and mental confusion. Sudden death is usually a fatal consequence of sudden illness.
Read too: What are the top 10 causes of death in the world?
Topics in this article
- 1 - Summary of sudden illness
- 2 - What is sudden illness?
- 3 - Causes of sudden illness
- 4 - Signs and symptoms of sudden illness
- 5 - What to do in case of sudden illness?
- 6 - Care to avoid sudden illness
- 7 - Sudden death
Summary of sudden illness
- Sudden illness is an acute and unexpected medical event.
- It can be caused by a variety of medical conditions, such as cardiac arrests, arrhythmias, strokes, and severe allergies.
- Its symptoms depend on the underlying cause, and common ones include loss of consciousness, shortness of breath, chest pain, and confusion.
- Defibrillators are often needed to try to save lives in cases of cardiac arrest.
- Regular consultations with a cardiologist and a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of sudden illness, especially in the presence of asymptomatic pre-existing conditions.
- Sudden death is often a fatal consequence of sudden illness, as rapid medical intervention is crucial for survival in cases of sudden illness.
What is sudden illness?
Sudden illness is a expression used to describe an event méI say it happens in a wayúbites and presents severe symptoms, such as loss of consciousness. This condition requires immediate medical attention and can be reversible with appropriate treatment. Sudden illness can be triggered by a variety of causes, ranging from dehydration to heart attack.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Causes of sudden illness
Most of the sudden illness is associated with cardiac causes. However, neurological and respiratory factors, severe allergic reactions, drug intoxication and metabolic diseases (such as diabetes) can also contribute to this event. Examples of cardiac, neurological and respiratory conditions related to sudden illness include:
- Cardiac problemsacos: heart attack (represents 80% of cases), cardiac arrest, cardiac arrhythmia and acute heart failure.
- Neurological problems: cerebrovascular accident (CVA), convulsions and cerebral hemorrhage.
- Breathing problemsrivers: respiratory failure, pneumothorax, acute asthma and pulmonary embolism.
It is important to highlight that other factors may influence the risk of illnessbite, such as age. The occurrence of heart attacks, for example, increases as age advances. Furthermore, Risk factors associated with lifestyle also contribute to poor health.bite, such as smoking, inadequate diet and sedentary lifestyle, as they increase the chances of developing serious diseases, especially cardiovascular diseases.
Conditionções genéticas or congênitas tooém can increase the risk of sudden illness, especially in the absence of symptoms. Examples include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (increased thickness of the heart) and coronary artery disease (blockage of the coronary arteries due to the accumulation of fatty plaques inside them).
Signs and symptoms of sudden illness
Symptoms of sudden illness are closely related to the underlying cause, and the most common signs include:
- chest pain;
- fainting or sudden loss of consciousness;
- shortness of breathe;
- palpitations;
- mental confusion or disorientation;
- weakness;
- convulsions;
- dizziness or vertigo;
- intense sweating;
- loss or blurring of vision;
- severe headache;
- paralysis of the face and leg, usually on one side of the body.
See too: Cardiorespiratory arrest — serious event characterized by interruption of heart and breathing function
What to do in case of sudden illness?
Sudden illness is considered a medical emergency and, in this scenario, the most recommended action is contact ServiçM Customer Serviceóemergency speedê(Samu - 192) and report the signs observed so that the attendant can offer appropriate support.
Quick response is essential, as it can prevent death or serious consequences. In the case of cardiac arrest, for example, ideal care should begin within four minutes. Until medical rescue arrives, it is possible for the patient's companion to perform cardiac resuscitation, an important first aid procedure.
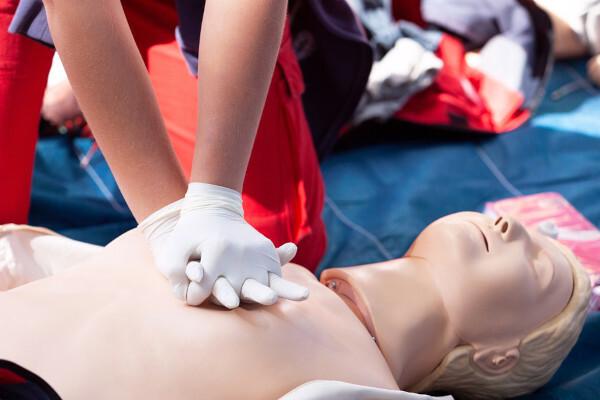
Important:Given the high mortality rate associated with sudden illness, it would be essential to have automatic external defibrillators (AED) in easily accessible locations for a response. quickly, especially in cases of cardiac arrest, as they are simple to use and can be operated by people outside the healthcare field to help the heart recover its function. beats. In addition, raising awareness among the population about the subject and offering first aid and emergency care courses Domestic emergency situations can also contribute to avoiding deaths due to sudden illness, speeding up emergency procedures. help.
Care to avoid sudden illness
To prevent or reduce the risk of sudden illness, some measures can be adopted, such as:
- Maintain healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular physical exercise, a balanced diet and maintaining adequate hydration.
- Avoid smoking.
- Implement strategies to manage and reduce levels of psychosocial stress.
- Actively control cholesterol levels and monitor health conditions such as hypertension and diabetes.
- Consult a doctor whenever unusual symptoms are observed, as they may be indicative of a warning.
- Maintain annual follow-up with a cardiologist, especially after the age of 30 and/or if there is a family history of heart problems. This helps in early identification of silent heart diseases.
Important: It is worth mentioning that people who have already had a heart attack, cardiac arrest or stroke should adopt these take special precautions, as the risk of a second episode is significantly likely.
Sudden death
For the World Health Organization (WHO), sudden death it's an ohunexpected and sudden death which, if witnessed, occurs within one hour of the onset of symptoms, or, if not witnessed, within 24 hours of the person last seen alive and without symptoms.
Its main causes are of cardiac origin, especially heart attack and cardiac arrhythmias, and it is often a consequenceêof an evilúbite. Once symptoms appear, it progresses extremely quickly, and the chance of survival decreases every minute. When a medical intervention prevents death from occurring, it can be considered that there has been an “aborted sudden death”.
Sources
FANTASTIC. Find out what to do to help those who have a serious illnessbite. Globoplay, 2012. Available in: https://globoplay.globo.com/v/1966316/.
KUMAR, A. et al. 2021. Sudden cardiac death: epidemiology, pathogenesis and management. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 22(1):147-158.
RIBEIRO, M. Heart attack in young people: why it happens and how to prevent it. Drauzio Varella, 2021. Available in: https://drauziovarella.uol.com.br/cardiovascular/infarto-em-jovens-por-que-acontece-e-como-prevenir/.
SEFTON, C. et al. 2023. Characteristics of sudden death by clinical criteria. Medicine (Baltimore). 102(16):e33029.
ZAIJIA, C. et al. 1985. Sudden cardiac death. World Health Organ Tech Re. 726:5–25.
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FLORES, Heloísa Fernandes. "Sudden illness"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/doencas/mal-subito.htm. Accessed on November 9, 2023.