The Earth is the planet in which we live. It is the only one known to harbor life.
Also called the blue planet, due to most of its surface (70%) being covered by water, it is the third planet from the Sun in Solar system.
It is considered a rocky or telluric planet, because it is part of the group of planets with a solid surface. The other telluric planets are Mercury, Venus and Mars.
The Earth is around 4.5 billion years old and is made up of several layers that are extremely important for life to exist.

Characteristics of planet Earth
Earth is a unique planet and its characteristics are what allow life as we know it to exist. It is approximately 12,756 km (along the Equator) in diameter and more than 510 million km2 of area.
Its mass is 5.972 × 1024 kg and the volume of 1.08321×1012 km³. It has a single natural satellite, the Moon.
Rotation and translation movements of the Earth
Planet Earth performs two types of movements: rotation and translation. The movement of rotation This is what the planet does around its own axis, the Earth's lasts 23 hours and 56 minutes. This movement is responsible for the existence of days and nights.
The movement of translation is the one in which the planet revolves around the Sun. The Earth takes around 365 days and 6 hours to carry out this movement, which is responsible for the existence of the seasons.
Earth's inner and outer layers
The Earth has several inner and outer layers made of very different materials. The inner layers are those that are inside the planet, we cannot see them, but we perceive its existence with the occurrence of earthquakes (movement of tectonic plates) or volcanic activity.
The inner layers are:
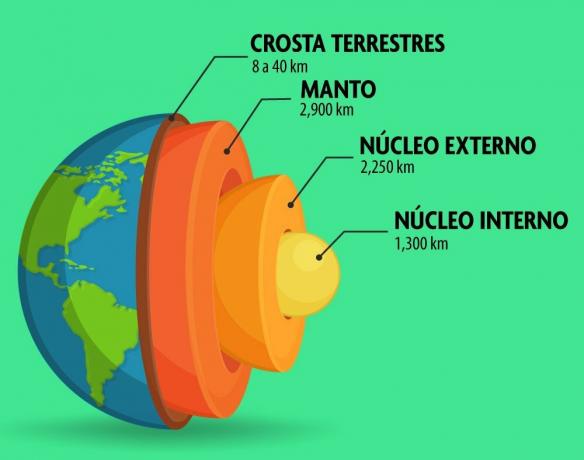
- Core - has an internal part, made up of solid iron and nickel, and an external part made up of the same substances, but in a liquid state. It has high pressure and temperature, around 5400°W.
- Cloak - is the layer of malleable rocks, located between the core and the Earth's crust, and the tectonic plates are located on the mantle.
- Earth's crust - is the surface of the Earth. It is on the Earth's crust that forests, cities and oceans are located.
The outer layers are on the earth's crust, we can see them in our daily lives. Are they:
- Lithosphere - is the other name given to the Earth's crust.
- Hydrosphere - is the part of the Earth's surface made up of water, such as oceans, rivers and lakes.
- Biosphere - corresponds to the living part of the earth, that is, all living beings, plants, animals and human beings.
- Atmosphere - is the outermost layer, it is mainly composed of gases such as nitrogen and oxygen.
Earth's magnetic field
The Earth has a magnetic field that is essential for the protection of life. A magnetic field is an area in which a magnetic force is exerted on particles that have moving electrical charges.
In the case of Earth, these particles are metals (iron and nickel) present in the outer core. They generate the magnetic field that has poles close to the North and South Poles.
It is the Earth's magnetic field that deflects the solar winds and prevents the Sun's radiation from reaching the Earth's surface. It is also thanks to this protection that our atmosphere exists as we know it, as the presence of solar winds would end up modifying it.
In other words, without the magnetic field, with strong radiation and a different atmosphere, the existence of most living beings would not be possible.
We can perceive the existence of the magnetic field through the northern and southern lights, which are the result of the interaction of the magnetic field with the solar winds.
As well as through compasses, which are orientation instruments that use the Earth's magnetic field to indicate the north direction of an area.
Formation of planet Earth
The most accepted theory for the origin of the Earth is that the planet emerged as a result of the birth of the Solar System. A Solar Nebula theory states that a large cloud of stardust collapsed due to gravitational force.
From this collapse emerged the Solar System. The central part of the nebula gave rise to the Sun, while the outer part gave rise to the planets, including the Earth, and other celestial bodies.
Over thousands of years, the Earth suffered several collisions with other bodies, causing it to gain the size it is today.
The Moon would have been formed thanks to one of these collisions, a celestial body of large proportions collided with the Earth, causing part of its mass to be torn away and become the satellite Natural.
Millions of years ago, the materials present on the planet also differentiated according to their density, with the Earth's core, mantle and crust.
The Earth then went through a slow cooling process, in which liquid water was formed, essential for the emergence of life.
Find out more about the solar system and difference between astronomy and astrology.