A force only performs Work if there is displacement of the body on which it acts. That way, if a person at rest holds an object, he is not doing Work. Analyzing this way, we can relate these events to the following mathematical equation for the Work performed by a force: 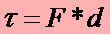 , where τ (Greek letter tau) = work, F = force and d = displacement.
, where τ (Greek letter tau) = work, F = force and d = displacement.
In some situations the work is done more quickly. For example, a marathon course was taken by two people at different times. In this case, we say that the person who completed the route in less time developed a higher average power in relation to another person. Based on this definition, the mathematical equation responsible for calculating the power of a body is given by the expression: 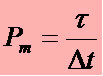 , where ∆t: time variation.
, where ∆t: time variation.
Example 1
Determine the work done by a force of intensity 250 N (Newton) applied to a body, which moves for 20 meters in the same direction as the force.
τ = F * d
τ = 250 * 20
τ = 5000 N/m
τ = 5000 J (joule)
Example 2
A force of 40 N intensity is applied to a body, displacing it for 5 meters in the direction and direction of the force, for 10 seconds. Based on this information calculate:
a) the work performed by force.
b) the average power of this force.
a) τ = F * d
τ = 40 * 5
τ = 200 N/m
τ = 200 J (joule)
B) 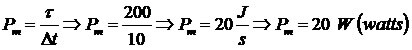
by Mark Noah
Graduated in Mathematics
Brazil School Team
Equations - Math - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/matematica/equacoes-matematicas-relacionadas-ao-trabalho-potencia-.htm

