Acids and bases are two types of corrosive substances, but they are considered chemical opposites.
One of the biggest differences between acids and bases is that bases, in contact with aqueous solution, release negative ions, hydroxyls (OH-). Acids, in contact with water, release positive hydrogen ions (H+).
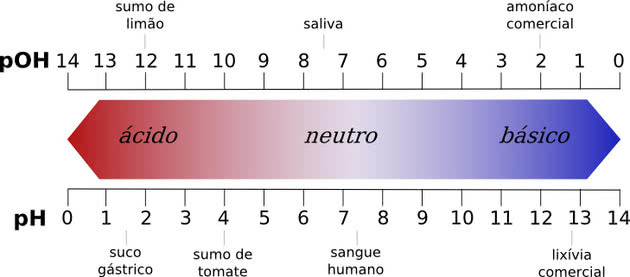
Any substance with a pH value between 0 to 7 is considered acidic, while a pH value of 7 to 14 is a base. The value 7 is neutral, which corresponds to water.
| Acids | Bases | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition of Arrhenius | An acid is any chemical compound that, in aqueous solution, releases hydrogen ions (H+). |
A base, or alkali, is a substance that, in aqueous solution, releases hydroxyls, negative ions (OH-) |
| Definition of Bronsted-Lowry | An acid is a substance that donates a proton. | A base is any substance that accepts a proton. |
| definition of lewis | During a chemical bond, acids are the ones that receive electron pairs. | In a chemical bond, the bases are the ones that donate electron pairs. |
| pH value | Less than 7.0. | Greater than 7.0. |
| Physical characteristics | Acids can occur in solid, liquid or gaseous form, depending on the temperature. | Often solid except ammonia which is a gas. |
| Structure | Acids are molecular, that is, formed by covalent bonds in which electrons are shared. | Bases can be ionic or molecular. |
| chemical formula | Acids have a chemical formula with H at the beginning, for example, HCl (hydrochloric acid). Acetic acid (vinegar) is an exception, with CH3COOH. | Bases have OH at the end of their formula, for example NaOH (sodium hydroxide). |
| Solubility in water | They tend to be quite soluble in water. | Most bases are practically insoluble. |
| Reaction on the Phenolphthalein indicator | It remains colorless. | Make the solution pink. |
| Ph test (with litmus paper) | It turns red. | It turns blue. |
| Electric conductivity | They only conduct electricity when dissolved in water. | They also conduct electric current in aqueous solution. |
| Examples | Acetic acid, sulfuric acid. | Sodium hydroxide, ammonia |
What are acids and bases
Acids are ionic compounds that when dissolved in water generate a positive hydrogen ion (H+). Bases, on the other hand, are ionic compounds that form a negatively charged hydroxide ion (OH-) in water.
This definition, created by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius, is the most used to classify acids and bases, however, there are other definitions.
The definition given by Johannes N. Bronsted and Thomas Lowry, known as the proton definition, says that acids are substances that donate a proton, while bases are those that accept a proton.
In the definition given by the North American Gilbert Newton Lewis, acids are substances that receive electron pairs in a chemical bond, while bases give away pairs.
pH of acids and bases
All chemical compounds have a pH value, which can range from 0 to 14, where the numbers represent the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Neutral pH is the pH of pure water, which is 7. Any substance with a pH value between 0 to 7 is considered acidic, while a pH value of 7 to 14 is a base.
The lower the acid is below 7.0, the stronger it is. In bases, the higher the pH value, the stronger it will be.
Characteristics of Acids:
- It has a bitter taste;
- May burn skin when touched;
- May corrode metals and skin;
- Makes litmus paper red;
- In the universal indicator it is identified by red or orange colors.
Characteristics of the Bases
- Astringent taste;
- When touching, you feel something viscous;
- Many bases react with acids and generate salts;
- Strong bases can react violently with acids;
- Bases turn litmus paper blue;
Indicators of acids and bases
pH indicators, or acid-base indicators, are substances used to find out whether a solution is an acid or a base.
This is possible because of its physical-chemical properties, which have the ability to change color according to the pH of the tested substance.
Among the many artificial indicators used in the laboratory, the best known are phenolphthalein, litmus paper and universal indicators.
- Phenolphthalein remains colorless in contact with acid, and turns pink in contact with bases.
- Litmus paper turns blue with bases and red with acids.
- The universal indicator is the most accurate of the acid-base indicators as it shows different colors according to each pH value.

Applications for acids and bases in everyday life
Acids are often used to remove rust from metals, as an electrolyte in batteries, for processing minerals, to produce fertilizers and gasoline, and as additives in food and drinks.
Bases are primarily used in cleaning, such as dishwashing detergents and laundry soap, oven cleaners, and stain removers.