O sunflower (Helianthus annuus Linnaeus) is a plant known for its impressive yellow inflorescence and its movement of “following” the sun throughout the day during its growth phase. These characteristics underlie the symbolism associated with the joy and vitality that the sunflower represents, making it a plant appreciated in different cultures.
Originally from the Americas, sunflower is currently cultivated all over the world due to its diverse applications. Its seeds are used in the production of sunflower oil, commonly used in cooking, and as a food source for humans and other animals. The nectar present in flowers attracts pollinators and is used in the production of honey. Its potential as a biofuel has driven the increase in cultivated areas. Furthermore, the sunflower also has ornamental applications in landscaping.
Read too: Corn — a plant whose fruit also has several applications
Topics in this article
- 1 - Summary about sunflower
- 2 - Origin of the sunflower
- 3 - Taxonomic classification of sunflower
- 4 - Main characteristics of the sunflower
- 5 - Types of sunflower
- 6 - Sunflower fruit
- 7 - What is sunflower used for?
- 8 - Why does the sunflower turn towards the sun?
- 9 - Sunflower cultivation
- 10 - Importance of sunflower
- 11 - Sunflower meanings
- 12 - Curiosities about the sunflower
Summary about sunflower
- The sunflower is a plant well known for its impressive yellow inflorescence and its movement of “following” the sun throughout the day.
- Its inflorescence is of the capitulum type, and its yellowish color places it as a symbol of joy and vitality in different cultures.
- The sunflower is native to the Americas and has been domesticated since around 3,000 years ago. W. by North American indigenous peoples before spreading throughout the world.
- There are different varieties of sunflower, which include different flower colors and heights.
- Sunflower seeds, in addition to being consumed raw or roasted in the human diet, are also a valuable source of sunflower oil.
- In addition to being consumed by humans, sunflowers are also an important food source for birds and ruminants.
- Sunflower flowers attract bees and other pollinators, and the nectar from the flowers is used in the production of sunflower honey.
- The sunflower is also valued for its ornamental appearance and is often used in landscaping.
- Ukraine and Russia are among the largest sunflower producers in the world.
- The sunflower inspired one of the most famous series of paintings in the world, The Sunflowers, by the painter Vincent van Gogh.
Origin of the sunflower
The sunflower is a plant native to America. Recently, fossils of an ancient sunflower collected in Argentina pointed to a likely origin of the sunflower in South America 47.5 million years ago.
In turn, sunflower domestication is mainly attributed to North America. Archeology works indicate that North American indigenous peoples cultivated and domesticated the sunflower thousands of years ago (around 3,000 years BC). C.) for a variety of purposes, such as obtaining edible seeds, extracting edible oil, and ceremonial uses.
With the European colonization of the Americas, sunflowers were brought to Europe in the 16th century, where they enchanted people with their ornamental beauty. The plant spread throughout Europe and other parts of the world, being cultivated in different regions of the planet, not only by its edible seeds and oil, but also as an ornamental plant in gardens and as a commercial crop in areas agricultural.
In Brazil, cultivation dates back to the 19th century, in the southern region, having been brought by European colonists, who consumed its roasted seeds in the form of tea.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Sunflower taxonomic classification
The scientific name of the sunflower is Helianthus annus Linnaeus, which derives from the Greek “helius”, which means sun, and “anthos”, which means flower, that is, the “flower of the sun”. It is part of the Asteraceae family, the largest family of angiosperms (flowering plants), which includes other plants such as daisies.
Kingdom: Plantae
Phylum: Antophyta
Class: Eudicotyledoneae
Order: Asterales
Family: Asteraceae
Gender: Helianthus Linnaeus
Species: Helianthus annuus Linnaeus
Main characteristics of the sunflower
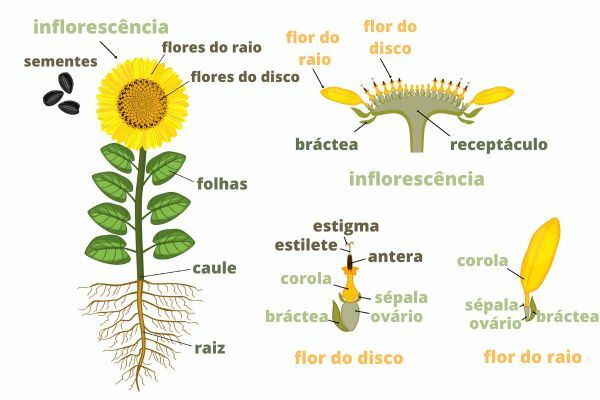
The stem The sunflower is robust, erect and can reach up to 3 meters in height, depending on growing conditions and variety. It has few branches at the apex, fast growth and phyllotaxis (leaf distribution) of the opposite crossed type. The leaves are large, lance-shaped (lanceolate), green, rough and with serrated edges. In turn, the root system is deep and expansive, being able to absorb water and nutrients from deep layers of the soil, in addition to contributing to plant anchorage and reducing soil erosion.
The sunflower it presents inflorescence (group of flowers located in branch systems) chapter type, which form a striking disc that reaches between 10 and 30 centimeters in diameter. The plant's yellow petals, which are around the crown, are sterile flowers that have the function of attracting pollinators and are known as bracts. The core of the inflorescence is composed of a set of fertile and bisexual tubular flowers. Each seed (fruit) originates of a flower. Each sunflower can have 100 to 8,000 seeds.

It is an annual species, flowering for approximately 20 days.. The sunflower is ready to harvest when the “flower” dries.
Types of Sunflower
Although the most common sunflowers are yellow ones with an average height of 2 meters, there are other varieties with different characteristics in terms of size, color and shape of the stem and flowers.

- Giant sunflower: are varieties that have exceptionally large stems and/or flowers, often used in sunflower growing competitions.
- Multiple Sunflower: Some varieties have several flowers on a single stem, which are smaller and folded, giving a furry appearance.
- Dwarf sunflower: are smaller varieties of sunflower that do not grow as tall as standard varieties, reaching between 30 and 60 centimeters. They are used for limited spaces or for potted gardens.
- Red sunflower: There are sunflower varieties with red flowers, instead of the traditional yellow color.
- Wild sunflower: is a native plant that grows naturally in fields and roadsides in some regions. It attracts pollinators, contributing to local biodiversity.
Sunflower fruit
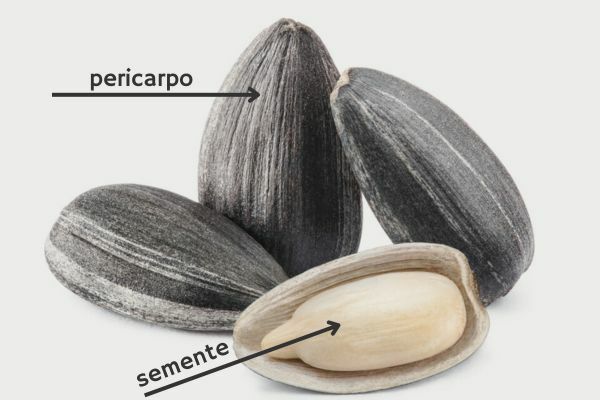

The fruit of the sunflower is the structure popularly known as “sunflower seed”. It is of the achene type, consisting of the pericarp (shell) and the seed. The shell is made up of the outer, middle and inner layers. Now the seed It consists of the integument, endosperm and embryo. The fruit forms within the central disc of the sunflower flower after fertilization of the ovule through pollination.

Sunflower seeds are classified according to their use as oily and non-oily.. The oily seeds are black in color, smaller, have a tightly adherent shell and are intended for the production of oil and bran. The non-oily, striated seeds are larger, have a more fibrous and easily removable shell, and are mainly used for human consumption (like almonds) or as bird feed.
See too: Strawberry — a pseudofruit whose true fruits are also of the achene type
What is sunflower used for?
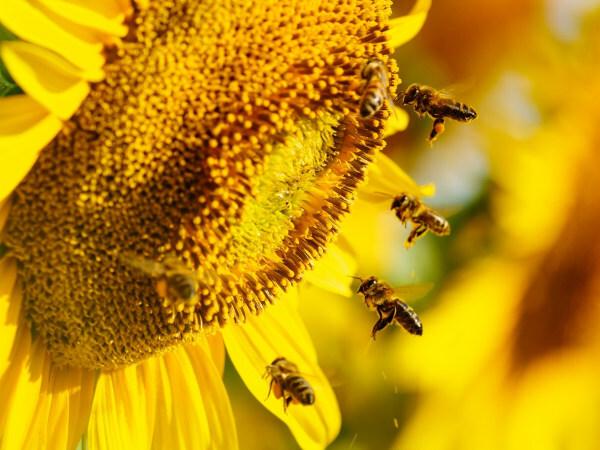

Sunflower is a versatile product, and its applications span several sectors. See some of its uses below.
- Food source for humans: sunflower seeds are edible and nutritious, forming part of the human diet. They can be consumed raw or roasted and are a good source of protein, fiber, fats (such as fatty acids), vitamins (such as vitamin E) and minerals (such as selenium). From its seeds, it is also possible to extract sunflower oil, which is edible and has high nutritional quality.
- Food source for other animals: In addition to being food for humans, sunflower seeds are also used to feed other animals, such as birds. Sunflower is also widely used to feed ruminants due to its high fiber and protein content, whether in the form of bran or silage.
- Pollination and honey production: sunflower flowers provide a rich source of pollen and nectar for polarizers, particularly bees. In addition to the plant itself and others in the surrounding area benefiting from pollination, the nectar from sunflower flowers is used by bees to produce sunflower honey.
- Crop rotation: sunflower is used as an alternative in crop rotation, especially in the second harvest, being planted alternately with other crops to improve soil health, reduce the incidence of pests and diseases, and diversify agricultural practices.
- Biofuel production: Due to their high oil content, sunflower seeds have been used as a raw material for biofuel production. Biodiesel sunflower is an alternative to traditional diesel, and its cultivation is considered more sustainable than some other biofuel crops, mainly due to the resources that sunflower offers to its pollinators.
- Landscaping: The large, brightly colored inflorescence, coupled with the symbolism of happiness and vitality associated with the sunflower, makes it a popular choice as an ornamental plant. It is often used to add color to gardens and arrangements or as a gift, showing great acceptance in the floriculture market.
Why does the sunflower face the sun?
It is common to hear that the sunflower “turns” towards the sun. This movement or change of orientation of sessile plants or animals in response to sunlight is known as heliotropism. In the case of sunflower, the phenomenon of heliotropism occurs during the plant's growth phase.
This behavior can be explained by the differentiated growth that occurs in the plant, in which the side of the inflorescence that does not receive light grows more than the side that receives sunlight directly. The shaded side accumulates auxin, a hormone that regulates plant growth. This accumulation causes the part that is in the shade to grow faster than the part that is in the sun. In this way, the stem and the capitulum lean towards the sun. As the sun sets, auxin is redistributed throughout the plant and the capitulum returns to its initial position. This phenomenon allows the plant to make the most of sunlight, which contributes to photosynthesis and growth hormones.
Also access: Phototropism — the growth movement that the plant performs in the opposite direction to the light source
Sunflower cultivation
The sunflower It is a plant that can grow in most agricultural soils due to its tolerance to drought and lower incidence of pests and diseases. The presence of deep roots helps the plant to explore the soil more and absorb more water and nutrients.
In this way, the sunflower can be cultivated in practically the entire Brazilian territory. Currently, commercial plantations are concentrated in Mato Grosso, Minas Gerais and Goiás, regions strong in grain production, with approximately 63 thousand hectares. In these places, sunflower is generally grown in the “safrinha” or second harvest, following the cultivation of soybeans. The bioenergetic potential of sunflower boosts the potential for expansion of cultivation in the country in the coming years.

On the world stage, the largest sunflower producers are Ukraine, Russia, the European Union and Argentina, which total approximately 26 million hectares of cultivated areas.
Importance of sunflower
The sunflower It is a significant plant in several aspects, both from an economic, environmental and cultural point of view.. This species is an important agricultural crop, and its cultivation is widespread in different parts of the world. Its deep root system helps to improve the quality of the soil, making it more fertile and resistant to erosion. Flowers attract pollinators, such as bees, contributing to the maintenance of biodiversity. Its seeds provide nutritious food for humans and other animals. Furthermore, the sunflower's cultural significance in human society makes it one of the most valued and versatile ornamental plants in the world.
Sunflower meanings
See below some of the main meanings of the sunflower:
- In popular wisdom, the yellowish and orange tones of the sunflower flower make it a plant associated with happiness, energy, joy and vitality.
- In love, it often symbolizes respect and honesty, while in friendships, it represents loyalty.
- In some cultures, the sunflower is also a symbol of courage.
- It is also believed that giving a sunflower to someone who is starting a new business is a way of wishing them success and good fortune.
- Within the scope of feng shui, a technique for harmonizing environments, the sunflower plays the role of bringing positive energy, welcome, health and prosperity to the home.
- In Greek mythology, the sunflower is related to Helios, the Sun God:
- According to history, the nymph Clície fell in love with Hélio. He, seducing the young woman, gave her hope that they would experience love together, but in the end he chose to stay with her sister. Lovingly disillusioned, Clície stopped eating and cried for whole days in a field. During the day, she only looked at the sky while the sun was there. At night, Clície looked at the floor and shed tears. Begging the gods to transform her into something she could continue to watch Helios, her feet changed into roots, the body into a thin and resistant stem and his face and yellow hair became a flower, the sunflower.
Curiosities about the sunflower

- The sunflower was a source of great inspiration for Dutch painter Vincent van Gogh. One of his most famous works is the series of paintings The Sunflowers, which includes five large canvases of this flower in a vase, with shades of yellow. For van Gogh, sunflowers conveyed gratitude. Currently, the work is not for sale, but it is considered one of the most famous and valuable in the world.
- In Brazil, brega singer Falcão wears a sunflower flower in his jacket pocket. Despite helping to popularize the plant, it also contributed to it being considered tacky in decor for a while.
- According to the book Guinness As of 2021, the largest sunflower flower was grown in Canada and measured 82 centimeters.
- Sunflower pollen grains are sticky and heavy, making them difficult to transfer between plants by wind.
Sources
LEITE, R.M.V.B. of C. et al. Sunflower in Brazil. Londrina: Embrapa Soja. 2005. 642 p.
EMBRAPA PORTAL. sunflower. Available in: https://www.embrapa.br/soja/tecnologias/girassol.
ECOLOGICAL MAGAZINE. Sunflower. Available in: http://revistaecologico.com.br/revista/edicoes-anteriores/edicao-114/girassol/.
SCIENTIFIC AMERICAN. Early bloomer: Ancient sunflower fossil colors picture of Eocene flora. Available in: https://www.scientificamerican.com/gallery/early-bloomer-ancient-sunflower-fossil-colors-picture-of-eocene-flora/.
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FLORES, Heloísa Fernandes. "Sunflower"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/girassol.htm. Accessed September 27, 2023.
Understand what Nipah virus is. Find out how its transmission occurs. Check out what the...
Click here, find out the origin of the sunflower and learn about its main characteristics and its...
Find out the origin and objective of National Reading Day. See activity suggestions for...


