A Potsdam Conference was a meeting between the three main allied nations at the end of the Second World War (1939-1945). England, USA and USSR, through their heads of state (Clement Attlee, Harry S. Truman and Josef Stalin respectively), met between July 17 and August 2, 1945 in the German city of Potsdam. The purpose of the conference was to organize the administration and occupation of Germany after its defeat in the war.
Read too: Paris Peace Conference — the conference held after World War I
Topics in this article
- 1 - Summary of the Potsdam Conference
- 2 - Objectives of the Potsdam Conference
- 3 - How was the Potsdam Conference?
- 4 - What was decided at the Potsdam Conference?
-
5 - Other conferences that took place in the context of the Second World War
- → Tehran Conference
- → Yalta Conference
- → San Francisco Conference
- 6 - Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan
Summary of the Potsdam Conference
- It was a meeting between the three main Allied nations at the end of World War II.
- Each nation was represented by the leader of its government: Clement Attlee (England); Harry S. Truman (United States); and Josef Stalin (Soviet Union).
- Its objective was to organize the administration and occupation of Germany.
- The meetings took place amid the latest conflicts in Japan.
- The conference decided that the Allies' objective, when occupying Germany, would be its demilitarization, denazification, democratization and decartelization.
- In addition to it, other conferences held in the final period of the Second World War were: the Yalta Conference, the Tehran Conference and the San Francisco Conference.
- The Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan were the result of the United States' discomfort with the expansion of Soviet communism.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Objectives of the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference it was a meeting between the three main allied nations, England, USA and USSR, in the context of the end of the Second World War (1939-1945). This meeting took place between July 17 and August 2, 1945 in the city of Potsdam, Germany. Each nation was represented by the leader of its government: England, by Prime Minister Clement Attlee; the United States, by President Harry S. Truman; It is the Soviet Union, by Josef Stalin.
The Potsdam Conference Its main objective was to organize the administration and occupation of Germany, recently defeated and which had signed its unconditional surrender on May 8.
How was the Potsdam Conference?
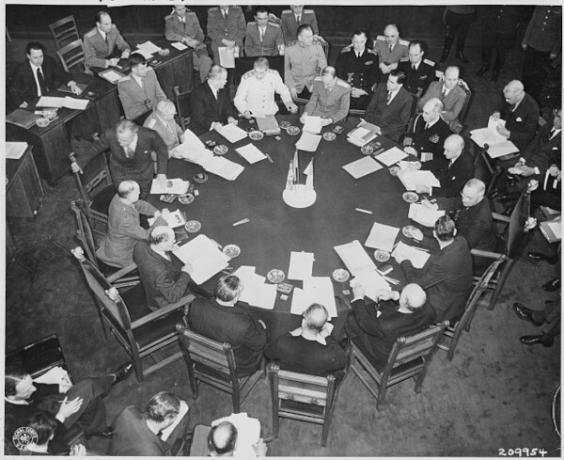

The Potsdam Conference took place in the German city of Potsdam and consisted of several negotiation sessions. In them, the leaders of the allied countries discussed how to occupy and administer the recently surrendered and defeated Germany. The meetings took place amid the latest conflicts in Japan, notably during the US atomic bomb tests and the subsequent attacks on Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
Important: Winston Churchill participated in the opening and first days of the Potsdam Conference as Prime Minister of England. His term ended during the conference, on July 26, 1945, and he was replaced by Clement Attlee, who went on to represent England in the remaining days of the event.
What was decided at the Potsdam Conference?
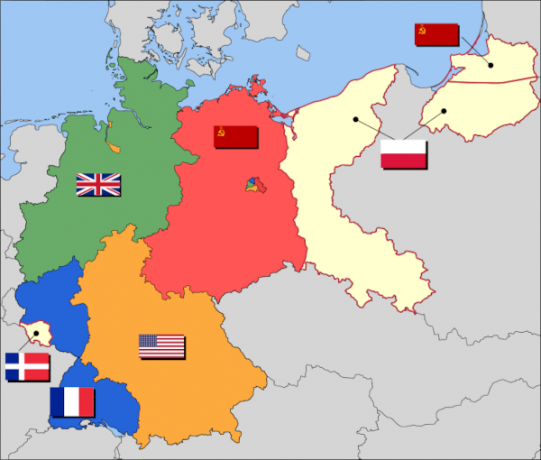
At the Potsdam Conference, it was decided that:
- All territories annexed by Germany since 1937 would be dismembered.
- Austria would be separated from Germany.
- The Allies' objective, when occupying Germany, was its demilitarization, denazification, democratization and decartelization.
- Germany would be divided into four occupation zones: American, French, British and Soviet.
- Defeated countries would pay war reparations to the Allies.
- An ultimatum would be sent to Japan, expecting its surrender.
See too: Nuremberg Tribunal — the international court that judged Nazi crimes committed in World War II
Other conferences that took place in the context of the Second World War
→ Tehran Conference
It was the first of three major conferences that took place in the final period of the Second World War. It took place between November 28 and December 1, 1943 in Tehran, Iran. In it, the leaders of the USA, USSR and England decided and organized the invasion of France (occupied by the Nazis) by English and American troops. To learn more about this conference, click here.
→ Yalta Conference
It was the second of three major conferences that took place in the final period of the Second World War. It was held between February 4 and 11, 1945 in the city of Yalta, Crimea, Ukraine. In it, the leaders of the allied countries (USA, USSR and England) decided the strategies that would lead to the division of the West and East areas of influence and the end of the war in Europe. To learn more about this conference, click here.
→ San Francisco Conference
It occurred between April 25 and June 26, 1945 in the city of San Francisco, USA. Its objective was the production and approval of the United Nations Charter by 50 allied nations, and it was identified as the inaugural milestone of the United Nations (UN).
Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan
After World War II, the United States and the Soviet Union became the world's great powers. Despite being allies in the war, the United States was uncomfortable with the expansion of Soviet communism. The Truman Doctrine and the Marshall Plan were the results of this discomfort:
- Truman Doctrine: was the set of economic and political practices on a global scale developed and applied during the government of Harry S. Truman (1945-1953), especially in the context of the Cold War (1947-1991). Officially, the doctrine was announced in an important speech by the president to Congress on March 12, 1947, in which he made clear that the objective His government's foreign policy was to contain the Soviet communist advance on European, American, African, Asian and Middle Eastern countries.
- Marshall Plan: was the European Recovery Program developed by US government secretary George Marshall. His intention was to apply the ideals of the Truman Doctrine in practice through American economic aid to other European economies. With this, the plan aimed to strengthen economies so that governments and society were not conquered by Soviet communism.
Image credit
[1] 52 Pickup / IEG-Maps / Wikimedia Commons (reproduction)
Sources
MAGNOLI, Demetrio. History of Peace. São Paulo: Contexto, 2012.
MIRANDA, Monica; FARIA, Ricardo. From the Cold War to the new world order. São Paulo: Contexto, 2003.
VASCONCELLOS, Charlemagne; MANSANI, Roberta. The Yalta and Potsdam international conferences and their contribution to the construction of North American international economic hegemony in post-World War II capitalism. International Relations of the Current World Magazine, v. 2, n.16, 2013. Available in: http://revista.unicuritiba.edu.br/index.php/RIMA/article/view/731/557.
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
CAMPOS, Tiago Soares. "Potsdam Conference"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/historiag/conferencia-de-potsdam.htm. Accessed September 10, 2023.
Check the conjugation of the verb effect in all possible verb tenses.
Check the conjugation of the verb effect in all possible verb tenses.
Check the conjugation of the verb edulcorar in all possible verb tenses.



