THE ketoneis an oxygenated organic function whose substances have as their main characteristic the functional group carbonyl (carbon that makes a double bond with oxygen) between two other carbon atoms, as we can see in the general formula below:
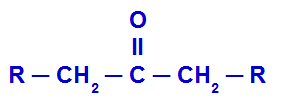
Representation of the general structure of a ketone
For name the ketones, there are two rules that can be applied: the rule of official IUPAC nomenclature and the usual naming rule. Both have their own characteristics and can be used. In this text, we will emphasize the usual naming rule.
THE usual nomenclature of a ketone depends directly on the nomenclature of organic radicals or substituents. It is stated as follows:
Radical name + Ketone
in order
alphabetical
To identify the radicals or branches present in a ketone, just highlight the carbonyl group (C = O). By highlighting the carbonyl, everything attached to it will be a radical. See an example:
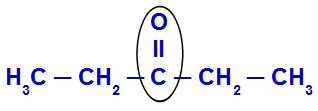
Radials or branches attached to a carbonyl
In the example above, we can see that, by highlighting the carbonyl group (with the black oval), we have an ethyl group
(CH3-CH2) to the left of the carbonyl and, to the right, another ethyl radical (CH3-CH2).Follow some examples of application of the usual naming rule for some ketones:
Example 1: ethyl methyl ketone
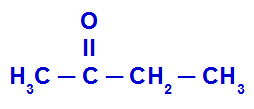
The structure above has a methyl radical (CH3) to the left of the carbonyl (C = O) and a radical ethyl (CH2-CH3) in the right side. So, putting the name of each of these radicals in alphabetical order, the compound name is:
ethyl methyl ketone
Example 2: Butyl propyl ketone

The structure above has a propyl radical (CH2- CH2- CH3) to the left of the carbonyl (C = O) and a butyl radical (CH2- CH2- CH2- CH3) in the right side. So, putting the name of each of these radicals in alphabetical order, the compound name is:
Butyl propyl ketone
Example 3: diethyl ketone

The structure above has a radical ethyl (CH2- CH3) to the left of the carbonyl (C = O) and a radical ethyl (CH2- CH3) in the right side. As we have two equal radicals, we write their name preceded by the term di:
diethyl ketone
Example 4: Isobutyl vinyl ketone
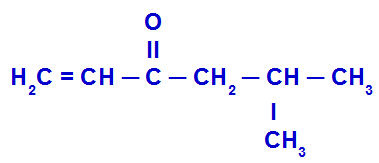
The structure above has a radical vinyl (H2C = CH) àcarbonyl left (C = O) and a isobutyl radical (CH2- CH(CH2)- CH3) in the right side. So, putting the name of each of these radicals in alphabetical order, the compound name is:
Isobutyl vinyl ketone
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/nomenclatura-usual-das-cetonas.htm

