Isomerism flat it is a phenomenon that occurs between substances that have the same molecular formula, but present specific differences in their structural formulas, such as:
Show groups that belong to organic functions many different;
present carbon chains different (saturated or unsaturated, homogeneous or heterogeneous, normal or branched, open or closed);
They have components (such as double or triple bonds, branches or functional groups) in different positions;
Know the types of plane isomerism:
→ flat function isomer
is the type of flat isomerism where there are compounds of the same molecular formula but with different chemical functions. For example:

Ethanol and methyl ether are functional isomers
Ethanol (C2H6O), a type of alcohol, and methyl ether (C2H6O), a type of ether, are functional isomers because they have different chemical functions (ether and alcohol).
→ Position plane isomer
is the type of flat isomerism where we have compounds with the same molecular formula, same chemical function, same type of carbon chain, but at least one item (functional group, unsaturation, or branch) is in different positions in your structures.

But-1-ene and but-2-ene are position isomers
But-1-ene (C4H8) and but-1-ene (C4H8), unsaturated hydrocarbons, are position isomers because they have the double bond at different positions in the chain (positions 1 and 2).
→ Flat chain isomer
is the type of flat isomerism where we have compounds with the same molecular formula, the same chemical function, but different types of carbon chains. For example:

But-1-ene and cyclobutane are chain isomers
But-1-ene (C4H8) and cyclobutane (C4H8), unsaturated hydrocarbons, are chain isomers because they have an open and closed chain, respectively.
→ Compensation flat isomer or metamerism
It's a kind of flat isomerismof position which involves compounds of the same molecular formula, with heterogeneous carbon chains and different chemical functions.
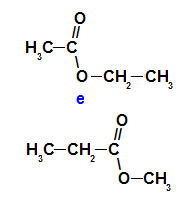
Ethyl ethanoate and methyl propanoate are compensating isomers
Ethyl ethanoate (C4H8O2) and methyl propanoate (C4H8O2), unsaturated esters, are metameric isomers because they have a heterogeneous carbon chain.
→ Flat isomer of tautomery
is the type of flat isomerism ofoccupation in which the compounds involved have the same molecular formula and are necessarily an enol and an aldehyde or an enol and a ketone. This is because enols are extremely unstable compounds, and when they decompose, they turn into an aldehyde or a ketone.
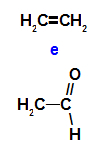
Ethanol and ethanal are tautomeric isomers
Ethenol is an enol, therefore, it is an unstable compound that, when decomposed, forms the aldehyde ethanal in a reversible decomposition process.
By Me. Diogo Lopes Dias
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/quimica/o-que-e-isomeria-plana.htm

