leukocytes are blood cells known to many people as white blood cells. These cells can be classified into several types, however, they all act in favor of a common good: the body's defense.
→ General characteristics of leukocytes
You leukocytes they are large, colorless and spherical-shaped cells. Furthermore, unlike red blood cells, they have a nucleus, which varies in shape from one type to another. Leukocytes are the figurative elements found in the smallest amounts in the blood. Typically, there are about 6,000 to 10,000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter of blood.
Leukocytes have the incredible ability to exit blood vessels and migrate to adjacent tissue (diapedesis) to defend the organism. These blood cells defend our body in different ways, standing out The phagocytosis and the production of antibodies. In phagocytosis (see figure below), the cells are able to project their cytoplasm in order to engulf foreign particles and, later, carry out the digestion, destroying the invader. already the
antibodies they are specific glycoproteins produced by B lymphocytes to attack a specific (foreign organism or substance).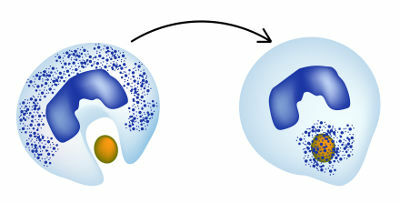
Leukocytes can carry out the phagocytosis process, in which invading particles are digested
→ Types of leukocytes
Leukocytes can be classified into two types: granulocytes and agranulocytes. The first group concerns cells with granules that can be observed under a microscope. Agranulocytes do not have these granules.
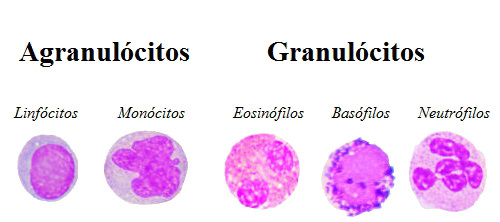
Observe the different types of leukocytes in our body
-
agranulocytes
Lymphocytes: A type of spherical leukocyte that has a very large nucleus. They can be classified into B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes. Mature B lymphocytes (plasma cells) are responsible for producing antibodies. T lymphocytes, on the other hand, have several types that act on the stimulation of B lymphocytes, speeding up the end of the immune response, induce cells to enter the programmed death process, among others actions.
Monocytes: They are large-sized leukocytes with a variable-shaped nucleus. They have a great capacity for phagocytosis.
-
Granulocytes
Neutrophils:Type of leukocyte found in the greatest amount in our blood. Its nucleus contains three to five lobes. This cell stands out for its high phagocytic power.
Eosinophils:Cells that are also capable of phagocytosis, but slower than neutrophils. Its nucleus has, in general, two lobes. They are common when allergies occur and represent from 2% to 4% of the total white blood cells in the body.
Basophiles:A type of voluminous leukocyte with an irregularly shaped nucleus. It is characterized by producing heparin and histamine, substances that have, respectively, anticoagulant and vasodilating action.
→ Leukopenia and leukocytosis
Sometimes the number of white blood cells in the blood rises or falls considerably. In cases where the body has an increased production of white blood cells, it is said that this is a case of leukocytosis. When the number of leukocytes is lower than normal, it is said that it is a leukopenia. This last situation can bring risks to the patient, since there is a drop in the cells responsible for defense.
→ Leukemia
THE leukemia it is a type of cancer, often of unknown origin, that affects white blood cells. In this disease, it is observed that these cells start to multiply in an uncontrolled way, however, they do not reach their mature stage. Therefore, there is an accumulation of young cells, which, little by little, become superior to normal cells.
There are different types of leukemia, but it is possible to group them into two basic types taking into account the evolution of the disease: acute and chronic leukemia. The acute worsens quickly, and the chronic one has a slow evolution.
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/biologia/o-que-e-leucocito.htm


