Improve your knowledge with our list of exercises about plane mirrors. All exercises are solved and commented for you to answer your questions.
Regarding the images formed by plane mirrors, evaluate the statements:
I - An object reflected by a plane mirror that is at a distance of 1.75 m from the mirror is at a distance of 3.50 m from its image.
II - The images formed by plane mirrors are not superimposable.
III - An image is formed in a flat mirror by the prolongation of incident rays.
IV - A plane mirror forms real images.
Select the option that correctly represents the statements above.
a) I - F, II - V, III - F, IV - V
b) I - V, II - F, III - F, IV - V
c) I - V, II - V, III - F, IV - F
d) I - V, II - V, III - V, IV - V
I (TRUE) - The distance between the object and the mirror is equal to the distance between the mirror and the object.
II (TRUE) - The images are inverted from right to left. It has the opposite shape to the object.
III (FALSE) - Images in plane mirrors are formed by the extensions of emerging rays.
IV - (FALSE) - A plane mirror forms virtual images.
Two flat mirrors are associated so that their edges are touching, forming a certain angle, where eight images are formed. Therefore, the angle between the mirrors is
a) 8th
b) 20th
c) 80º
d) 40º
To determine the angle formed by the association between mirrors, we use the relationship:
Where is the angle between the mirrors and N is the number of images.
Substituting into the formula, we have:
A commercial building has its facade covered with mirrored glass, flat and perpendicular to the ground. In front of the building there is a large avenue with a 24 meter wide pedestrian crossing.
Suppose a person is at the opposite end of the building, on this avenue, and starts to cross it with a constant speed of 0.8 m/s. The distance between the person and their image will be 24 m after
c) 8 s.
b) 24 s.
c) 15 s.
d) 12 s.
The distance between the real object and its virtual image in a plane mirror is twice the distance between the object and the mirror.
At the beginning, the distance between the person and the mirror is 24 m, so the distance between the person and their image is 48 m.
Therefore, the distance between the person and their image will be 24 m when they are 12 m away from the mirror.
As its speed is 0.8 m/s and the distance is 12 m, we have:
A person 1.70 m tall wants to observe himself full body in a flat mirror fixed to a wall perpendicular to the ground. The height of his eyes in relation to the floor is 1.60 m. Under these conditions, so that the person can observe themselves in full body, the length of the mirror must be, in centimeters, at least
170cm
165cm
80cm
85 cm
To resolve the issue, let's illustrate it.

Let's use two triangles: the one formed by the lines between your eyes, at 1.60 m, and the mirror; and the other, formed by the same rays (dotted blue) and its image.
These triangles are similar because they have three equal angles.
The distance between the person and the mirror is x, which, as it is perpendicular to the mirror, is also the height of the smaller triangle.
Likewise, the distance between the person and their image is 2x, the height of the triangle being greater.
Assembling the similarity ratio between the segments of the triangles:
Therefore, the length of the mirror must be at least 85 cm.
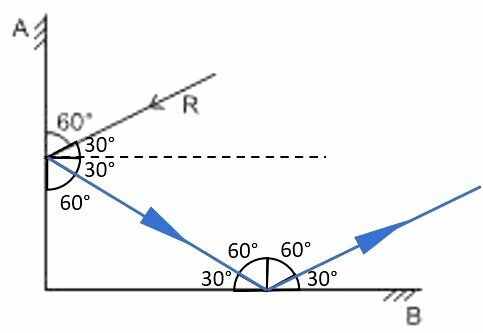
(Unicenter) A ray of light R hits a plane mirror A, is reflected and hits another plane mirror B, perpendicular to each other, undergoing a second reflection.
Under these conditions, it is correct to state that the ray reflected in B

a) is parallel to R.
b) is perpendicular to R.
c) is inclined with respect to R.
d) makes an angle of 30º with R.
e) makes an angle of 60º with R.
The angle formed between mirror A and the normal line is 90º. Thus, the angle of incidence on mirror A is 30º, as is the angle of reflection.
In relation to mirror B, the angle of reflection is 60º, making it 30º in relation to mirror B. As the angle in relation to the normal line is also 30º, the ray of incidence at A and the ray of reflection at B are parallel.
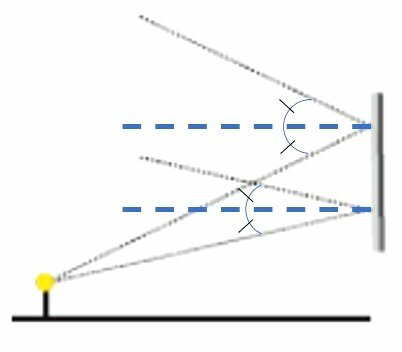
(CEDERJ) A small lamp is lit in front of a flat mirror as illustrated in the figures.
Select the alternative that represents how two incident rays of light are reflected in the mirror.
The) 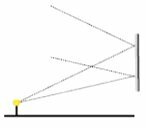
B) 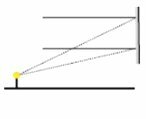
w) 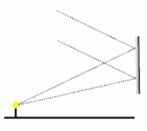
d) 
The angle of incidence must be equal to the angle of refraction. Therefore, the correct option is letter a.
(UECE) Two coplanar rays of light fall on a flat mirror. The first ray normally falls on the mirror, and the second has an angle of incidence of 30°. Consider that the mirror is rotated so that the second ray has normal incidence. In this new configuration, the first ray has an angle of incidence equal to
a) 15°.
b) 60°.
c) 30°.
d) 90°.
A good strategy is to sketch the situation. At first, we have:
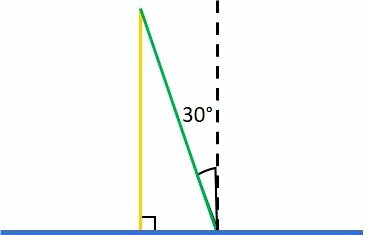
The first ray is represented in yellow, making 90 degrees with the mirror, in blue. The second ray, green, has an angle of incidence of 30º. The dotted line is the normal line.
After rotating the mirror, the configuration becomes:
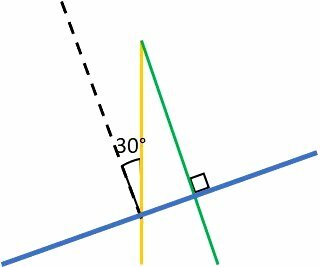
In this configuration, the green ray becomes 90º with the mirror, and the angle between the yellow ray and the normal is 30º degrees.
Notice that the light rays have not changed, only the mirror and the normal.
(EFOMM ) Observe the following figure.
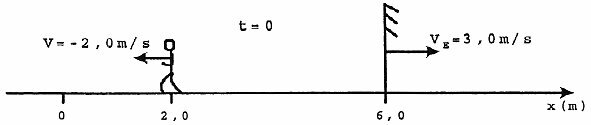
At time t=0, there is a boy in position plane at position above. How far did the boy's image travel during the time interval from zero to two seconds?
a) 20m
b) 19m
c) 18m
d) 17m
e) 16m
In the image, we must orient ourselves according to the reference point at zero, which is to the left of the boy. The direction for both is horizontal, with a positive direction to the right.
At the first moment, t=0 s, we have:
The boy is two meters from the origin, 4 m from the mirror.
X0m = 2m
d0 = 4 m
The distance of the image in relation to the reference is:
d0 = X0m + d0 = 2 + 4 = 6 m
At the second moment, t = 2 s, the configuration is:
As the boy's speed is 2 m/s, in two seconds he travels 4 m, being - 2 m from the origin.
X2m = - 2m
The distance from the mirror to the origin is:
As the speed of the mirror is 3 m/s, it travels 6 m to the right, being 12 m from the origin.
X2e = 12 m
The distance from the boy to the mirror is, in modules:
X2m + X2e = 2 + 12 = 14 m
The distance from the image to the origin is:
d2 = 2.14 + X2m = 28 - 2 = 26 m
Distance traveled by the image:

